- About Me
- Courses/Projects
- Programming
- Research
- Resume
- Useful Links and Comments
- Financial Models
- Design Patterns
- Reading List
- News
- 心情驿站
I spent quite a few years studying engineering and was trained to use practical methods for solving the real world problems. However, I became insatiated with just the know-how, I was always self motivated to know what happened behind the scenes. I started auditing a few math courses offered in the math faculty and have been deeply enthralled by the beauty of mathematical optimization and mathematical finance. To my greatest honor, my supervisor, Prof. Yuying Li gave me an opportunity to do studies and research in the area of Computational Finance in her seasoned supervision, in pursuit of my second master's degree at the University of Waterloo. I am so grateful for having being given this great opportunity to take/audit various courses taught by so many wonderful professors: to name a few, Prof. Peter Forsyth, Prof. Carole Bernard, Prof. Christopher Small, Prof. Levent Tuncel, Prof. Henry Wolkowicz, Prof. Stephen A. Vavasis, Prof. Nick Wormald etc.
During my studies at the University of Waterloo, I got to know many gifted colleagues and leared so much from them. I always hold the tenet that learning process is a lifelong process so I need to work hard to overcome my weakness and keep up with the fast pace of those talents. Some of my best friends, Wei Zhou(PhD at UW), Jun Chen (PhD at UW), Tiantian Bian (Microsoft), Xiangxian Ying (PhD, Professor), Shilei Niu (PhD at UW), Jenny Jin (Capable California Girl), Vris Cheung (PhD at UW), Leo Liu (Manulife Financial) and many more, have been generously giving me every support and encouragement whenever in need.
After graduation, I started my career as a software developer. It is very exciting to know many useful tools in industry to make what we believe happen in the real word. I got the exposure to CSV to XML converter to Castor Object to Domain Object to the storage and retrieval of Java domain objects via Hibernate's Object/Relational Mapping, Apache Struts for developing Java EE web application, JSTL/Javascript/jQuery for JSP page design, JUnit test in the test-driven development. This period of work experience greatly enhanced my knowledge and skills in dealing with a large credit application and batch program processing system.
Currently I am working at BMO Capital as a technical specialist. I am mostly involved in ETL/Model Conversion for the Stress Testing Framework in accordance with Basel II/III capital accord requirements. My most recent resume in PDF version can be found at this link for 3-page or 2 page version.
- Finance 1: Course Notes and References
- Finance 2: Course Notes and Project
- Finance 3: Course Notes and References
- Stat 901 Probability Theory 1: Course Notes
- Stat 902 Probability Theory 2: Course Notes
- Stat 833 Stochastic Processes: Course Notes
- PMath 354 Measure Theory and Fourier Analysis: Course Notes
- CS 860 Geometric Data Structures: Course Notes and Project
- ECE610 Broadband Networks: Project
- ECE710 Space Time Coding for Wireless Communication:Course Notes and Project
- CO 671 Semidefinite Optimization: Course Notes and Reports
- CO 663 Convex Optimization and Analysis: Course Notes
- CO 739 Random Graph: Course Notes
- CO 759 Topics in Discrete Optimization: Algorithmic Game Theory Course Notes
- CO 769 Topics in Continuous Optimization: Compressive Sensing Course Notes
- CO 778 Portfolio Optimization: Course Notes
Finance One
This course provides the current paradigms in the theory of finance and the supporting empirical evidence. Prof. David Saunders introduced the basic concepts of the field, with an emphasis on the economic principles that underlie the main models. Discrete time models were mainly explained. Pricing and hedging of financial assets, portfolio selection, risk management and equilibrium models for asset valuation were examined. The electronic version of the course notes is available upon request.
Finance Two
Finance 2, taught by Prof. Carole Bernard is a subsequent course to finance 1. It mainly covers the continuous-time finance models, e.g, Black-Scholes-Merton framework, Fixed Income models including Vasciek, CIR, Hull-White etc. Ito's lemma, change of measure (Radon Nikodym Theorem, Girsanov Theorem), change of numeraire techniques have been thoroughly investigated and applied to pricing the various kinds of financial derivatives, e.g., call on call, exchange option etc. The link to the course notes is here.
As for the project, I worked on the derivation of the pricing formulas for global cap and monthly sum cap under Black-Scholes' Framework. Thanks to Ms. Jenny Jin for providing the Matlab code for the verification of the results using FFT method. The project report can be found here.
Finance Three
Finance 3 is more on the research side whileas it mainly covers 3 big chunks. As for topic 1, portfolio optimization is investigated in depth. Efficient portfolios: the efficient frontier, the capital market line, Sharpe ratios and threshold returns. Practical portfolio optimization: short sales restrictions target portfolios, transactions costs. Quadratic programming theory. Special purpose quadratic programming algorithms for portfolio optimization. Risk management in a quantitative framework including stress testing are represented in the second part. In particular, Bayesian net is a very power tool, which indeed has already been applied in many areas to estimate/calculate the risk quantile (LGD) in a systemically correlated setting. The third part is dedicated to some more advanced finance models, Levy's process etc. (in year 2009). The electronic version of the course notes including midterm answers are available upon request.
Probability Theory 1
Probability Theory 1 is a must-take course on your course list if you really want to become a quant who wants know-why in addition to know-how. Sigma-algebra and set theory are introduced at a glimpse. Monotone Convergence Theorem, Central Limit Theorem and Conditional Probability/Expectation are rigorously explained here. The link to the course notes is here.
Probability Theory 2
Probability Theory 2 is an advanced math course to establish the main principles of stochastic calculus within the simplest setting of stochastic integration with respect to continuous semimartingales. The course mainly covers discrete-parameter martingales, continuous-parameter martingales, stochastic integration of progressively measurable integrands and representation of local martingales as stochastic integrals. This course content is deep and prof. Andrew J. Heunis knows this subject really well and he always tried to explain the meaning behind the abstract formulas. The link to the course notes is here. The official course notes is also available in PDF.
STAT 833
Random walks, renewal theory and processes and their application, Markov chains, branching processes, statistical inference for Markov chains are covered in this course. The link to the course notes is here. Prof. Christopher Small is an excellent instructor in teaching. I audited this course and Probability Theory 1 taught by him. He knows exactly how to communicate complex ideas within the scope of students' knowledge base.
Pure Math 354
It is always good to take pure math courses whenever you want to get a deep and comprehensive understanding of the topic. Lebesgue measure on the line, the Lebesgue integral, monotone and dominated convergence theorems, Lp-spaces: completeness and dense subspaces. Separable Hilbert space, orthonormal bases. Fourier analysis on the circle, Dirichlet kernel, Riemann-Lebesgue lemma, Fejer's theorem and convergence of Fourier series. This is a very good course for non-math major students to ramp up measure theory. The course notes is available here.
Computational Geometry
This course covers selected topics on data structures in low-dimensional computational geometry including “Orthogonal range searching”, “Point location”, “Nonorthogonal range searching”, “Dynamic data structures”, “Approximate nearest neighbor search”. The link to the course notes is here.
In particular, my course project presentation on “Maximum Independent Set of Rectangles” is also provided here.
Abstract: The maximum independent set of rectangles problem has lots of application from map labelling to data mining in practice. A collection of objects is called independent if no pair of objects in the collection intersect. The unweighted MISR problem is designed to find an independent set with maximum cardinality among all independent sets. The MISR problem is just a special case of Maximum Independent Set (MIS) problem in graph theory. However, even for MISR, it has been proved to be an NP-hard problem. Hence researchers are focused on finding good approximation algorithms for this problem. The current best known algorithm for general MIS problem yields O(n/(log n)^2)-approximation factor. For MISR, O(log n)-factor algorithm has been well established by several researchers independently. The contribution of Parinya and Julia’s paper lies in that they proposed an O(log log n)-approximation algorithm for MISR, which for the first time beats the O (log n)-factor barrier. In Chan and Peled’s paper, they used local search method and novel rounding scheme to solve maximum independent set of pseudo-disks, which give constant approximation algorithms for both unweighted and weighted cases. In the appendix, they gave an O(logn/loglogn)-approximation algorithm for MISR problem.
Broadband Networks
This course is concerned with the fundamentals of broadband communication networks including network architecture, Switch fabrics, design methodology; traffic management, connection admission control (CAC), usage parameter control (UPC), flow and congestion control; capacity and buffer allocation, service scheduling, performance measures, performance modeling and queueing analysis. The instructor, Prof. Ravi. R. Mazumdar is very math oriented. Intensive mathematical derivations were introduced in this course. One course project was to ask students to implement different models of queues and compare the performance. The project itself was not very difficult, but one needs to be a bit more extra thinking. I also provided some mathematical results on some models and a more robust pseudo random number generating algorithm after a literature survey so I was the only one who got full marks on this project. The manuscript for this project can be found here.
Space-Time Coding
I audited this course, which was taught by Prof. Murat Uysal , just because I was very interested in coding theory. This course mainly covered “Error Probability Analysis”, “Space-Time Trellis Coding (STTC)”, “Space-Time Block Coding (STBC)”, “Multiple-input Multiple-output (MIMO) Information Theory”. I did both two written assignments/projects on implementing the space-time coding algorithms and evaluated the performance. I got 98/100 for these two assignments. The write-ups can be found at the following links Simulation of Random Fading Channels and STTC Using Convolutional Codes.
Semidefinite Optimization
I have complied the courses notes in Section 1: Basics and Section 2: Combinatorial Applications in PDF format. Prof. Levent Tuncel gets this monograph published very recently at Amazon Web Link. This is a very good book which I highly recommend to those who want to get a deep understanding of semidefinite programming and its applications to many practical problems including Max Cut, Geometric Representation of Graphs and Lift-and-Project procedures for Combinatorial Optimization problems. I referred in my thesis to Chapter 4 in this monograph for details on how Primal-Dual Interior-Point Method works.
Convex Optimization and Analysis
An introduction to the modern theory of convex programming, its extensions and applications. Structure of convex sets, separation and support, set-valued analysis, subgradient calculus for convex functions, Fenchel conjugacy and duality, Lagrange multipliers, minimax theory. Algorithms for condifferentiable optimization. Lipschitz functions, tangent cones and generalized derivatives, introductory non-smooth analysis and optimization. The course notes can be found here.
Random Graphs
This course is deep. In the last few lectures, a very difficult theorem “Large random d-regular graphs are almost always Hamiltonian (for d at least 3)” was proved step by step. I always remembered the moment spent with Dr. Zhou Wei going through every detail of the proof for 12 hours. The course notes can be found here.
Topics in Discrete Optimization: Algorithmic Game Theory
This course was taught by Prof. Chaitanya Swamy. Algorithmic game theory applies algorithmic reasoning to game-theoretic settings. A prototypical motivating example for the problems we will consider is the Internet, which is a fascinating computational artifact in that it was not designed by any one central authority, or optimized for one specific purpose, but rather emerged from the interaction of several entities, such as network operators, ISPs, users, in varying degrees of coordination and competition. This course will investigate a variety of questions that arise from looking at problems (often classical optimization problems) from this point of view. We will examine, in part, algorithmic issues in games, and in part, algorithmic problems that arise in settings with strategic players. The course notes can be found here and the course web site is here.
Topics in Continuous Optimization: Compressive Sensing
This is a very good course taught by Prof. Stenphen A. Vavasis. Compressive sensing was introduced independently by Candes, Romberg and Tao (2006) and Donoho (2006) and has attracted a considerable amount of attention from the signal processing, statistical, computer science and optimization communities. An earlier paper by Gilbert, Guha, Indyk, Muthukrishnan and Strauss (2002) also anticipated the results. The main result in this field states that a signal (i.e., a vector), if it is sufficiently sparse, can be recovered exactly from its inner product with a small number of random vectors. The recovery algorithm is L1 minimization, which is equivalent to linear programming. In general, recovery of the sparsest solution to linear equations is NP-hard, but in this special (and practically applicable) case, recovery can be solved in polynomial time. Specialized algorithms for l1 minimization have been around for many years in the optimization community. In the statistics community, L1 minimization is known as a data-fitting technique that is sometimes more robust than linear least-squares and is closely related to a technique called Lasso regression. These two original papers have led to dozens of follow-up works. The course notes can be found here and the course web site is here.
Portfolio Optimization
Basic optimization: quadratic minimization subject to linear equality constraints. Efficient portfolios: the efficient frontier, the capital market line, Sharpe ratios and threshold returns. Practical portfolio optimization: short sales restrictions target portfolios, transactions costs. Quadratic programming theory. Special purpose quadratic programming algorithms for portfolio optimization: today's large investment firms expect to solve problems with at least 1000 assets, transactions costs and various side constraints in just a few minutes of computation time. This requires very specialized QP algorithms. An overview of such algorithms will be presented with computational results from commercial problems. The efficient frontier, the capital market line, Sharpe ratios and threshold returns in practice. The simplified course notes can be found here.
- One Day Coding Project: Properties Server in JAVA
- Addepar Ant Project: it is worth invesitigating if time allowed
- Iterative Tree Traversal in C/C++
- Recursively Reverse Singly Linkedlist in C/C++
- Stack Sort in C/C++
- Print All Combinations of Paired Parentheses in C/C++
- Binary Tress Serialization in C
- Test a given string is the interleaved combination of other two given strings (JAVA) March 4, 2012
- Setup sibling links for a tree (C/C++) March 4, 2012
- Print out all mutation paths using #(Edit Distance) steps (C/C++) March 7, 2012
- Compute # of places a knight can visit (Java) March 9, 2012
- Spirally print out actresses names in C/C++ March 16, 2012
- Quicksort Singly Linked List in C/C++ March 20, 2012
- Naive Approach for deciding identical BSTs in C/C++ April 4, 2012
- Recursion Approach for deciding identical BSTs in Java April 5, 2012
- A simple in-place circular shift of char string in C/C++ April 5, 2012
- Unidirectional Jump game: A naive approach using Dijkstra in C/C++ April 7, 2012
- Unidirectional Jump game: A Greedy approach in C/C++ April 7, 2012
- Trapping Rain Water: A bi-directional scanning approach in C/C++ April 14, 2012
- Longest Palindromic Substring: A suffix sort based approach in Java April 15, 2012
- Find the celebrity in O(N) in C++ April 18, 2012
- N-Queens Problem in Java April 18, 2012
- O(N)-time finding the longest Palindromic substring: Manacher's Algorithm in C++ April 21, 2012
- Finding the minimum window that contains the given character set in O(N)-time Java April 21, 2012
- Find the first missing positive integer in O(N)-time with O(1)-space (C/C++) April 22, 2012
- Sort 3-colored balls in O(N)-time with O(1)-space (Java) April 23, 2012
- Minimum Path Sum: recursion approach with backtracking (C/C++) April 23, 2012
- Minimum Path Sum: O(N*M)-DP approach (C/C++) April 24, 2012
- Flip sort on an integer array in Java April 28, 2012
- Brain teaser: Move guests in/out ball room in C/C++ April 28, 2012
- Tough Question (Open): Find the positions of milestones April 28, 2012
- Brain teaser: Find the positive integer generating sequence using factoring in C/C++ May 2nd, 2012
- Judge if a given string can be scrambled from another given string in C/C++ May 6th, 2012
- DP approach: Judge if a given string can be scrambled from another given string in C/C++ May 7th, 2012
- Approach 1: Sort nearly K-sorted array in O(NlogK)-time in Java May 12th, 2012
- Approach 2: Sort nearly K-sorted array in O(NlogK)-time in C/C++ May 13th, 2012
- Find the time period of the shuffling process in Java May 22nd, 2012
- Find path on a binary tree Java Oct 07, 2012
- Format data in CSV in Java Oct 18, 2012
- Grundy Number and Stone Piles Game in C++(referenced), April 15, 2013
- Extract FX Rate in SAS Macro Program, May 14, 2013
- Tricky Group By Statement in SAS SQL, May 14, 2013
- Validating a given column in all SAS libraries, May 27, 2013
- Specific Column Length Check in all SAS libraries, May 27, 2013
Property Service
Write a socket service that maintains a central collection of shared properties for a large distributed system. It should accept telnet-style connections (and will be tested using a telnet client). The service should be able to support a large number of clients concurrently. The service should be a Java application that can be started from the command line as follows: java PropertiesService [port number] If the optional port number is omitted, the service should default to port 4444. If the port is improperly specified (i.e., cannot be interpreted as an integer) or if unrecognized arguments are provided, the application should fail with an appropriate error message. The protocol is text-based and has three commands: set, get, and clear. The following table shows the command syntax and the required responses. Arguments are separated by whitespace (other than a newline); commands and responses are terminated by a newline.
The source code, report and screenshots can be found here.
Ant Project
The instructions for this project can be found at http://addepar.com/challenge.php. I wrote an email to the people at Addepar and realized that this problem was indeed very challenging. While it is a good exercise if you have time to ponder on. The project jar lib can be found here.
Iterative Tree Traversal
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
class NodeClass{
public:
int nodeValue;
NodeClass * leftPtr;
NodeClass * rightPtr;
NodeClass(int initializationValue){
this->nodeValue=initializationValue;
this->leftPtr=NULL;
this->rightPtr=NULL;
}
};
void IterativePreOrderTraversal(NodeClass * rootPtr){
stack<NodeClass *> nodeStack;
NodeClass * currPtr;
nodeStack.push(rootPtr);
while(nodeStack.size()!=0){
currPtr=nodeStack.top();
nodeStack.pop();
if (currPtr->rightPtr!=NULL)
nodeStack.push(currPtr->rightPtr);
if (currPtr->leftPtr!=NULL)
nodeStack.push(currPtr->leftPtr);
//print out the current node value
cout<<"Node value: "<<currPtr->nodeValue<<endl;
}
}
void IterativeInOrderTraversal(NodeClass * rootPtr){
//In-order traversal using iterative approach
NodeClass * currPtr=rootPtr;
stack<NodeClass *> nodeStack;
for(;;){
//keep pushing left child into stack
if (currPtr!=NULL){
nodeStack.push(currPtr);
currPtr=currPtr->leftPtr;
continue;
}
if (nodeStack.size()==0)
return;
// visit the current node
currPtr=nodeStack.top();
nodeStack.pop();
cout<<"Node value: "<<currPtr->nodeValue<<endl;
// visit the right child
currPtr=currPtr->rightPtr;
}
}
/*************************************************************************************
We use a prev variable to keep track of the previously-traversed node. Let’s assume
curr is the current node that’s on top of the stack. When prev is curr’s parent,
we are traversing down the tree. In this case, we try to traverse to curr’s left child
if available (ie, push left child to the stack). If it is not available, we look at
curr’s right child. If both left and right child do not exist (ie, curr is a leaf node),
we print curr’s value and pop it off the stack.
If prev is curr’s left child, we are traversing up the tree from the left. We look at
curr’s right child. If it is available, then traverse down the right child (ie, push right
child to the stack), otherwise print curr’s value and pop it off the stack.
If prev is curr’s right child, we are traversing up the tree from the right. In this case,
we print curr’s value and pop it off the stack.
*******************************************************************************************/
void IterativePostOrderTraversal(NodeClass *rootPtr) {
if (!rootPtr) return;
stack<NodeClass*> nodeStack;
nodeStack.push(rootPtr);
NodeClass *prev = NULL;
while (!nodeStack.empty()) {
NodeClass *curr = nodeStack.top();
if (!prev || prev->leftPtr == curr || prev->rightPtr == curr) {
if (curr->leftPtr)
nodeStack.push(curr->leftPtr);
else if (curr->rightPtr)
nodeStack.push(curr->rightPtr);
} else if (curr->leftPtr == prev) {
if (curr->rightPtr)
nodeStack.push(curr->rightPtr);
} else {
cout << "Node value: "<< curr->nodeValue << endl;
nodeStack.pop();
}
prev = curr;
}
}
/*************************************************************************************
1. Push the root node to the first stack.
2. Pop a node from the first stack, and push it to the second stack.
3. Then push its left child followed by its right child to the first stack.
4. Repeat step 2) and 3) until the first stack is empty.
5. Once done, the second stack would have all the nodes ready to be traversed in post-order.
Pop off the nodes from the second stack one by one and you?re done.
**************************************************************************************/
void postOrderTraversalIterativeTwoStacks(NodeClass *rootPtr) {
if (!rootPtr) return;
stack<NodeClass*> s;
stack<NodeClass*> output;
s.push(rootPtr);
while (!s.empty()) {
NodeClass *curr = s.top();
output.push(curr);
s.pop();
if (curr->leftPtr)
s.push(curr->leftPtr);
if (curr->rightPtr)
s.push(curr->rightPtr);
}
while (!output.empty()) {
cout <<"Node value: "<< output.top()->nodeValue <<endl;
output.pop();
}
}
void CreateTree(NodeClass ** rootPtr){
NodeClass* tmp0= new NodeClass(0);
NodeClass* tmp1=new NodeClass(1);
NodeClass* tmp2=new NodeClass(2);
tmp0->leftPtr=tmp1;
tmp0->rightPtr=tmp2;
NodeClass* tmp3=new NodeClass(3);
NodeClass* tmp4=new NodeClass(4);
NodeClass* tmp5=new NodeClass(5);
tmp1->leftPtr=tmp3;
tmp1->rightPtr=tmp4;
tmp2->rightPtr=tmp5;
*rootPtr=tmp0;
// tmp1,..., tmp5 local variables will be deleted after terminiation, but the tree structure remains
}
void BFSTraversal(NodeClass *rootPtr){
queue<NodeClass* > nodeQueue;
nodeQueue.push(rootPtr);
while(!nodeQueue.empty()){
NodeClass *currPtr = nodeQueue.front();
nodeQueue.pop();
cout <<"Node value: "<< currPtr->nodeValue <<endl;
if (currPtr->leftPtr)
nodeQueue.push(currPtr->leftPtr);
if (currPtr->rightPtr)
nodeQueue.push(currPtr->rightPtr);
}
}
void DeleteTree(NodeClass *rootPtr){
if (rootPtr!=NULL){
DeleteTree(rootPtr->leftPtr);
DeleteTree(rootPtr->rightPtr);
delete rootPtr;
}else
return;
}
Recursively Reverse Singly Linkedlist
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int nodeValue;
Node* nextPtr;
Node(int v){
this->nodeValue=v;
this->nextPtr=NULL;
}
};
void PrintLinkedList(Node* beginPtr){
while(beginPtr!=NULL){
cout<<beginPtr->nodeValue<<" ";
beginPtr=beginPtr->nextPtr;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void ReverseLinkedList(Node *startPtr){
if (startPtr->nextPtr!=NULL){
ReverseLinkedList(startPtr->nextPtr);
startPtr->nextPtr->nextPtr=startPtr;
}
}
void DeleteLinkedList(Node* iterPtr){
Node* tmpPtr=iterPtr;
while(iterPtr!=NULL){
tmpPtr=iterPtr->nextPtr;
delete iterPtr;
iterPtr=tmpPtr;
}
}
void InsertIntoLinkedList(Node **head, int v)
{
Node *newnode = new Node(v);
newnode->nextPtr = *head;
*head = newnode;
}
void ReverseInPlace(Node **headPtr, Node **tailPtr)
{
Node *pre, *cur, *next;
pre = NULL;
cur=*headPtr;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
next = cur->nextPtr;
cur->nextPtr=pre;
pre=cur;
cur = next;
}
*tailPtr=*headPtr;
*headPtr=pre;
}
bool deleteANode(Node **headPtr, Node **tailPtr, int v)
{
if(*headPtr==NULL)
return false;
if((*headPtr)->nodeValue == v)
{
Node *temp = *headPtr;
*headPtr = (*headPtr)->nextPtr;
delete temp;
if(*headPtr==NULL)
*tailPtr=NULL;
return true;
}
Node *cur = (*headPtr)->nextPtr;
Node *pre = *headPtr;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
if(cur->nodeValue == v)
{
pre->nextPtr=cur->nextPtr;
delete cur;
if(pre->nextPtr==NULL)
*tailPtr=pre;
return true;
}
pre=cur;
cur=cur->nextPtr;
}
return false;
}
//insert value v after a
bool InsertAfter(Node **head, Node **tail, int a, int v)
{
Node *cur = *head;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
if(cur->nodeValue == a)
{
Node *newnode = new Node(v);
newnode->nextPtr=cur->nextPtr;
cur->nextPtr=newnode;
if(newnode->nextPtr==NULL)
*tail=newnode;
return true;
}
cur=cur->nextPtr;
}
return false;
}
int main(int,char*[]){
//build a singly linked list
Node* headPtr=NULL;
/* Node* tmp1=new Node(1);
headPtr=tmp1;
Node* tmp2=new Node(2);
tmp1->nextPtr=tmp2;
tmp1=new Node(3);
tmp2->nextPtr=tmp1;
tmp2=new Node(4);
tmp1->nextPtr=tmp2;
tmp1=new Node(5);
tmp2->nextPtr=tmp1;
tmp1->nextPtr=NULL; */
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++)
InsertIntoLinkedList(&headPtr, i);
//Print out the node values in the linked list, should be 1 2 3 4 5
PrintLinkedList(headPtr);
//Reverse the linked list in recursion
Node* tailPtr=headPtr;
while (tailPtr->nextPtr!=NULL){
tailPtr=tailPtr->nextPtr;
}
ReverseLinkedList(headPtr);
headPtr->nextPtr=NULL;
headPtr=tailPtr;
PrintLinkedList(headPtr);
DeleteLinkedList(headPtr);
headPtr=NULL;
//verify on deletion operation
// PrintLinkedList(headPtr); error headPtr points to unallocated memeory space
}
Sorting using stack
#include <time.h>
void createStack(stack<int>& createStack){
/* initialize random seed: */
srand ( time(NULL) );
const int n=50;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
createStack.push(rand()%100);
}
}
void stackSort(stack<int>& opStack,int terminateLevel,int currLevel){
if (currLevel<=terminateLevel)
return;
else{
int x=opStack.top();
opStack.pop();
int newx=opStack.top();
if (x<newx){
opStack.pop();
opStack.push(x);
x=newx;
}
stackSort(opStack,terminateLevel,--currLevel);
opStack.push(x);
}
}
int main(){
stack<int> numberStack;
createStack(numberStack);
int n=numberStack.size();
// sort in ascending order
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
stackSort(numberStack,i,n);
}
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<numberStack.top()<<endl;
numberStack.pop();
}
}
Print all valid combinations of parentheses
int n=3;
char stk[100];
void printlegal( int ipos, int ileft, int iright)
{
if (ipos==2*n-1)
{
stk[ipos]=')';
for (int i=0; i<n*2; i++)
printf("%c", stk[i]);
printf("\n");
}else if (ileft==iright)
{
stk[ipos] = '(';
printlegal( ipos+1, ileft-1, iright );
}else if (ileft==0)
{
stk[ipos] = ')';
printlegal( ipos+1, ileft, iright-1 );
}else{
stk[ipos] = '(';
printlegal( ipos+1, ileft-1, iright );
stk[ipos] = ')';
printlegal( ipos+1, ileft, iright-1 );
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printlegal(0, n, n);
return 0;
}
Serialization of BT
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct Node{
char val;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
}TreeNode;
void serialize(TreeNode* node){
if (node == NULL){
printf("()");
return;
}
printf("(%c", node->val);
serialize(node->left);
serialize(node->right);
printf(")");
}
TreeNode* deserialize(char* arr, int* offset){
//printf("%c %d \n", arr[*offset], *offset);
if (arr[(*offset)]=='('){
char val = arr[ (*offset) + 1];
*offset = (*offset) + 1;
if (val == ')'){
*offset = *offset + 1;
return NULL;
}else{
TreeNode* n = (TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
n->val = val;
//printf("%c %d\n", n->val, *offset);
//initialize
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
(*offset) = (*offset) + 1;
if (arr[*offset] == ')'){
*offset = (*offset) + 1;
return n;
} else{
TreeNode* left = deserialize(arr, offset);
//printf("left: %c %d\n", n->val, *offset);
n->left = left;
}
//printf("me: %c %d\n", n->val, *offset);
if (arr[*offset] == ')'){
(*offset) = (*offset) + 1;
return n;
}else{
TreeNode* right = deserialize(arr, offset);
//printf("right: %c %d\n", n->val, *offset);
n->right = right;
}
(*offset) = (*offset) + 1;
return n;
}
}
}
int main(){
char* tree = "(a(b(e()())())(c()(d()())))";
int len = strlen(tree);
int* offset=(int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
*offset = 0;
TreeNode* root = deserialize(tree, offset);
printf("done\n");
serialize(root);
}
Test Interleaving of strings
import java.util.Stack;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
/**
* @author Li, Larry
* Java implementation of testing whether a given string is the interleaved
* combination of two other given strings
*
*/
public class TestInterleaving {
private class CursorLocation{
private int testStringCursor = 0;
private int str1Cursor = 0;
private int str2Cursor = 0;
public CursorLocation(int testStringCursor, int str1Cursor, int str2Cursor ) {
this.testStringCursor = testStringCursor;
this.str1Cursor = str1Cursor;
this.str2Cursor = str2Cursor;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public int getStr1Cursor() {
return str1Cursor;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public int getStr2Cursor() {
return str2Cursor;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public int getTestStringCursor() {
return testStringCursor;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String testStr = "keeptomorrowworkingwillbeharbetterd";
String strOne = "keepworkinghard";
String strTwo = "tomorrowwillbebetter";
TestInterleaving testInterleaving = new TestInterleaving();
boolean isTestStringInterleaved = testInterleavingRecursion(testStr, strOne, strTwo);
boolean isTestStringInterleavedIter = testInterleavingIteration(testStr, strOne, strTwo,
testInterleaving);
System.out.println("The test string that is the interleaved of two given strings is: "
+ isTestStringInterleaved);
System.out.println("The test string that is the interleaved of two given strings is: "
+ isTestStringInterleavedIter);
}
private static boolean testInterleavingRecursion(String testStr, String str1, String str2){
if (testStr.length()!= (str1.length()+str2.length())){
return false;
} else {
if (testStr.length()==0)
return true;
boolean isFirstCharacterEqualForStr1 = isFirstCharacterEqual(testStr,str1);
boolean isFirstCharacterEqualForStr2 = isFirstCharacterEqual(testStr, str2);
if (isFirstCharacterEqualForStr1 || isFirstCharacterEqualForStr2){
if (isFirstCharacterEqualForStr1 && isFirstCharacterEqualForStr2){
return testInterleavingRecursion(testStr.substring(1), str1.substring(1), str2)
|| testInterleavingRecursion(testStr.substring(1), str1, str2.substring(1));
} else if (isFirstCharacterEqualForStr1){
return testInterleavingRecursion(testStr.substring(1), str1.substring(1), str2);
} else {
return testInterleavingRecursion(testStr.substring(1), str1, str2.substring(1));
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
private static boolean isFirstCharacterEqual(String str1, String str2){
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(str1) && StringUtils.isNotEmpty(str2)){
return str1.charAt(0) == str2.charAt(0);
} else {
return false;
}
}
private static boolean testInterleavingIteration(String testStr, String str1, String str2,
TestInterleaving testInterleaving){
// The trick is to use stack to track down all possible combinations
if (testStr.length()!= (str1.length()+str2.length())){
return false;
} else {
Stack<CursorLocation> stackTrace = new Stack<CursorLocation>();
int testStrCursor =0;
int str1Cursor = 0;
int str2Cursor= 0;
stackTrace.add(testInterleaving.new CursorLocation(testStrCursor, str1Cursor, str2Cursor));
while (!stackTrace.isEmpty()){
// pop up the cursor location and do the test
CursorLocation cursorLocation = stackTrace.pop();
testStrCursor = cursorLocation.getTestStringCursor();
str1Cursor = cursorLocation.getStr1Cursor();
str2Cursor= cursorLocation.getStr2Cursor();
while (testStrCursor<testStr.length()-1){
boolean isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr1 = false;
boolean isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr2 = false;
if (str1Cursor<str1.length())
isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr1 = testStr.charAt(testStrCursor)
== str1.charAt(str1Cursor);
if (str2Cursor<str2.length())
isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr2 = testStr.charAt(testStrCursor)
== str2.charAt(str2Cursor);
if (isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr1 && isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr2){
stackTrace.add(testInterleaving.new CursorLocation(testStrCursor,
str1Cursor, str2Cursor));
//Deal with the first match with string one, the 2nd case saved to the
//stack for later processing
testStrCursor++;
str1Cursor++;
} else if (isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr1){
testStrCursor++;
str1Cursor++;
} else if (isCurrentCharacterEqualForStr2){
testStrCursor++;
str2Cursor++;
} else {
break;
}
}
// decide if the string is matched to the end
if (testStrCursor == testStr.length()-1){
if (str1Cursor == str1.length()-1){
if (testStr.charAt(testStrCursor) == str1.charAt(str1Cursor))
return true;
} else if (str2Cursor == str2.length()-1){
if (testStr.charAt(testStrCursor) == str2.charAt(str2Cursor))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
Setup sibling links for a tree (May not be a binary tree)
We use a singly linked list to store the pointer to the first node at each level, once the sibling links are setup, traverse from this first node until meet a null pointer. The given example's linked list looks like this:
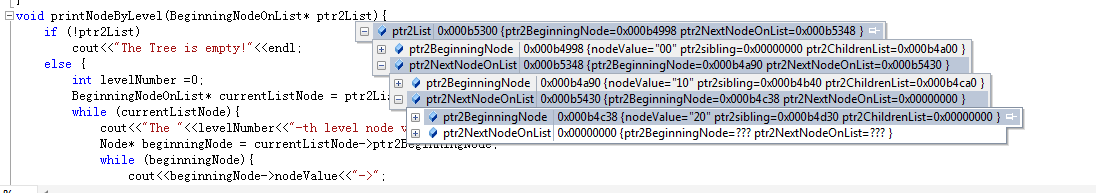
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
/***********************************************************
* Author: Larry (Zhirong) Li March 4, 2012
* Setup Sibling Link for a tree, the given example is
* (00)
* / \
* (10) (11)
* / | \ / \
* (20)(21)(22) (23)(24)
************************************************************/
class Node;
class ChildrenListNode{
public:
Node* ptr2Child;
ChildrenListNode* ptr2NextChild;
ChildrenListNode(Node* ptr1){
this->ptr2Child =ptr1;
this->ptr2NextChild = NULL;
}
};
class Node{
public:
string nodeValue;
Node* ptr2sibling;
ChildrenListNode* ptr2ChildrenList;
Node(string value){
this->nodeValue = value;
this->ptr2sibling = NULL;
this->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
}
};
class BeginningNodeOnList{
public:
Node* ptr2BeginningNode;
BeginningNodeOnList* ptr2NextNodeOnList;
BeginningNodeOnList(Node* ptr){
this->ptr2BeginningNode = ptr;
this->ptr2NextNodeOnList = NULL;
}
};
Node* createSampleTree(){
Node* ptr00 = new Node(string("00"));
Node* ptr10 = new Node("10");
ChildrenListNode* childPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr10);
Node* ptr11 = new Node("11");
ChildrenListNode* nextChildPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr11);
ptr00->ptr2ChildrenList = childPtr;
childPtr->ptr2NextChild = nextChildPtr;
//Create the child node 20,21,22 for parent node 10
Node* ptr20 = new Node("20");
Node* ptr21 = new Node("21");
Node* ptr22 = new Node("22");
childPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr20);
nextChildPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr21);
ptr10->ptr2ChildrenList = childPtr;
childPtr->ptr2NextChild = nextChildPtr;
childPtr = nextChildPtr;
nextChildPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr22);
childPtr->ptr2NextChild = nextChildPtr;
//Create the child node 23,24 for parent node 11
Node* ptr23 = new Node("23");
Node* ptr24 = new Node("24");
childPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr23);
nextChildPtr = new ChildrenListNode(ptr24);
ptr11->ptr2ChildrenList = childPtr;
childPtr->ptr2NextChild = nextChildPtr;
ptr20->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
ptr21->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
ptr22->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
ptr23->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
ptr24->ptr2ChildrenList = NULL;
return ptr00;
}
BeginningNodeOnList* setupSiblingLink(Node* ptr){
//always point to the tail of the list
BeginningNodeOnList* headPtr2BeginningNodeList = NULL;
BeginningNodeOnList* currPtr2BeginningNodeList = NULL;
if (!ptr)
return headPtr2BeginningNodeList;
else {
queue<Node*> nodeQueue;
queue<Node*> sameLevelNodeQueue;
nodeQueue.push(ptr);
bool firstNode = true;
while(!nodeQueue.empty()){
//pop all elements in the queue to the second queue
while(!nodeQueue.empty()){
sameLevelNodeQueue.push(nodeQueue.front());
nodeQueue.pop();
}
/*Since the sameLevelNodeQueue is not empty here, the first element
must be the beginnng node at each level */
BeginningNodeOnList* ptr2BeginningNodeList =
new BeginningNodeOnList(sameLevelNodeQueue.front());
if (firstNode){
headPtr2BeginningNodeList = ptr2BeginningNodeList;
currPtr2BeginningNodeList = ptr2BeginningNodeList;
firstNode = false;
} else {
currPtr2BeginningNodeList->ptr2NextNodeOnList = ptr2BeginningNodeList;
currPtr2BeginningNodeList = ptr2BeginningNodeList;
}
while(!sameLevelNodeQueue.empty()){
//push all children of the popped nodes to the node queue
Node* currPtr = sameLevelNodeQueue.front();
sameLevelNodeQueue.pop();
ChildrenListNode* ptr2ChildrenList = currPtr->ptr2ChildrenList;
while(ptr2ChildrenList){
if (ptr2ChildrenList->ptr2Child)
nodeQueue.push(ptr2ChildrenList->ptr2Child);
ptr2ChildrenList = ptr2ChildrenList->ptr2NextChild;
}
//Setup the sibling link
if(!sameLevelNodeQueue.empty())
currPtr->ptr2sibling = sameLevelNodeQueue.front();
}
}
return headPtr2BeginningNodeList;
}
}
void printNodeByLevel(BeginningNodeOnList* ptr2List){
if (!ptr2List)
cout<<"The Tree is empty!"<<endl;
else {
int levelNumber =0;
BeginningNodeOnList* currentListNode = ptr2List;
while (currentListNode){
cout<<"The "<<levelNumber<<"-th level node values are:"<<endl;
Node* beginningNode = currentListNode->ptr2BeginningNode;
while (beginningNode){
cout<<beginningNode->nodeValue;
beginningNode=beginningNode->ptr2sibling;
if (beginningNode)
cout<<"->";
}
cout<<endl;
levelNumber++;
currentListNode = currentListNode->ptr2NextNodeOnList;
}
}
}
void freeChildrenListMemory(ChildrenListNode* currChildrenListPtr){
if(!currChildrenListPtr) return;
freeChildrenListMemory(currChildrenListPtr->ptr2NextChild);
delete currChildrenListPtr;
}
void freeTreeMemory(Node* rootPtr){
if (!rootPtr) return;
ChildrenListNode* currChildrenListPtr = rootPtr->ptr2ChildrenList;
if (currChildrenListPtr){
while (currChildrenListPtr){
freeTreeMemory(currChildrenListPtr->ptr2Child);
currChildrenListPtr = currChildrenListPtr->ptr2NextChild;
}
freeChildrenListMemory(rootPtr->ptr2ChildrenList);
}
delete rootPtr;
}
void freeLinkedListMemory(BeginningNodeOnList* ptr2List){
if(!ptr2List) return;
freeLinkedListMemory(ptr2List->ptr2NextNodeOnList);
delete ptr2List;
}
int main(){
Node* rootPtr = createSampleTree();
BeginningNodeOnList* ptr2List = setupSiblingLink(rootPtr);
printNodeByLevel(ptr2List);
//Delete Allocated Memory
freeLinkedListMemory(ptr2List);
freeTreeMemory(rootPtr);
}
Enumerate all mutation paths using #(Edit Distance) steps
The edit distance between two strings is the minimum number of characters in one string to be updated, inserted, or deleted to get the second string. This is a classic application of dynamic programming to solve this problem. There are many online code examples in calculating this edit distance. However, I was not lucky enough to find an algorithm to print out all such mutation paths using #(edit distance) steps.
I am using recursion to capture all such transition paths. In order to calculate the edit distance, notice that f(i,j) means how many steps at minimum cost are needed to convert the first i characters in the original(optString) to the first j characters in the target (targetString). Suppose the length of original string is I and the length of target string is J. Then i can take values from 0 to I and j can take values from 0 to J. So I create a 2D array of size (I+1)-by-(J+1). Then the following recursion can be established.
f(i,j) =
if optString.at(i-1) == targetString.at(j-1)
f(i,j)=f(i-1,j-1)
else {
f(i,j)= min(f(i-1,j),f(i,j-1),f(i-1,j-1)) +1
}
Have in mind that f(i-1,j) +1 = f(i,j) corresponds to deletion, i.e., the first (i-1) characters can already be converted to the first j characters in target string, then in order to reach f(i,j), the i-th character has to be deleted, then operation to f(i,j) is achieved.
Notice that in an optimized transition, insertion and deletion can not be paired (otherwise it is not the minimum step transition)
The boundary condition is simple to set,
f(0,j) =j, since we have to insert the first j characters from the target string to optString.
f(i,0) =i, since we have to delete the first i characters from the optString.
Then using two for loops to get the edit distance for every f(i,j)
The second part is to print the mutation paths.
The optStringCursor and targetStringCursor always point to the current location of the string. We traverse from the end f(I,J) ( optStringCursor=I-1, targetStringCursor=J-1) see how the optimal path is reached here. If f(i,j) = f(i-1,j)+1 and f(i-1,j-1)+1, that means both deletion and replacement can reach the same destination. So we need to traverse both paths to enumerate all possible paths of such kind.
The base case in the recursion is:
either we backward traverse to some f(i,j)=0, then we can directly start from here for printing or we encounter the case f(i,0) or f(0,j) so we directly delete/insert characters then print out the rest using the decode sequence.
The decodeSequence is used to record how we reach the current f(i,j) from f(I,J), for example,
optString ="la"
targetString = "dis"
the edit distance for the above is 3, and we could have decode sequence (I: insertion, D: deletion, R: replacement, S: skip)
RRI: la->(l->d)a->d(a->i)-> di(+s)->dis
RIR: la->(l->d)a->d(+i)a->di(a->s)->dis
IRR: la->(+d)la->d(l->i)a->di(a->s)->dis
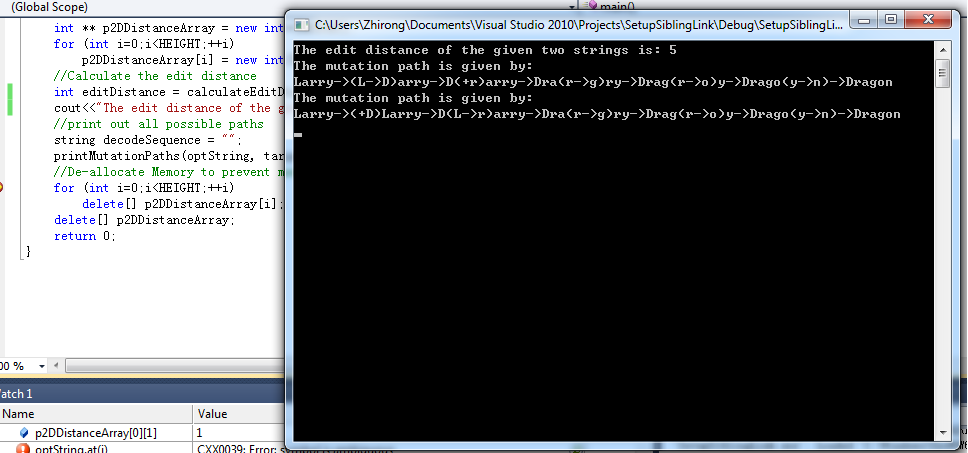
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
/***************************************************
Author: Larry (Zhirong), Li
March 07,2012@Toronto
Print out all transition paths using edit distance
*****************************************************/
int calculateEditDistance(string optString, string targetString, int HEIGHT, int WIDTH, int** p2DDistanceArray){
for(int i=0;i<HEIGHT;i++)
p2DDistanceArray[i][0] = i;
for(int j=0;j<WIDTH;j++)
p2DDistanceArray[0][j] = j;
for (int i=1;i<HEIGHT;i++){
for(int j=1;j<WIDTH;j++)
{
if (optString.at(i-1) == targetString.at(j-1))
p2DDistanceArray[i][j] = p2DDistanceArray[i-1][j-1];
else {
//f(i,j-1)+1=f(i,j)
int insertion = p2DDistanceArray[i][j-1] + 1;
//f(i-1,j)+1=f(i,j)
int deletion = p2DDistanceArray[i-1][j] + 1;
//f(i-1,j-1)+1=f(i,j)
int replacement = p2DDistanceArray[i-1][j-1] + 1;
p2DDistanceArray[i][j] = min(min(insertion, deletion), replacement);
}
}
}
return p2DDistanceArray[HEIGHT-1][WIDTH-1];
}
void printMutationPaths(string& optString, string& targetString, int optStringCursor, int targetStringCursor,
int** p2DDistanceArray, string decodeSequence){
//base cases
if ((p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor+1][targetStringCursor+1] == 0) || (optStringCursor+1 == 0)
|| (targetStringCursor+1 ==0) ){
//Print mutation path
cout<<"The mutation path is given by:"<<endl;
cout<<optString;
//There should be #decodeSequence.length() mutation steps
string currMuatedOptString = optString.substr(0, optStringCursor+1);
//Decide which boundary case we are in
if (optStringCursor+1 == 0){
//insert #(targetStringCursor-optStringCursor) characters from targetString
int currCursor = -1;
for (int i=0;i<targetStringCursor-optStringCursor;++i){
cout<<"->"<<currMuatedOptString<<"(+"<<targetString.substr(currCursor+1,1)<<")"
<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+1);
currMuatedOptString = currMuatedOptString + targetString.substr(currCursor+1,1);
currCursor++;
}
}else if (targetStringCursor+1 ==0) {
//delete # (optStringCursor-targetStringCursor) characters from optString
int currCursor = -1;
currMuatedOptString = optString.substr(0, currCursor+1);
for (int i=0;i<optStringCursor-targetStringCursor;++i){
cout<<"->"<<currMuatedOptString<<"(-"<<optString.substr(currCursor+1,1)<<")"
<<optString.substr(currCursor+2);
currCursor++;
}
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<decodeSequence.length();++i){
switch(decodeSequence.at(i)){
case 'I':
cout<<"->"<<currMuatedOptString<<"(+"<<targetString.substr(targetStringCursor+1,1)
<<")"<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+1);
currMuatedOptString = currMuatedOptString +
targetString.substr(targetStringCursor+1,1);
targetStringCursor++;
break;
case 'D':
cout<<"->"<<currMuatedOptString<<"(-"<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+1,1)<<")"
<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+2);
optStringCursor++;
break;
case 'R':
cout<<"->"<<currMuatedOptString<<"("<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+1,1)
<<"->"<<targetString.substr(targetStringCursor+1,1)<<")"
<<optString.substr(optStringCursor+2);
currMuatedOptString = currMuatedOptString +
targetString.substr(targetStringCursor+1,1);
optStringCursor++;
targetStringCursor++;
break;
case 'S':
currMuatedOptString = currMuatedOptString +
targetString.substr(targetStringCursor+1,1);
optStringCursor++;
targetStringCursor++;
break;
default:
cout << "unknown decoding sequence: terminate";
exit(1);
}
}
cout<<"->"<<targetString<<endl;
}else if(optString.at(optStringCursor) == targetString.at(targetStringCursor)){
printMutationPaths(optString, targetString, optStringCursor-1, targetStringCursor-1,
p2DDistanceArray, "S" + decodeSequence);
}else {
//f(i,j-1)+1=f(i,j)
if (p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor+1][targetStringCursor+1]
== p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor+1][targetStringCursor]+1)
printMutationPaths(optString, targetString, optStringCursor, targetStringCursor-1,
p2DDistanceArray, "I" + decodeSequence);
//f(i-1,j)+1=f(i,j)
if (p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor+1][targetStringCursor+1]
== p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor][targetStringCursor+1]+1)
printMutationPaths(optString, targetString, optStringCursor-1, targetStringCursor,
p2DDistanceArray, "D" + decodeSequence);
//f(i-1,j-1)+1=f(i,j)
if (p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor+1][targetStringCursor+1]
== p2DDistanceArray[optStringCursor][targetStringCursor]+1)
printMutationPaths(optString, targetString, optStringCursor-1, targetStringCursor-1,
p2DDistanceArray, "R" + decodeSequence);
}
}
int main(){
string optString ("Larry");
string targetString ("Dragon");
int HEIGHT = optString.length()+1;
int WIDTH = targetString.length()+1;
//Allocate Memory
int ** p2DDistanceArray = new int*[HEIGHT];
for (int i=0;i<HEIGHT;++i)
p2DDistanceArray[i] = new int[WIDTH];
//Calculate the edit distance
int editDistance = calculateEditDistance(optString, targetString, HEIGHT, WIDTH, p2DDistanceArray);
cout<<"The edit distance of the given two strings is: "<<editDistance<<endl;
//print out all possible paths
string decodeSequence = "";
printMutationPaths(optString, targetString, optString.length()-1, targetString.length()-1,
p2DDistanceArray,decodeSequence);
//De-allocate Memory to prevent memory leak
for (int i=0;i<HEIGHT;++i)
delete[] p2DDistanceArray[i];
delete[] p2DDistanceArray;
return 0;
}
Calculate # visited points on an infinite chessboard
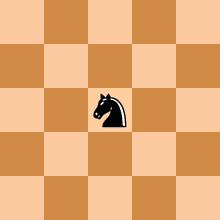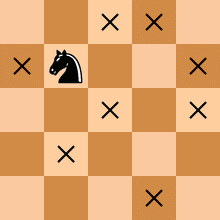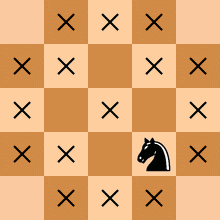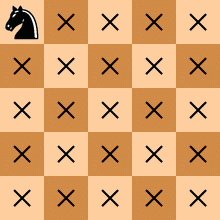
This is not the Knight's tour problem (Hamiltonian Cycle problem). Indeed, one needs to find out how many positions (including the start point) a knight/horse can jump to after 10 moves. :) The code answer is 1345, within the 41-by-41 search range.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.EqualsBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.HashCodeBuilder;
/**
* imagine an infinite chess board. If the horse jumps from the origin, how many
* distinct positions can the horse possibly visit after 10 moves.
* @author Larry, Li March 9, 2012 @ Toronto
*
*/
public class ComputeHorseJumps {
class Coordinate {
private int x;
private int y;
public Coordinate(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setX(int i) {
x = i;
}
public void setY(int i) {
y = i;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (obj == this)
return true;
if (obj.getClass() != getClass())
return false;
Coordinate other = (Coordinate) obj;
return new EqualsBuilder().append(this.getX(), other.getX())
.append(this.getY(), other.getY()).isEquals();
}
public int hashCode() {
return new HashCodeBuilder().append(this.getX()).append(this.getY()).toHashCode();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numberOfMoves=0;
String line = null;
ComputeHorseJumps classInstance = new ComputeHorseJumps();
try {
BufferedReader is = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
line = is.readLine();
numberOfMoves = Integer.parseInt(line);
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
System.err.println("Not a valid number: " + line);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Unexpected IO ERROR: " + e);
}
int numberOfDistinctPoints = calculateNumberOfDistinctPoints(numberOfMoves, classInstance);
System.out.println("The total number after " + numberOfMoves + " move(s) is " + numberOfDistinctPoints);
}
/**
* @param numberOfMoves
* @param classInstance
* @return
*/
private static int calculateNumberOfDistinctPoints(int numberOfMoves, ComputeHorseJumps classInstance) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Coordinate startingPoint = classInstance.new Coordinate(0,0);
Set<Coordinate> visitedPoints = new HashSet<Coordinate>();
visitedPoints.add(startingPoint);
//create a processing queue
List<Coordinate> processQueue = new ArrayList<Coordinate>();
List<Coordinate> newProcessQueue = new ArrayList<Coordinate>();
processQueue.add(startingPoint);
for(int i=0;i<numberOfMoves;i++){
newProcessQueue.clear();
for(Iterator<Coordinate> iter = processQueue.iterator(); iter.hasNext();){
Coordinate currentPoint = (Coordinate) iter.next();
int xCoordinate = currentPoint.getX();
int yCoordinate = currentPoint.getY();
// traverse 8 cases
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate+1, yCoordinate+2, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate-1, yCoordinate+2, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate-2, yCoordinate+1, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate-2, yCoordinate-1, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate-1, yCoordinate-2, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate+1, yCoordinate-2, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate+2, yCoordinate-1, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
putIntoSetAndList(xCoordinate+2, yCoordinate+1, visitedPoints, newProcessQueue, classInstance);
}
processQueue.clear();
processQueue.addAll(newProcessQueue);
}
return visitedPoints.size();
}
private static void putIntoSetAndList(int xCoordinate, int yCoordinate, Set<Coordinate> visitedPoints,
List<Coordinate> newProcessQueue, ComputeHorseJumps classInstance) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Coordinate newPoint = classInstance.new Coordinate(xCoordinate, yCoordinate);
if (!visitedPoints.contains(newPoint)){
visitedPoints.add(newPoint);
newProcessQueue.add(newPoint);
}
}
}
Spiral Print of Actresses (Except for Clark Gable)Names
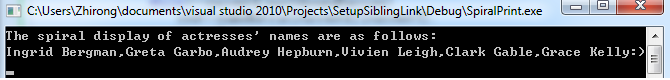
The purpose of this problem is to clockwise spirally print out the names. These names are fairly well-known if you love movies of old time.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/****************************************************
* Spiral print of movie stars' names
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li on March 16, 2012
* Toronto
***************************************************/
const int columnWidth = 10;
const int rowHeight = 8;
static char nameMatrix[rowHeight][columnWidth] =
{ {'I','n','g','r','i','d',' ','B','e','r'},
{'e','y',' ','H','e','p','b','u','r','g'},
{'r','C','l','a','r','k',' ','G','n','m'},
{'d',',','e',' ','K','e','l','a',',','a'},
{'u','h','c',')',':','y','l','b','V','n'},
{'A','g','a','r','G',',','e','l','i',','},
{',','i','e','L',' ','n','e','i','v','G'},
{'o','b','r','a','G',' ','a','t','e','r'}
};
void spiralPrint(){
// initialize the value of 4-way barriers
int eastboundBarrier = columnWidth;
int southboundBarrier = rowHeight;
int westboundBarrier = -1;
int northboundBarrier = 0;
int currentX = 0;
int currentY = 0;
cout<<"The spiral display of actresses' names are as follows:"<<endl;
cout<<nameMatrix[currentX][currentY];
while(true){
// heading east
if (currentY == eastboundBarrier-1 ){
break;
} else {
while(++currentY<eastboundBarrier)
cout<<nameMatrix[currentX][currentY];
eastboundBarrier--;
}
currentY--;
// heading south
if (currentX == southboundBarrier-1){
break;
} else {
while(++currentX<southboundBarrier)
cout<<nameMatrix[currentX][currentY];
southboundBarrier--;
}
currentX--;
// heading west
if (currentY == westboundBarrier+1){
break;
} else {
while(--currentY>westboundBarrier)
cout<<nameMatrix[currentX][currentY];
westboundBarrier++;
}
currentY++;
// heading north
if (currentX == northboundBarrier+1){
break;
} else {
while(--currentX>northboundBarrier)
cout<<nameMatrix[currentX][currentY];
northboundBarrier++;
}
currentX++;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
spiralPrint();
return 0;
}
Quicksort On Singly Linked List
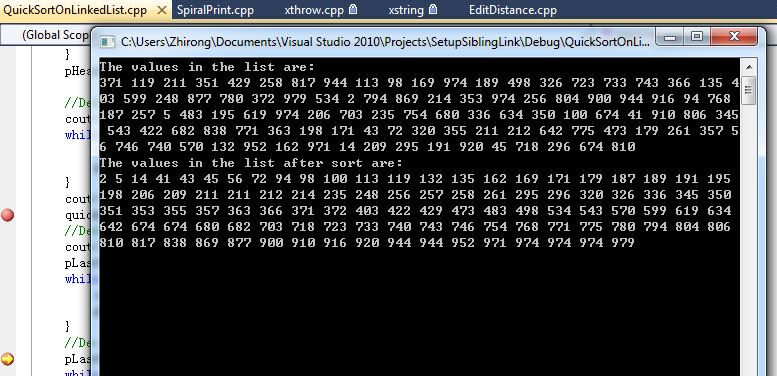
You are not allowed to change the node values of a singly linked list of integers. You are also required to use O(1) space to sort this list. Quicksort is the best candidate. One important thing that should get your attention is that you can only manipulate the pointers and the header pointer could be changed. Thus pointer to the pointer to the list is passed in.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
/**************************************************************************************************
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li March 20, 2012 in Toronto
***************************************************************************************************
* Assume you are given a list of integers with node definition
* typedef struct Node{
* const int nodeValue;
* Node * pNextNode;
* Node(int value=0, Node* ptr=NULL): nodeValue(value),pNextNode(ptr){}
* }SinglyLinkedListNode;
*
* You are only allowed to use O(1) space, how would you sort out this list in ascending order
*
* Refer to the following partition logic in the quicksort algorithm
*
* The Core of the Partition Algorithm
* int i = left - 1;
* int j = right;
* while (true) {
* while (less(a[++i], a[right])) // find item on left to swap
* ; // a[right] acts as sentinel
* while (less(a[right], a[--j])) // find item on right to swap
* if (j == left) break; // don't go out-of-bounds
* if (i >= j) break; // check if pointers cross
* exch(a, i, j); // swap two elements into place
* }
* exch(a, i, right); // swap with partition element
* return i;
*************************************************************************************************/
typedef struct Node{
const int nodeValue;
Node * pNextNode;
Node(int value=0, Node* ptr=NULL): nodeValue(value),pNextNode(ptr){}
}SinglyLinkedListNode;
Node* AdvancePointerToGivenIndexNode(Node ** prevPointer, Node** currPointer, int index, Node ** p2pHeader){
*prevPointer = NULL;
*currPointer = *p2pHeader;
for(int i=0;i<index;i++){
*prevPointer = *currPointer;
*currPointer = (*currPointer)->pNextNode;
}
return *currPointer;
}
bool less(Node* leftOprand, Node* rightOprand){
return (leftOprand->nodeValue<rightOprand->nodeValue);
}
void exch(Node* p2PrevBigNode, Node* p2BigNode, Node* p2PrevSmallNode, Node* p2SmallNode){
// pHeader->(3)->(2)->(1) case: swap (3) and (1)
if (p2PrevBigNode)
p2PrevBigNode->pNextNode = p2SmallNode;
// pHeader->(2)->(1) case: swap (2) and (1)
if (p2PrevSmallNode != p2BigNode)
p2PrevSmallNode->pNextNode = p2BigNode;
Node* tempNode = p2SmallNode->pNextNode;
if (p2SmallNode!=p2BigNode->pNextNode)
p2SmallNode->pNextNode = p2BigNode->pNextNode;
else
p2SmallNode->pNextNode = p2BigNode;
p2BigNode->pNextNode = tempNode;
}
int partition(Node ** p2pHeader, int firstElement, int lastElement){
int i = firstElement -1;
int j = lastElement;
Node* p2PreviousNodeOfFirstBigElement, *p2FirstBigElement,*p2PreviousNodeOfFirstSmallElement,
*p2FirstSmallElement;
Node* p2LastNode = *p2pHeader;
for(int k=0;k<lastElement;k++){
p2LastNode = p2LastNode->pNextNode;
}
while(true){
// find item on left to swap
//Important note: The linked list keeps changing so have to scan from header for (i+1)th element
// and that is the reason to use ** p2pHeader to point to the start position all the time
while (less(AdvancePointerToGivenIndexNode(&p2PreviousNodeOfFirstBigElement,&p2FirstBigElement,
++i,p2pHeader), p2LastNode));
// find item on right to swap
while (less(p2LastNode,AdvancePointerToGivenIndexNode(&p2PreviousNodeOfFirstSmallElement,
&p2FirstSmallElement,--j,p2pHeader))){
// don't go out-of-bounds
if (j == firstElement)
break;
}
// check if pointers cross
if (i >= j)
break;
//exch(i, j)
exch(p2PreviousNodeOfFirstBigElement, p2FirstBigElement, p2PreviousNodeOfFirstSmallElement,
p2FirstSmallElement);
if (i==0) *p2pHeader = p2FirstSmallElement;
}
if (i!=lastElement){
AdvancePointerToGivenIndexNode(&p2PreviousNodeOfFirstSmallElement,&p2FirstSmallElement,lastElement,
p2pHeader);
//exch(i,lastElement)
exch(p2PreviousNodeOfFirstBigElement, p2FirstBigElement,p2PreviousNodeOfFirstSmallElement,
p2FirstSmallElement);
if (i==0) *p2pHeader = p2FirstSmallElement;
}
return i;
}
void quickSortOnSinglyLinkedList(Node ** p2pHeader, int firstElement, int lastElement){
if (firstElement>=lastElement)
return;
int pivotPosition = partition(p2pHeader, firstElement, lastElement);
quickSortOnSinglyLinkedList(p2pHeader,firstElement, pivotPosition-1);
quickSortOnSinglyLinkedList(p2pHeader,pivotPosition+1, lastElement);
}
int main(int argc, char ** argv){
const unsigned int QUEUELENGTH = 100;
//initialize the seed of the PRNG
srand(time(NULL));
//Create a singly linked list
Node* pHeader = NULL;
Node* pLastNode = NULL;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<QUEUELENGTH;i++){
Node* pNewNode = new Node(rand()%1000,pLastNode);
pLastNode = pNewNode;
}
pHeader = pLastNode;
//Debug: Print out the list
cout<<"The values in the list are: "<<endl;
while (pLastNode){
cout<<pLastNode->nodeValue<<" ";
pLastNode = pLastNode->pNextNode;
}
cout<<endl;
quickSortOnSinglyLinkedList(&pHeader,0,QUEUELENGTH-1);
//Debug: Print out the list after the sorting process
cout<<"The values in the list after sort are: "<<endl;
pLastNode = pHeader;
while (pLastNode){
cout<<pLastNode->nodeValue<<" ";
pLastNode = pLastNode->pNextNode;
}
//De-allocate list memory
pLastNode = pHeader;
while (pLastNode){
Node * pTemp = pLastNode->pNextNode;
delete pLastNode;
pLastNode = pTemp;
}
}
Check if identical BSTs from given number streams
Given two number streams (Assume the numbers are distinct, your task is to find whether they will create the same BST or not. I give a naive approach but in a more OOP framework.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**************************************************************
* Given two number streams (Assume the numbers are distinct
* your task is to find whether they will create the same BST
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li on April 4, 2012
* Toronto
*************************************************************/
struct TreeNode{
int _nodeValue;
TreeNode *_leftChild;
TreeNode *_rightChild;
TreeNode(int nodeValue): _nodeValue(nodeValue){
_leftChild = NULL;
_rightChild = NULL;
}
};
class TreeTest{
public:
TreeTest(const int *pValueList =NULL, int length=0):_pRootTree(NULL){
if (length>0){
TreeNode *ptr = new TreeNode(pValueList[0]);
for(int i=1;i<length;++i){
buildBST(ptr, pValueList[i]);
}
_pRootTree = ptr;
}
}
~TreeTest(){
deleteBST(_pRootTree);
}
TreeNode * getTreeRoot(){
return this->_pRootTree;
}
protected:
private:
TreeNode * _pRootTree;
void buildBST(TreeNode * const ptr, const int& nodeValue){
if (nodeValue< ptr->_nodeValue){
if (ptr->_leftChild == NULL){
TreeNode *tmp = new TreeNode(nodeValue);
ptr->_leftChild = tmp;
} else
buildBST(ptr->_leftChild, nodeValue);
} else {
if (ptr->_rightChild == NULL){
TreeNode *tmp = new TreeNode(nodeValue);
ptr->_rightChild = tmp;
} else
buildBST(ptr->_rightChild, nodeValue);
}
}
void deleteBST(TreeNode *ptr){
if (ptr == NULL) return;
deleteBST(ptr->_leftChild);
deleteBST(ptr->_rightChild);
delete ptr;
}
};
bool isBSTEquals(const TreeNode * const ptr1, const TreeNode * const ptr2){
if (ptr1 == NULL && ptr2 == NULL)
return true;
else if (ptr1 != NULL && ptr2 != NULL){
if (ptr1->_nodeValue == ptr2->_nodeValue)
return isBSTEquals(ptr1->_leftChild, ptr2->_leftChild) &&
isBSTEquals(ptr1->_rightChild, ptr2->_rightChild);
else
return false;
} else
return false;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
static struct {
const int valueList1[5];
const int valueList2[5];
const int length;
const bool equals;
} testCases[] = {
{{10,5,20,15,30},{10,20,15,30,5}, 5, true},
{{10,5,20,15,30},{10,15,30,20,5}, 5, false}
};
for(size_t i=0;i<sizeof(testCases)/sizeof(testCases[0]);++i){
//Assume object always successfully created.
TreeTest * pTreeTest1 = new TreeTest(testCases[i].valueList1, testCases[i].length);
TreeTest * pTreeTest2 = new TreeTest(testCases[i].valueList2, testCases[i].length);
if (isBSTEquals(pTreeTest1->getTreeRoot(), pTreeTest2->getTreeRoot()) != testCases[i].equals){
cout<<"The "<<i<<"-th test failed."<<endl;
delete pTreeTest1;
delete pTreeTest2;
return 1;
}
delete pTreeTest1;
delete pTreeTest2;
}
cout<<"Test succeeds!"<<endl;
}
Check if identical BSTs from given number streams in Java
The same problem as above, this time we don't bother to create the BSTs. The key idea is similar to quicksort except that we keep the relative order of smaller/bigger items with respect to the pivoting element. By doing so, we don't interfere with the creation order.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* The same problem as the above.
* @author Larry, Zhirong Li
* Creation Date: Apr 5, 2012
*/
public class TestIdenticalBSTs {
private static boolean is_BST_identical(List<Integer> array1, List<Integer> array2){
if (array1.isEmpty() && array2.isEmpty())
return true;
else if (array1.size() != array2.size())
return false;
else {
//decide the root node is identical
if (!((Integer)array1.get(0)).equals((Integer)array2.get(0)))
return false;
else {
List<Integer> array1LeftSublist = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> array1RightSublist = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> array2LeftSublist = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> array2RightSublist = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// array1.size() = array2.size() here
for(int i=1;i<array1.size();i++){
if (((Integer)array1.get(i)).compareTo((Integer)array1.get(0))<0)
array1LeftSublist.add(array1.get(i));
else
array1RightSublist.add(array1.get(i));
if (((Integer)array2.get(i)).compareTo((Integer)array2.get(0))<0)
array2LeftSublist.add(array2.get(i));
else
array2RightSublist.add(array2.get(i));
}
return is_BST_identical(array1LeftSublist, array2LeftSublist) &&
is_BST_identical(array1RightSublist, array2RightSublist);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//{10,5,20,15,30},{10,20,15,30,5} true
List<Integer> inputStream1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inputStream1.add(new Integer(10));
inputStream1.add(new Integer(5));
inputStream1.add(new Integer(20));
inputStream1.add(new Integer(15));
inputStream1.add(new Integer(30));
List<Integer> inputStream2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inputStream2.add(new Integer(10));
inputStream2.add(new Integer(20));
inputStream2.add(new Integer(15));
inputStream2.add(new Integer(30));
inputStream2.add(new Integer(5));
boolean isEqual = TestIdenticalBSTs.is_BST_identical(inputStream1, inputStream2);
System.out.println("\"The given two input stream will generate the same BST\" is " +isEqual);
}
}
In place circular shift of character strings.
Rotate a one-dimensional array of n elements to the right by k steps. For instance, with n=7 and k=3, the array {a, b, c, d, e, f, g} is rotated to {e, f, g, a, b, c, d}.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*****************************************************************************************************
* In place circular shift of character string, we don't bother to use double string reverse approach
* Instead, since we know where each character belongs after the rotation, we can do a chain of replacement
* of length N as compared to 2N changes for double string reverse
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li on April 05, 2012 in Toronto
****************************************************************************************************/
void circularShift(char * const p2CharArray, int length, int shifts){
int num_shifts = 0;
int curr_position = 0;
char currChar = p2CharArray[curr_position];
while (num_shifts<length){
int target_position = ((curr_position + shifts )%length + length)%length;
char tmpChar = p2CharArray[target_position];
p2CharArray[target_position] = currChar;
currChar = tmpChar;
curr_position = target_position;
num_shifts++;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
char charArray[] = "veYouILo";
const char resultArray[] = "ILoveYou";
const int n = strlen(charArray);
const int k = 3;
if (n>0){
circularShift(charArray, n, k);
if (strcmp( charArray, resultArray) == 0)
cout<<"Rotation is correctly performed!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Rotation is not correctly performed!"<<endl;
}
}
Jump Game: Naive Approach (Dijkstra Algorithm)
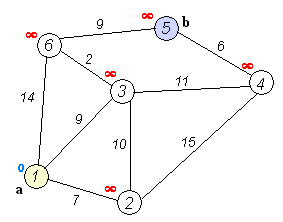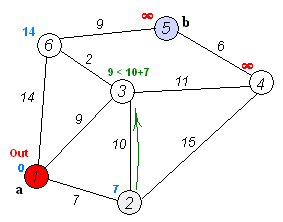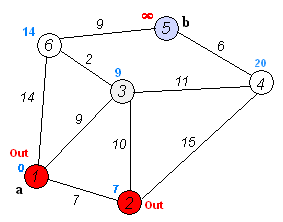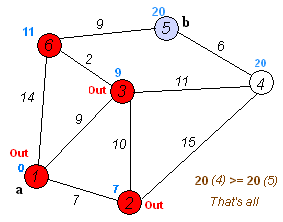
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Your goal is to reach the last index in the minimum number of jumps.
For example:
Given array A = [2,3,1,1,4]
The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. (Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.)
Notice that this game only contains unidirectional jumps, so there must exist a better solution. Look at above figure illustrating how Dijkstra algorithm works. The worst case complexity is O(|E| + |V| log |V|).
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
/**************************************************************************************************
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Your goal is to reach the last index in the minimum number of jumps.
For example:
Given array A = [2,3,1,1,4]
The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. (Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3
steps to the last index.)
Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 7, 2012 in Toronto
Implementation of Dijkstra algorithm: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm
1 function Dijkstra(Graph, source):
2 for each vertex v in Graph: // Initializations
3 dist[v] := infinity ; // Unknown distance function from source to v
4 previous[v] := undefined ; // Previous node in optimal path from source
5 end for ;
6 dist[source] := 0 ; // Distance from source to source
7 Q := the set of all nodes in Graph ; // All nodes in the graph are unoptimized - thus are in Q
8 while Q is not empty: // The main loop
9 u := vertex in Q with smallest distance in dist[] ;
10 if dist[u] = infinity:
11 break ; // all remaining vertices are inaccessible from source
12 end if ;
13 remove u from Q ;
14 for each neighbor v of u: // where v has not yet been removed from Q.
15 alt := dist[u] + dist_between(u, v) ;
16 if alt < dist[v]: // Relax (u,v,a)
17 dist[v] := alt ;
18 previous[v] := u ;
19 decrease-key v in Q; // Reorder v in the Queue
20 end if ;
21 end for ;
22 end while ;
23 return dist[] ;
24 end Dijkstra.
***************************************************************************************************/
int main(){
const int A[] = {2,3,1,1,4};
// const int A[] = {3,2,1,0,4};
const size_t array_len = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
// shortest distance from s
int * dist = new int[array_len];
// previous node along the shortest path
int * prev = new int[array_len];
for (int i=0;i<array_len;++i){
prev[i] = INT_MIN;
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
}
// incidence matrix
int ** p2IncidenceMatrix = new int*[array_len];
for (unsigned int i=0;i<array_len;++i)
p2IncidenceMatrix[i] = new int[array_len];
for (unsigned int i=0;i<array_len;++i)
for (unsigned int j=0;j<array_len;++j)
p2IncidenceMatrix[i][j] = 0;
// upper triangle incidence matrix here
for (int i=0;i<array_len;++i)
for (int j=1;j<=A[i];++j){
if (i+j<array_len)
p2IncidenceMatrix[i][i+j] =1;
else
break;
}
// unhandled nodes
vector<unsigned int> unhandledNodeSet;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<array_len;++i)
unhandledNodeSet.push_back(i);
dist[0] = 0;
while (!unhandledNodeSet.empty()){
unsigned int minDistNode;
int minDist = INT_MAX;
vector<unsigned int>::iterator itorMinDistNode;
for(vector<unsigned int>::iterator it=unhandledNodeSet.begin();
it<unhandledNodeSet.end(); it++){
//Note: should use <= instead of <, otherwise for unreachable case, will get exception!
if (dist[*it] <= minDist){
minDistNode = *it;
minDist = dist[*it];
itorMinDistNode = it;
}
}
if (dist[minDistNode] == INT_MAX)
break;
unhandledNodeSet.erase(itorMinDistNode);
//Find the neighbor of minDistNode in unhandledNodeSet
vector<unsigned int> neighborOfMinDistNode;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<unhandledNodeSet.size();i++)
if (p2IncidenceMatrix[minDistNode][unhandledNodeSet[i]] == 1)
neighborOfMinDistNode.push_back(unhandledNodeSet[i]);
// update the shortest path
for(vector<unsigned int>::iterator it=neighborOfMinDistNode.begin();
it<neighborOfMinDistNode.end(); it++){
int alt = dist[minDistNode] + 1;
if (alt < dist[*it]){
dist[*it] = alt;
prev[*it] = minDistNode;
}
}
}
// Print out the result
if (dist[array_len-1] == INT_MAX)
cout<<"The destination is not reachable!"<<endl;
else {
cout<<"The shortest path from the source (the start of the array) to
the destination (end of the array) is of "
<<dist[array_len-1]<<" steps."<<endl;
cout<<"One of the shortest paths is given by: "<<endl;
deque<unsigned int> shortestPath;
unsigned int target = array_len-1;
shortestPath.push_front(target);
while (prev[target] != INT_MIN ){
shortestPath.push_front(prev[target]);
target = prev[target];
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<shortestPath.size()-1;i++)
cout<<shortestPath.at(i)<<"->";
cout<<shortestPath.at(shortestPath.size()-1)<<endl;
}
// clean up the allocated memory
for(unsigned int i=0;i<array_len;++i)
delete [] p2IncidenceMatrix[i];
delete [] p2IncidenceMatrix;
delete [] dist;
delete [] prev;
return 0;
}
Jump Game II: A Greedy Approach

Bang, don't jump like this clumsy cat, LOL. Okay, let's get back to the same problem as given above, this time we use a greedy algorithm suggested by my friend Wei. We always jump to the next point such that within the current search window, the point we jump to corresponds to the furthest point we can jump to in the next round. The basic idea is that we only select the jump point such that it gives you the potential to jump to the farthest point. It can be easily seen that if you choose another jump point, within the same number of jump steps counted from the start point, it can not go beyond the greedy one. Hence greedy algorithm will always be the first to reach the destination (if reachable) and achieve the global optimal.
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/**************************************************************************************************
* A greedy algorithm: always jump to the next point so that from there, you can go furthest as you can
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 07, 2012 in Toronto
* Algorithm suggested by Wei
***************************************************************************************************/
int main(){
const int A[] = {2,3,1,1,4};
//const int A[] = {3,2,1,0,4};
const size_t array_len = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
int* pFurthestPosition = new int[array_len];
for(int i=0;i<array_len;++i){
//The rightmost point is just indexed by array_len-1
pFurthestPosition[i] = (A[i]+i>array_len-1)?(array_len-1):(A[i]+i);
}
int currentPosition = 0;
vector<int> shortestPath;
shortestPath.push_back(currentPosition);
while (currentPosition<array_len-1){
int nextPosition = currentPosition;
int furthestPositionCanJumpTo = currentPosition;
for(int i=1;i<=A[currentPosition];++i)
//Notice how a tie is handled, always select the last one
if (pFurthestPosition[currentPosition+i]>=furthestPositionCanJumpTo){
furthestPositionCanJumpTo = pFurthestPosition[currentPosition+i];
nextPosition = currentPosition+i;
}
if (nextPosition == currentPosition)
break;
currentPosition = nextPosition;
shortestPath.push_back(currentPosition);
}
if (currentPosition != array_len-1)
cout<<"The destination is not reachable!"<<endl;
else {
for(int i=0;i<shortestPath.size()-1;i++)
cout<<shortestPath[i]<<"->";
cout<<shortestPath[shortestPath.size()-1]<<endl;
}
delete [] pFurthestPosition;
return 0;
}
Trapping Rain Water: A very interesting question
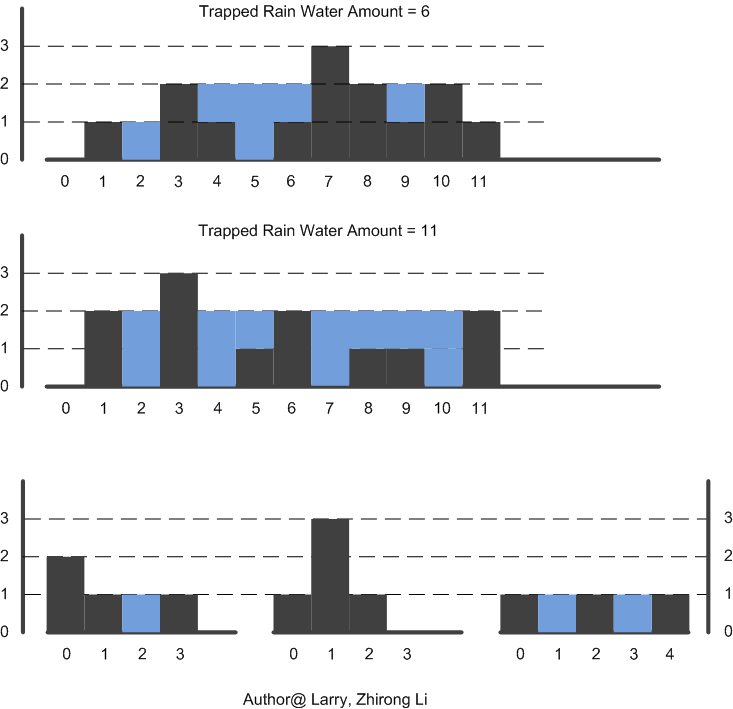
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example, Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6. I used to try searching for decrease-increase pattern but it turned out to be very problematic. As you can see, there might exist embedded tub case, so the current approach seems to be the best choice.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**********************************************************************************************************
* Author Larry, Zhirong Li April 14, 2012 in Toronto
*
* scan from both left to right and right to left, since we are considering the embedded tub case, the rain
* water amount really is determined by the outmost tub, hence we should also scan from both ends. If we scan
* from left and find a potential bar that can trap water, we need to continue sweeping to find a bar that is
* higher. If such bar is found, we just reduce the problem to a smaller dimension. Otherwise, if such bar
* does not exist, that means the current bar is the highest in the rest, if scan from the right and there does
* exist a potentical bar to trap water as well, from this direction, we know we can do similar things, so
* certain water can be trapped for sure, the tub may stop at this highest bar or earlier. No matter which case,
* we know the problem can be solved using this two direction scanning approach.
***********************************************************************************************************/
//Helper functions
int getBarArea(const int * const p2BarHeight, int startIndex, int endIndex){
int area=0;
for(int i=startIndex; i<=endIndex;++i)
area+=p2BarHeight[i];
return area;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
//const int barHeight[] = {0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1};
//const int barHeight[] = {0,2,0,3,0,1,2,0,1,1,0,2};
//const int barHeight[] = {2,1,0,1,0,1};
const int barHeight[] = {2,1,0,1,0};
const int array_len = sizeof(barHeight)/sizeof(int);
int leftTubBar = 0;
int rightTubBar = array_len-1;
int totalTrappedWaterAmount = 0;
bool isLHSSanning = true;
while(leftTubBar<rightTubBar){
//scan from the LHS first
if (isLHSSanning){
bool isTubFound = false;
while(!isTubFound){
if (leftTubBar+1<=rightTubBar){
if (barHeight[leftTubBar]>barHeight[leftTubBar+1]){
isTubFound = true;
break;
}else {
++leftTubBar;
}
}else break;
}
if (isTubFound){
//Find if there exists a stopping bar
int tubEndPosition = leftTubBar+2;
while (tubEndPosition<=rightTubBar){
if (barHeight[tubEndPosition]>=barHeight[leftTubBar])
break;
else
++tubEndPosition;
}
if (tubEndPosition<=rightTubBar){
//Found the stopping bar, update the trapped rain water amount and continue scanning LHS
totalTrappedWaterAmount+= barHeight[leftTubBar]*(tubEndPosition-leftTubBar-1)-
getBarArea(barHeight,leftTubBar+1,tubEndPosition-1);
leftTubBar = tubEndPosition;
}else{
//Not found, scan from the RHS
isLHSSanning = false;
}
}else break;
} else {
//RHS scanning
bool isTubFound = false;
while(!isTubFound){
if (rightTubBar-1>=leftTubBar){
if (barHeight[rightTubBar]>barHeight[rightTubBar-1]){
isTubFound = true;
break;
}else {
--rightTubBar;
}
}else break;
}
if (isTubFound){
//Find if there exists a stopping bar, actually there must exist one here since we go from LHS to RHS scanning
int tubEndPosition = rightTubBar-2;
while (tubEndPosition>=leftTubBar){
if (barHeight[tubEndPosition]>=barHeight[rightTubBar])
break;
else
--tubEndPosition;
}
if (tubEndPosition>=leftTubBar){
//Found the stopping bar, update the trapped rain water amount and continue scanning RHS
totalTrappedWaterAmount+= barHeight[rightTubBar]*(rightTubBar-tubEndPosition-1)-
getBarArea(barHeight,tubEndPosition+1,rightTubBar-1);
rightTubBar = tubEndPosition;
}else{
//Not found, scan from the LHS, you will never go into here.
isLHSSanning = true;
}
}else break;
}
}
return 0;
}
Finding Longest Palindromic Substring
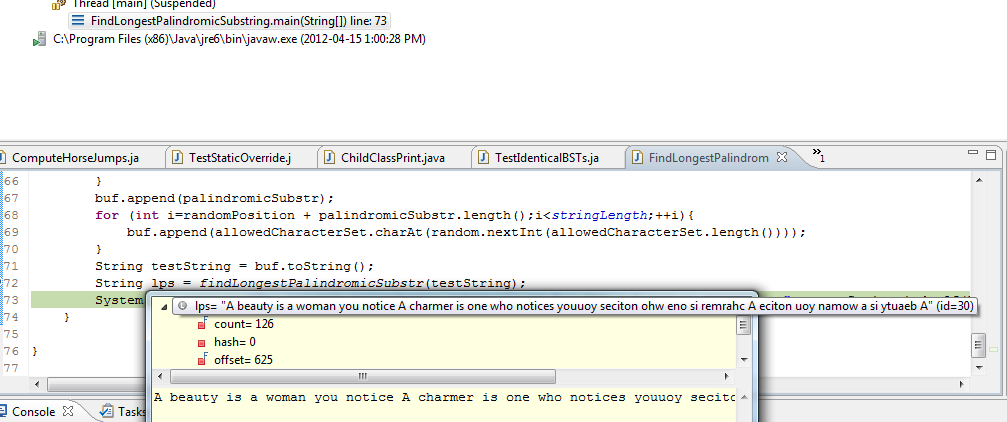
Given a string S, find the longest palindromic substring in S. You may assume that the maximum length of S is 1000, and there exists one unique longest palindromic substring. I just give an algorithm using suffix sort, which may be less familiar to people. :)
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
/*
* Author@ Larry, Zhirong Li April 15, 2012 in Toronto
* - O(NlogN)- complexity using suffix sort
* - refer to the finding the longest common substring algorithm
* */
public class FindLongestPalindromicSubstring {
private static final int stringLength = 1000;
// Helper Function: return the longest common prefix of s and t
private static String lcp(String s, String t) {
int n = Math.min(s.length(), t.length());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) != t.charAt(i))
return s.substring(0, i);
}
return s.substring(0, n);
}
private static String findLongestPalindromicSubstr(String testString) {
int N = testString.length();
String[] suffixesTestString = new String[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
suffixesTestString[i] = testString.substring(i, N);
}
Arrays.sort(suffixesTestString);
String testStringReverse = new StringBuffer(testString).reverse()
.toString();
String[] suffixesTestStringReverse = new String[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
suffixesTestStringReverse[i] = testStringReverse.substring(i, N);
}
Arrays.sort(suffixesTestStringReverse);
// Find the longest common prefix from the two sorted String list
String lrs = "";
int suffixCursorTestString = 0;
int suffixCursorTestStringReverse = 0;
while (suffixCursorTestString < N && suffixCursorTestStringReverse < N) {
String x = lcp(suffixesTestString[suffixCursorTestString],
suffixesTestStringReverse[suffixCursorTestStringReverse]);
if (x.length() > lrs.length())
lrs = x;
if (suffixesTestString[suffixCursorTestString]
.compareTo(suffixesTestStringReverse[suffixCursorTestStringReverse]) < 0)
++suffixCursorTestString;
else
++suffixCursorTestStringReverse;
}
return lrs;
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String palindromicSubstrPrefix = "A beauty is a woman you notice A charmer is one who notices you";
String palindromicSubstr = palindromicSubstrPrefix
+ new StringBuffer(palindromicSubstrPrefix).reverse()
.toString();
// (OddLength) palindromicSubstr = palindromicSubstrPrefix +
// new StringBuffer(palindromicSubstrPrefix.substring(0,
// palindromicSubstrPrefix.length()-1)).reverse().toString() ;
Random random = new Random();
int randomPosition = random.nextInt(stringLength
- palindromicSubstr.length() + 1);
String allowedCharacterSet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < randomPosition; ++i) {
buf.append(allowedCharacterSet.charAt(random
.nextInt(allowedCharacterSet.length())));
}
buf.append(palindromicSubstr);
for (int i = randomPosition + palindromicSubstr.length(); i < stringLength; ++i) {
buf.append(allowedCharacterSet.charAt(random
.nextInt(allowedCharacterSet.length())));
}
String testString = buf.toString();
String lps = findLongestPalindromicSubstr(testString);
System.out.println("The longest palindromic substring is \"" + lps
+ "\" and it starts at " + testString.indexOf(lps));
}
}
Finding the celebrity in a clique

Get bored? Here is another brain teaser type algorithm question. Among n people, a celebrity is defined as someone who is known to everyone, but who knows no one. Graph model: Person = node. If A knows B, draw a directed edge from A to B. Celebrity is a node with out-degree = 0; in-deg = n-1 (sink). A graph can have at most 1 sink/celebrity.
The problem is to identify the celebrity, if one exists, by asking only questions of the following form: "Excuse me, do you know person x?" There are n(n-1)/2 pairs of persons, so potentially we need to ask n(n-1) questions. Turns out one can solve the problem without even looking at all the input!
The goal of this problem is to find the celebrity within linear time.
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
/********************************************************************
* A celebrity finding problem in O(N) time
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 18, 2012 in Toronto
*********************************************************************/
int main(){
const int N = 100;
int ** p2IncMtx = new int*[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
p2IncMtx[i] = new int[N];
// probability for any two vertices to have an edge
const double p = 0.3;
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
if ( (i!=j) && (static_cast<double>(rand())/RAND_MAX<=p))
p2IncMtx[i][j]=1;
else
p2IncMtx[i][j]=0;
}
const int celebrity = rand()%N;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
p2IncMtx[celebrity][i] =0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
if (i!=celebrity) p2IncMtx[i][celebrity] =1;
// no celebrity case not known by everyone
/*while(true){
int randPpl = rand()%N;
if (randPpl!=celebrity) {
p2IncMtx[randPpl][celebrity] =0;
break;
}
}*/
// no celebrity case fraud celebrity knows someone
/*while(true){
int randPpl = rand()%N;
if (randPpl!=celebrity) {
p2IncMtx[celebrity][randPpl] =1;
break;
}
}*/
//Find the candidate in O(N) time: if A knows B, remove A else remove B
int peopleUnderInterrogation = 0;
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
if (p2IncMtx[peopleUnderInterrogation][i] ==1)
peopleUnderInterrogation = i;
}
//Double check the candiate is known by all other ppl and knows nobody in O(N) time
bool isCelebrity = true;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if (i!=peopleUnderInterrogation){
if (p2IncMtx[i][peopleUnderInterrogation]==0 ||
p2IncMtx[peopleUnderInterrogation][i] ==1 ){
isCelebrity = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (isCelebrity && celebrity == peopleUnderInterrogation)
cout<<"The celebrity is correctly found!"<<endl;
else if (isCelebrity)
cout<<"The celebrity is not correctly found!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"There is no celebrity in the clique."<<endl;
//clean up memory
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
delete [] p2IncMtx[i];
delete [] p2IncMtx;
}
N-Queen on a chessboard Problem
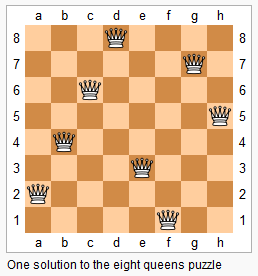
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other. Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '*' both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
There are #92 placement for 8-queens problem. The mathematical formula for general N can be found at MathWorld. The generated txt file is here.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* @author Larry, Zhirong Li April 18, 2012 in Toronto
*
*/
public class NQueenProblem {
private static int caseCounter =0;
private static void placeQueen(int row, int size, int[] queenPos) {
if (row == size) {
printToConsole(size, queenPos);
printToFile(size, queenPos);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (checkAvailability(i, row, queenPos)) {
queenPos[row] = i;
placeQueen(row + 1, size, queenPos);
}
}
}
private static void printToFile(int size, int[] queenPos) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
// Create file
FileWriter fstream = new FileWriter("out.txt", true);
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fstream);
++caseCounter;
out.write("This is " + size + "-queen problem, " + caseCounter + "-th case!\r\n");
out.write("The place of queens is given by: \r\n");
out.write("[ \r\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
out.write('[');
for (int j = 0; j < queenPos[i]; ++j)
out.write('*');
out.write('Q');
for (int j = queenPos[i] + 1; j < size; ++j)
out.write('*');
out.write("] \r\n");
}
out.write("] \r\n");
// Close the output stream
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {// Catch exception if any
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void printToConsole(int size, int[] queenPos) {
System.out.println("The place of queens is given by: ");
System.out.println("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int j = 0; j < queenPos[i]; ++j)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.print("Q");
for (int j = queenPos[i] + 1; j < size; ++j)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println("]");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
private static boolean checkAvailability(int trialPos, int row,
int[] queenPos) {
boolean isAvaialbe = true;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
if (queenPos[i] == trialPos
|| Math.abs(row - i) == Math.abs(queenPos[i] - trialPos)) {
isAvaialbe = false;
break;
}
}
return isAvaialbe;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Enter a line of chess board size: ");
int N = 0;
InputStreamReader converter = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(converter);
try {
N = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
// declare the array to store the position of queens in each row
int[] queenPos = new int[N];
placeQueen(0, N, queenPos);
}
}
Manacher's Algorithm in finding the longest palindromic substring
This is an elegant approach in finding the longest palindromic substring in linear time. The detailed explanation including complexity analysis is here. A subtle thing to the code is that when finding the maximum length palindrom, one can do an additional check to ensure that the palindrom lands at the actual character in the originl string to get rid of ties such that one is landing at '#'.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 21, 2012 */
int main(){
//const char* const ori_str = "babbab";
const char* const ori_str = "lsreuoYevoLILoveYouabsed";
const int ori_strlen = strlen(ori_str);
const int trans_strlen = 2*ori_strlen;
//debug: count # of char comparisons
int counter = 0;
char* str = (char*)malloc(trans_strlen+1);
if (str==NULL) exit (1);
str[0]='$';
str[1]= ori_str[0];
for (int n=1;n<ori_strlen;n++){
str[2*n]='#';
str[2*n+1] = ori_str[n];
}
str[trans_strlen]='\0';
printf ("Transformed string: %s\n",str);
int* P = (int*) malloc(trans_strlen*sizeof(int));
if (P==NULL) exit (1);
int id = 0;
int mx = 0;
P[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<trans_strlen;i++){
int j = 2*id-i;
if (mx>i){
P[i] = min(mx-i,P[j]);
//break;
}
else
P[i]=0;
++counter;
while(str[i+P[i]+1] == str[i-P[i]-1]){
++counter;
++P[i];
}
//update id and mx
if (i+P[i]>mx){
id = i;
mx = i+P[i];
}
}
//P[trans_strlen-1] =0;
int max_len = 0;
int max_index = 0;
for(int i=1;i<trans_strlen;++i){
if (P[i]>max_len){
max_len = P[i];
max_index = i;
}
}
//if land at #, the max-len should be reduced by one
if (str[max_index-max_len] == '#')
max_len--;
//The palindrom string length is max_len+1
char* longest_palindrom = (char*)malloc(max_len+2);
if (longest_palindrom == NULL) exit(1);
int longest_palindrom_pos = (max_index-max_len)/2;
for(int i=0;i<=max_len;i++)
longest_palindrom[i]= ori_str[longest_palindrom_pos++];
longest_palindrom[max_len+1]='\0';
printf("The longest palindromic substring: %s\n",longest_palindrom);
//clean up
free(str);
free(P);
free(longest_palindrom);
return 0;
}
Finding the minimum window that contains the given characters in O(N)
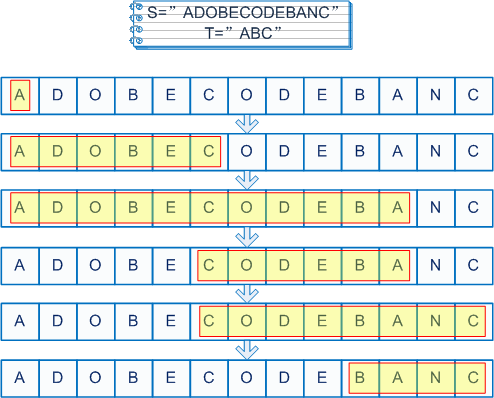
Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
For example, S = "ADOBECODEBANC" T = "ABC" and Minimum window is "BANC".
Note:
If there is no such window in S that covers all characters in T, return the emtpy string "". If there are multiple such windows, you are guaranteed that there will always be only one unique minimum window in S.
The complexity of the provided algorithm is just O(N). This is because on each iteration, we either increase the beginWindow or endWindow and both window values are within [0,N]. Thus the total number of comparisons will be in O(2N).
/**
* Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain
* all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
*/
/**
* @author Larry, Zhirong Li April 21, 2012
*
*/
public class MinimumWindowSubstring {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "ACBBACA";
String t = "ABA";
String str = FindTheMinimumWindow(s, t);
System.out.println("The minimum window is \"" + str
+ "\" and starts at index " + s.indexOf(str));
}
private static String FindTheMinimumWindow(String s, String t) {
int[] hasFound = new int[26];
int[] yetToFind = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); ++i)
yetToFind[t.charAt(i) - 'A']++;
int beginWindow = 0;
int endWindow = 0;
int totalFoundInT = 0;
while (t.indexOf(s.charAt(beginWindow)) == -1) {
beginWindow++;
}
if (beginWindow == s.length())
return "";
endWindow = beginWindow;
while (totalFoundInT < t.length() && endWindow < s.length()) {
if (t.indexOf(s.charAt(endWindow)) != -1) {
hasFound[s.charAt(endWindow) - 'A']++;
if (hasFound[s.charAt(endWindow) - 'A'] <= yetToFind[s
.charAt(endWindow) - 'A'])
totalFoundInT++;
}
endWindow++;
}
if (totalFoundInT < t.length())
return "";
else {
while (hasFound[s.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A'] > yetToFind[s
.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A']) {
hasFound[s.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A']--;
beginWindow++;
while (t.indexOf(s.charAt(beginWindow)) == -1) {
beginWindow++;
}
}
int minWinLength = endWindow - beginWindow + 1;
int minBeginWindow = beginWindow;
int minEndWindow = endWindow;
// Maintain the constraint
while (endWindow < s.length()) {
// increase the right boundary
endWindow++;
char beginningChar = s.charAt(beginWindow);
while (endWindow < s.length()
&& s.charAt(endWindow) != beginningChar) {
if (t.indexOf(s.charAt(endWindow)) != -1)
hasFound[s.charAt(endWindow) - 'A']++;
endWindow++;
}
// decrease the left boundary
if (endWindow == s.length())
return s.substring(minBeginWindow, minEndWindow + 1);
else
hasFound[s.charAt(endWindow) - 'A']++;
while (hasFound[s.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A'] > yetToFind[s
.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A']) {
hasFound[s.charAt(beginWindow) - 'A']--;
beginWindow++;
while (t.indexOf(s.charAt(beginWindow)) == -1) {
beginWindow++;
}
}
if (endWindow - beginWindow + 1 < minWinLength) {
minBeginWindow = beginWindow;
minEndWindow = endWindow;
minWinLength = endWindow - beginWindow + 1;
}
}
return s.substring(minBeginWindow, minEndWindow + 1);
}
}
}
Find the first missing positive integer in O(N) time with O(1) space
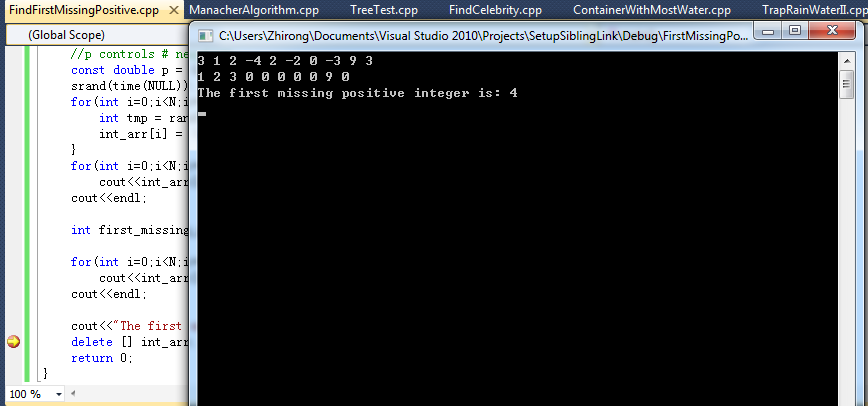
Given an unsorted integer array, find the first missing positive integer.
For example,given [1,2,0] return 3, and [3,4,-1,1] return 2.
I give a hack algorithm that modifies the input integer array. The basic idea is simple: we scan from the beginning of the integer array, if the current integer is in the right position (assume 1 is at arr[0], …., N is at arr[N-1]) we just skip to the next position. Otherwise, we need to put the integer to the right place. If it is supposed to be put before the current index, good, we are done with one copy and paste. Otherwise, there might be a series of changes.
This in-place algorithm runs in O(N) time. This is based on the following observations:
1) We scan this dynamically changing integer array once.
2) In each scan, we always move the integers in [1, N] to the right position and we always skip when the target integer is already in place. So the total number of movement is in O(N).
/*
* Given an unsorted integer array, find the first missing positive integer.
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 22,2012
*
* For example,
* Given [1,2,0] return 3, and [3,4,-1,1] return 2.
* Your algorithm should run in O(n) time and uses constant space.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int findFirstMissingPositive(int* const& int_arr, const int& N){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if (int_arr[i] == (i+1))
continue;
else if(1<=int_arr[i] && int_arr[i]<=N){
if (int_arr[i]<(i+1)){
int_arr[int_arr[i]-1]=int_arr[i];
int_arr[i] =0;
}
else{
//write to the right position
int tmp = int_arr[int_arr[i]-1];
if(int_arr[i] == tmp){
int_arr[i] =0;
continue;
}
int_arr[int_arr[i]-1] = int_arr[i];
int_arr[i] =0;
//a chain of overwriting may occur
while(1<=tmp && tmp<=N){
if (tmp-1<=i){
int_arr[tmp-1]=tmp;
break;
}
else{
int target_val = int_arr[tmp-1];
if (tmp == target_val)
break;
else{
int_arr[tmp-1] =tmp;
tmp = target_val;
}
}
}
}
}else{
int_arr[i]=0;
}
}
//find the first missing positive integer
int i =0;
while(i<N){
if (int_arr[i]==0)
return i+1;
i++;
}
return N+1;
}
int main(){
const int N = 10;
int* const int_arr = new int[N];
const int data_range = 10;
//p controls # negative
const double p = 0.7;
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int tmp = rand();
int_arr[i] = (static_cast<double>(tmp)/RAND_MAX<=p)? tmp%data_range: -tmp%data_range;
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
cout<<int_arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
int first_missing_positive = findFirstMissingPositive(int_arr, N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
cout<<int_arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"The first missing positive integer is: "<<first_missing_positive<<endl;
delete [] int_arr;
return 0;
}
In-place sort color balls in O(N) time
Given an array with n objects colored red, green or blue, sort them so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, green and blue.Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, green, and blue respectively.
This is an easy question if you are familiar with the partition step in quicksort. Apparently the complexity is of O(N). This is indeed a Dutch national flag problem. What if we have K colored balls? For example, K=6, i.e., red=0, green =1, blue =2, yellow =3, black=4 and grey =5. We can treat (0, 1) as the same color and similarly for (2, 3), (4, 5). We can sort twice to get every ball in the right place.
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author Larry, Zhirong Li April 23, 2012 in Toronto
*
*/
public class SortColor {
private static final int N = 100;
private static final double pRedCutoff = 0.3;
private static final double pGreenCutoff = 0.7;
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Random random = new Random();
int[] colorArray = new int[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
double randomFloat = random.nextDouble();
if(randomFloat<=pRedCutoff)
colorArray[i] = 0;
else if (randomFloat<=pGreenCutoff)
colorArray[i] = 1;
else
colorArray[i] = 2;
}
System.out.println("The generated color number array is given by:");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
System.out.print(colorArray[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//Sort the color array
sortArray(colorArray);
System.out.println("The sorted color number array is given by:");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
System.out.print(colorArray[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void sortArray(int[] colorArray) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int redBoundary = -1;
int blueBoundary = colorArray.length;
int index = 0;
while(index < blueBoundary){
if (colorArray[index] == 1)
index++;
else if (colorArray[index] == 0){
int tmp = colorArray[++redBoundary];
colorArray[redBoundary] = 0;
colorArray[index++] = tmp;
} else {
while (colorArray[index] == 2){
int tmp = colorArray[--blueBoundary];
colorArray[blueBoundary] = 2;
colorArray[index] = tmp;
}
if (colorArray[index] == 1)
index++;
else {
int tmp = colorArray[++redBoundary];
colorArray[redBoundary] = 0;
colorArray[index++] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
Minimum Path Sum: recursion approach with backtracking
Given an m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Needless to mention, the classic recursion approach with backtracking.
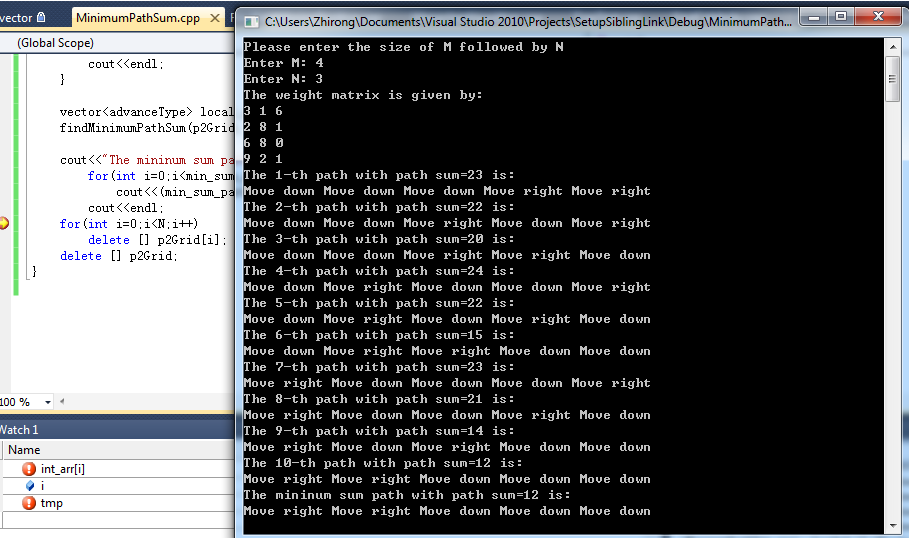
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/*
Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom
right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
*/
typedef enum {advanceX,advanceY} advanceType;
static vector<advanceType> min_sum_path;
static int M,N;
static int min_sum = INT_MAX;
static int path_number = 0;
void findMinimumPathSum(int **p2Grid, vector<advanceType> local_path,int currentX, int currentY){
if (currentX ==M-1 && currentY ==N-1){
//compute the path sum
path_number++;
int pathX = 0;
int pathY = 0;
int pathSum = p2Grid[0][0];
for(int i=0;i<M+N-2;i++){
if (local_path[i]== advanceX)
pathX++;
else
pathY++;
pathSum += p2Grid[pathX][pathY];
}
if (pathSum<min_sum){
min_sum = pathSum;
min_sum_path.clear();
min_sum_path = local_path;
}
cout<<"The "<<path_number<<"-th path with path sum="<<pathSum<<" is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<local_path.size();++i)
cout<<(local_path.at(i)==advanceX?"Move down":"Move right")<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return;
}
//not reaching the end yet
if (currentX == M-1){
local_path.push_back(advanceY);
findMinimumPathSum(p2Grid, local_path, currentX, ++currentY);
} else if (currentY == N-1){
local_path.push_back(advanceX);
findMinimumPathSum(p2Grid, local_path, ++currentX, currentY);
} else {
//two choices, traverse along X first then backtracking to Y
local_path.push_back(advanceX);
findMinimumPathSum(p2Grid, local_path, ++currentX, currentY);
//Important: backtracking here
local_path.pop_back();
--currentX;
local_path.push_back(advanceY);
findMinimumPathSum(p2Grid, local_path, currentX, ++currentY);
}
}
int main(){
cout<<"Please enter the size of M followed by N"<<endl;
const int data_range = 10;
//cin>>M>>N;
string line;
cout << "Enter M: ";
getline (cin,line);
stringstream(line) >> M;
cout << "Enter N: ";
getline (cin,line);
stringstream(line) >> N;
int ** p2Grid = new int*[M];
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
p2Grid[i] = new int[N];
srand(time(NULL));
//initialize the cell weights
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
p2Grid[i][j]=rand()%data_range;
}
//print out the weight matrix
cout<<"The weight matrix is given by:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
cout<<p2Grid[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
vector<advanceType> local_path;
findMinimumPathSum(p2Grid, local_path,0, 0);
cout<<"The mininum sum path with path sum="<<min_sum<<" is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<min_sum_path.size();++i)
cout<<(min_sum_path.at(i)==advanceX?"Move down":"Move right")<<" ";
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
delete [] p2Grid[i];
delete [] p2Grid;
}
Minimum Path Sum: DP approach in O(N*M) time

Recursion program is sort of easy to write. However, this is at the cost of efficiency. Recursion is powerful in enumerating all the possibilities. Whenever you encounter a min/max problem, dynamic programming should always be the first to come into your mind.
main(){
//...
vector<advanceType> dp_path(M+N-2);
int min_path_sum_dp;
findMinimumPathSumDP(p2Grid, dp_path, min_path_sum_dp);
//...
}
void findMinimumPathSumDP(int ** p2Grid, vector<advanceType>& dp_path, int & min_path_sum_dp){
int ** p2MinSumMtx = new int*[M];
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
p2MinSumMtx[i] = new int[N];
//DP: initialize the boundary
p2MinSumMtx[0][0] = p2Grid[0][0];
for(int i=1;i<M;i++)
p2MinSumMtx[i][0] = p2MinSumMtx[i-1][0] + p2Grid[i][0];
for(int i=1;i<N;i++)
p2MinSumMtx[0][i] = p2MinSumMtx[0][i-1] + p2Grid[0][i];
for(int i=1;i<M;i++)
for(int j=1;j<N;j++){
p2MinSumMtx[i][j] = min(p2MinSumMtx[i-1][j],p2MinSumMtx[i][j-1])+p2Grid[i][j];
}
//find one min-sum path
int it = M+N-2;
int curr_x = M-1;
int curr_y= N-1;
min_path_sum_dp = p2MinSumMtx[curr_x][curr_y];
while (curr_x !=0 || curr_y !=0){
if(curr_x ==0){
dp_path[--it] = advanceY;
--curr_y;
}else if (curr_y ==0){
dp_path[--it]= advanceX;
--curr_x;
}
else if (p2MinSumMtx[curr_x][curr_y] == p2MinSumMtx[curr_x-1][curr_y] + p2Grid[curr_x][curr_y]){
dp_path[--it]= advanceX;
--curr_x;
}
else {
dp_path[--it]= advanceY;
--curr_y;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
delete [] p2MinSumMtx[i];
delete [] p2MinSumMtx;
}
Brain teaser: Flip sort on integer array
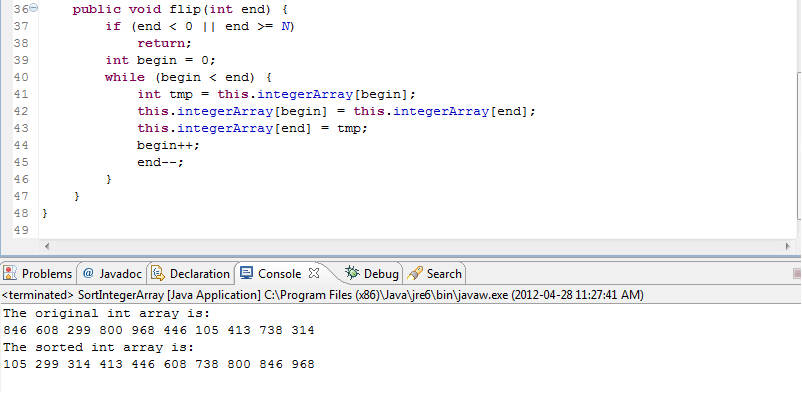
Assume you are given an integer array. There is a flip function which takes in an index as the parameter. The functionality of this flip(int index) is to reverse the sub-array from position 0 to index. For example, your integer array ={5, 6, -1, 3, 2}. After calling flip(3), the array becomes {3, -1, 6, 5, 2}. Can you sort this array using flip() only?
import java.util.Random;
public class EncapsulatedIntegerArray {
private static final int N = 10;
private int[] integerArray = new int[N];
private static final int dataRange = 1000;
/**
* @param integerArray
*/
public EncapsulatedIntegerArray() {
super();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
this.integerArray[i] = random.nextInt(dataRange);
}
}
/**
* @param index
* @return
*/
public int getElementByIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= N)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return this.integerArray[index];
}
/**
* @return
*/
public int getIntegerArrayLength() {
return N;
}
public void flip(int end) {
if (end < 0 || end >= N)
return;
int begin = 0;
while (begin < end) {
int tmp = this.integerArray[begin];
this.integerArray[begin] = this.integerArray[end];
this.integerArray[end] = tmp;
begin++;
end--;
}
}
}
/**
* @author Zhirong, Li in Toronto April 28, 2012
*
*/
public class SortIntegerArray {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
EncapsulatedIntegerArray encapsulatedIntegerArray = new EncapsulatedIntegerArray();
// sort the int array by calling flip() only
sortIntegerArray(encapsulatedIntegerArray);
}
private static void sortIntegerArray(
EncapsulatedIntegerArray encapsulatedIntegerArray) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int arraySize = encapsulatedIntegerArray.getIntegerArrayLength();
// print out the original int array
System.out.println("The original int array is:");
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
System.out.print(encapsulatedIntegerArray.getElementByIndex(i)
+ " ");
System.out.println();
for (int index = arraySize - 1; index > 0; --index) {
int max = encapsulatedIntegerArray.getElementByIndex(index);
int maxIndex = index;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (encapsulatedIntegerArray.getElementByIndex(i) > max) {
max = encapsulatedIntegerArray.getElementByIndex(i);
maxIndex = i;
}
}
// move the current max to the right position
encapsulatedIntegerArray.flip(maxIndex);
encapsulatedIntegerArray.flip(index);
}
// print out the original int array
System.out.println("The sorted int array is:");
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
System.out.print(encapsulatedIntegerArray.getElementByIndex(i)
+ " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
Brain teaser: Application of Gray code to sequentially enumerating all subsets
There are N guests outside the ballroom. Given a move(i) function, if person i is outside, this function will move person i into the ballroom. Otherwise, person i will be popped out. How would you design this move sequence such that every subset of N people occurs once and only once? For example, for the complete set of two people, Alice and Bob.
Initial: {}
move(Alice): {Alice}
move(Bob): {Alice, Bob}
move(Alice): {Bob}
Notice that if we represent each subset in its binary form, every pair of consecutive moves corresponds to change of 1 bit only. By the construction process of binary-reflected Gray Code, it satisfies the above requirement. I use recursion to generate this type of Gray code and scan this sequence once to move people around the ball room.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/*
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li April 28,2012 in Toronto
*
*/
enum People {Alice, Bob, Charlie, David, Einstein};
//Assume Alice corresponds to LSB and Einstein corresponds to MSB of the binary representation,
//i.e., {Alice, Einstein} maps to 0b10001=0x11
char* people_name[] = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David", "Einstein"};
vector<People> ballRoom;
void generateGrayCode(int curr_bits, int target_bits, int*& Gray_Code ){
if (curr_bits>target_bits) return;
int indexOfLastRound = (0x1<<(curr_bits-1))-1;
for(int i=0;i<=indexOfLastRound;i++){
Gray_Code[(0x1<<curr_bits)-1-i] = Gray_Code[i];
Gray_Code[(0x1<<curr_bits)-1-i]|=1<<(curr_bits-1);
}
generateGrayCode(++curr_bits, target_bits, Gray_Code);
}
void printBallRoom(){
cout<<"The current ball room has people:"<<endl<<"{ ";
for(unsigned int i=0;i<ballRoom.size();i++){
cout<<people_name[ballRoom[i]]<<" ";
}
cout<<"}"<<endl;
}
void movePeople(People ppl, bool isMoveIn ){
if (isMoveIn){
ballRoom.push_back(ppl);
}else{
for( vector<People>::iterator it = ballRoom.begin(); it<ballRoom.end();it++){
if(ppl == *it){
ballRoom.erase(it);
break;
}
}
}
}
void movePeopleInAndOut(const int* const Gray_Code, int N){
printBallRoom();
for(int i=1;i<1<<N;i++){
int xor_neighbor_bit = Gray_Code[i-1]^Gray_Code[i];
int change_bit_position = 0;
bool isMoveIn = (xor_neighbor_bit&Gray_Code[i])==xor_neighbor_bit;
while((xor_neighbor_bit&0x1) !=0x1){
xor_neighbor_bit>>=1;
change_bit_position++;
}
People peopleUnderOperation = static_cast<People>(change_bit_position);
movePeople(peopleUnderOperation, isMoveIn);
printBallRoom();
}
}
int main(){
const int N = 5;
int* Gray_Code = new int[1<<N];
Gray_Code[0]=0;
Gray_Code[1]=1;
generateGrayCode(2,N, Gray_Code);
//move people in and out to generate the non-repeating sequence
movePeopleInAndOut(Gray_Code, N);
delete [] Gray_Code;
return 0;
}
Tough Question (Open): Find the positions of milestones
There is a straight road with N number of milestones. You are given an array with the distance between all the pairs of milestones in some random order. Find the positions of the milestones. Assume N>1 and one milestone is located at the origin.
Example:
Consider a road with 4 milestones(a,b,c,d) :
a <--- 3Km --->b<--- 5Km --->c<--- 2Km --->d
Distance between a and b = 3
Distance between a and c = 8
Distance between a and d = 10
Distance between b and c = 5
Distance between b and d = 7
Distance between c and d = 2
All the above values are given in a random order say 7, 10, 5, 2, 8, 3.
The output must be 3,5,2 or 2,5,3
I use reservoir sampling method to randomly generate the positions of milestones for the test setup. (A simple proof of reservoir sampling can be found right here.) However, I could not figure out a work-out except brute force methods for this moment. If you have any ideas/suggestions, please feel free to contact me through email at zhirong.lee@gmail.com.
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
static int N;
static int distance_vec_size;
/* There is a straight road with N number of milestones. You are given an array with the distance between
* all the pairs of milestones in some random order. Find the positions of the milestones. Assume N>1 and
* one milestone is located at the origin.
*/
void findMilestoneLocations(int *found_milestone_positions, int* distance_vector, int begin, int end){
//TO-DO: This is a difficult question
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
N = 4;
distance_vec_size = N*(N-1)/2;
const int position_range = 1000;
//create the milestones positions
int* pos_milestones = new int[N];
srand(time(NULL));
//use reservoir sampling :)
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
pos_milestones[i] = i;
for(int i=N;i<=position_range;i++){
int j = rand()%i+1;
if(j<N) pos_milestones[j]=i;
}
//sort the milestone array
sort(pos_milestones,pos_milestones+N);
cout<<"The generated milestone array is :"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cout<<pos_milestones[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//set up the distance matrix
int * distance_vector = new int[distance_vec_size];
int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<N;j++)
distance_vector[index++]= pos_milestones[j]-pos_milestones[i];
//sort the distance in ascending order
sort(distance_vector, distance_vector+distance_vec_size);
cout<<"The sorted distance vector is :"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<distance_vec_size;i++){
cout<<distance_vector[i]<<" ";
}
int* found_milestone_positions = new int[N];
//found_milestone_positions[0]=0;
//findMilestoneLocations(found_milestone_positions,distance_vector,0,N-1);
delete [] found_milestone_positions;
delete [] pos_milestones;
delete [] distance_vector;
return 0;
}
Brain teaser: Find the positive integer generating sequence using factoring
You are given a positive integer A. The goal is to construct the shortest possible sequence of integers ending with A, using the following rules:
the first element of the sequence is 1, each of the successive elements is the sum of any two preceding elements (adding a single element to itself is also permissible), each element is larger than all the preceding elements; that is, the sequence is increasing.
For example, for A = 42, a possible solutions is [1, 2, 3, 6, 12, 18, 21, 42].
It is quite interesting this problem indeed can be related to the factoring of numbers. The recursion formula for step(n) is as follows:
If n is even, then step(n)=step(n/2)+1; if n is odd and if n is prime, step(n)=step(n-1)+1; if n is odd composite, assume n=k1*k2*...*km (k1,...,km are all prime) then step(n)=sum(step(ki)-1)+1 where i is in {1,...,m}. I use "Sieve of Eratosthenes" to generate the prime table. Similar to DP assignment process, larger prime's generating sequence is based on smaller prime's generating sequence and merge all of them using the above recursion formula.
The problem becomes much harder when you are required to provide the minimum-step generating sequence. To be continued.
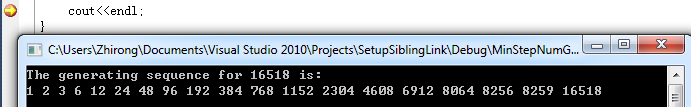
This factoring process reminds me of an old classic brain teaser: Suppose you are in a hallway lined with 100 closed lockers. You begin by opening all 100 lockers. Next, you close every second locker. Then you go to every third locker and close it if it is open or open it if it is closed (call this toggling the locker). You continue toggling every nth locker on pass number n. After your hundredth pass of the hallway, in which you toggle only locker number 100, how many lockers are open?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
/* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li on May 2nd, 2012 in Toronto
we do find prime number's generating sequence like this as a result of the fact that smaller prime number's generating
sequence is already available (Like DP assignment process)
*/
void generatePrimeSequence(vector<vector<int>>& prime_number_gen_seq, int* prime_number_list){
int num_prime = prime_number_gen_seq.size();
for(int i=1;i<num_prime;i++){
int prev_num = prime_number_list[i]-1;
int index =-1;
while(++index<num_prime)
if (prev_num%prime_number_list[index] == 0) break;
prime_number_gen_seq[i]=prime_number_gen_seq[index];
int removeFactor = prev_num/prime_number_list[index];
while(removeFactor !=1){
index =-1;
while(++index<num_prime)
if (removeFactor%prime_number_list[index] == 0) break;
int last_number = prime_number_gen_seq[i][prime_number_gen_seq[i].size()-1];
for(unsigned int j=1;j<prime_number_gen_seq[index].size();j++){
prime_number_gen_seq[i].push_back(last_number*prime_number_gen_seq[index][j]);
}
removeFactor/=prime_number_list[index];
}
prime_number_gen_seq[i].push_back(prime_number_list[i]);
}
}
void findGeneratingSequence(int N, vector<int>& gen_seq){
int odd_part = N;
int num_two_factor = 0;
while((odd_part&0x1) ==0x0){
num_two_factor++;
odd_part>>=1;
}
bool* prime_table = new bool[odd_part+2];
prime_table[0] = false;
prime_table[1] = false;
prime_table[2] = true;
for(int i=3;i<=odd_part;i++)
prime_table[i] = true;
int upper_bound = static_cast<int>(sqrt(static_cast<double>(odd_part)));
for(int i=2;i<=upper_bound;i++){
for(int j=i*i;j<=odd_part;j+=i){
if (prime_table[i]){
prime_table[j] = false;
}
}
}
//fetch the prime number
int num_prime = 0;
for(int i=2;i<=odd_part;i++)
if (prime_table[i]) num_prime++;
if (num_prime>0){
int * prime_number_list = new int[num_prime];
int index = -1;
for(int i=2;i<=odd_part;i++)
if (prime_table[i]) prime_number_list[++index] = i;
//factor the odd_part
vector<vector<int> > prime_number_gen_seq(num_prime);
//0-th prime corresponds to prime number 2
prime_number_gen_seq[0].push_back(1);
prime_number_gen_seq[0].push_back(2);
//intialize all generating sequences for prime factor upto odd_part
generatePrimeSequence(prime_number_gen_seq, prime_number_list);
index =0;
while(++index<num_prime)
if (odd_part%prime_number_list[index] == 0) break;
gen_seq=prime_number_gen_seq[index];
int removeFactor = odd_part/prime_number_list[index];
while(removeFactor !=1){
index =0;
while(++index<num_prime)
if (removeFactor%prime_number_list[index] == 0) break;
int last_number = gen_seq[gen_seq.size()-1];
for(unsigned int i=1;i<prime_number_gen_seq[index].size();i++){
gen_seq.push_back(last_number*prime_number_gen_seq[index][i]);
}
removeFactor/=prime_number_list[index];
}
delete [] prime_number_list;
}
int double_prev = odd_part;
for(int i=0;i<num_two_factor;i++){
double_prev<<=1;
gen_seq.push_back(double_prev);
}
delete [] prime_table;
}
int main(){
//Assume N is large, N>=2
const int N = 42;
vector<int> gen_seq;
findGeneratingSequence(N,gen_seq);
cout<<"The generating sequence for "<<N<<" is:"<<endl;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<gen_seq.size();i++){
cout<<gen_seq[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
Judge if a given string can be scrambled from another given string in C/C++
The problem is elaborated in the comment part in the code. This is a recursion approach. DP-approach will be provided in the next section.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/****************************************************************************************
Author@Larry, Zhirong Li May 06, 2012 at Toronto
Scramble string: given a string e.g. "tiger" arbitrarily select a partition tree
tiger
/ \
ti ger
/ \ / \
t i g er
/ \
e r
You can choose to swap the order of the two children at any non-leaf node, for example,
itreg
/ \
it reg
/ \ / \
t i g re
/ \
e r
Then we say "itreg" can be scrambled via "tiger". Given s1, s2 judge if it is possible
to find a partition tree and swap scheme for s1 such that s2 is the output.
*****************************************************************************************/
bool canScramble(const char* const src_str, const char* const tgt_str, int n){
//base case: size n =1
if (n == 1){
if (src_str[0] == tgt_str[0])
return true;
else
return false;
}
// try every block level scrambling
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if (canScramble(src_str, tgt_str, i) && canScramble(src_str+i, tgt_str+i, n-i))
return true;
if (canScramble(src_str, tgt_str+n-i, i) && canScramble(src_str+i, tgt_str, n-i))
return true;
}
// no match, can not be scrambled in the provided way
return false;
}
int main(){
char* const src_str = "tiger";
//char* const tgt_str = "itreg";
char* const tgt_str = "etgri";
bool can_scramble;
if (strlen(src_str) != strlen(tgt_str))
can_scramble = false;
else {
can_scramble = canScramble(src_str,tgt_str,strlen(src_str));
}
if (can_scramble)
cout<<"The provided two strings can be scrambled from each other."<<endl;
else
cout<<"The provided two strings can not be scrambled from each other."<<endl;
}
Judge if a given string can be scrambled from another given string: DP approach in C/C++
This is a DP approach. I referred to blog post with user id "wwwyhx"'s proposed algorithm.
bool CanScrambleDP(const char* const szStr1, const char* const szStr2)
{
int nLen1 = strlen(szStr1);
int nLen2 = strlen(szStr2);
if (nLen1 != nLen2)
return false;
//allocate
//pRec[i][j][k] means can szStr1(i ... i+k)
//be scrambled to szStr2(j ... j+k)
bool*** pRec = new bool**[nLen1];
for (int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
pRec[i] = new bool*[nLen1];
for (int j = 0; j < nLen1; j++)
{
pRec[i][j] = new bool[nLen1];
for (int k = 0; k < nLen1; k++)
pRec[i][j][k] = false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nLen1; j++)
pRec[i][j][0] = (szStr1[i] == szStr2[j]);
}
for (int l = 1; l < nLen1; l++)
{
for (int i = 0; i+l < nLen1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j+l < nLen1; j++)
{
bool bRes = false;
for (int k = i+1; k <= i+l; k++)
{
if ((pRec[i][j][k-i-1] && pRec[k][k][i+l-k])
|| (pRec[i][j+l+1-k+i][k-i-1] && pRec[k][j][i+l-k]))
{
pRec[i][j][l] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
bool bRet = pRec[0][0][nLen1-1];
for (int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nLen1; j++)
delete []pRec[i][j];
delete []pRec[i];
}
delete []pRec;
return bRet;
}
Sort nearly K-sorted array in O(NlogK) time in Java
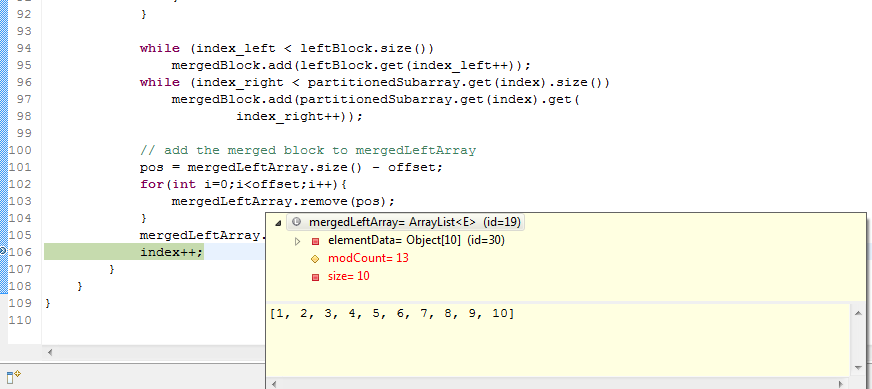
Given an array of N elements , each which is at most K positions from its target position, devise an algorithm sorts in O(NlogK) time.
We can divide the array into N/K pieces of size K, and sort each piece in O(KlogK) time, say using mergesort. Note that this preserves the property that no element is more than K element out of position.
This is because that each block is of size K. For every element i, let A[i] denote its current position and B[i] denote its correct position. Suppose A[i] is in block M, then if B[i] is also in block M, it is obvious after sorting all the elements in block M, element i is still at most K out of position. Otherwise without loss of generality, B[i] is in block (M-1). If element i is > K out of position, that means there must exist proceeding element j (A[j]>A[i]), which is less than i (j<i) and push element i backwards after sorting. The problem is that for the RIGHTMOST such j in Block M: A[j]>A[i] and B[j]<B[i], A[j]-B[j]>K which contradicts the assumption that the given array is nearly K-sorted.
Now, merge each block of K elements with block to its left. Keep in mind only the last K elements in the left merged block will participate in the merge process
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author Zhirong May 12, 2012 in Toronto
*
*/
public class NearlySorted {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int K = 2;
final int N = 10;
Integer[] nearlySortedArray = new Integer[N];
int index = 0;
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(2);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(1);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(5);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(3);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(4);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(8);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(7);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(6);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(10);
nearlySortedArray[index++] = Integer.valueOf(9);
sortNearlySortedArray(nearlySortedArray, K);
System.out.println("The sorted array is :");
for (int i = 0; i < nearlySortedArray.length; i++) {
System.out.print(nearlySortedArray[i]+ " ");
}
}
/**
* @param nearlySortedArray
* @param offset
*/
private static void sortNearlySortedArray(Integer[] nearlySortedArray,
int offset) {
int numberOfSubarray = (int) Math.ceil(nearlySortedArray.length
/ offset);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> partitionedSubarray = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(
numberOfSubarray);
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSubarray - 1; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> tmpArray = new ArrayList<Integer>(offset);
for (int j = 0; j < offset; j++) {
tmpArray.add(nearlySortedArray[index++]);
}
partitionedSubarray.add(tmpArray);
}
ArrayList<Integer> tmpArray = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while (index < nearlySortedArray.length) {
tmpArray.add(nearlySortedArray[index++]);
}
partitionedSubarray.add(tmpArray);
// sort each sub-array
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSubarray; i++) {
Collections.sort(partitionedSubarray.get(i));
}
// merge each block of K elements with the block to its left, notice
// that the overall complexity is linear
index = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> mergedLeftArray = new ArrayList<Integer>();
mergedLeftArray.addAll(partitionedSubarray.get(index++));
while (index < numberOfSubarray) {
ArrayList<Integer> leftBlock = new ArrayList<Integer>(offset);
int pos = mergedLeftArray.size() - offset;
for (int i = 0; i < offset; i++) {
leftBlock.add(mergedLeftArray.get(pos++));
}
// two-way merge of left block and the current block
ArrayList<Integer> mergedBlock = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int index_left = 0;
int index_right = 0;
while (index_left < leftBlock.size()
&& index_right < partitionedSubarray.get(index).size()) {
if (leftBlock.get(index_left) < partitionedSubarray.get(index)
.get(index_right)) {
mergedBlock.add(leftBlock.get(index_left++));
} else {
mergedBlock.add(partitionedSubarray.get(index).get(
index_right++));
}
}
while (index_left < leftBlock.size())
mergedBlock.add(leftBlock.get(index_left++));
while (index_right < partitionedSubarray.get(index).size())
mergedBlock.add(partitionedSubarray.get(index).get(
index_right++));
// add the merged block to mergedLeftArray
pos = mergedLeftArray.size() - offset;
for (int i = 0; i < offset; i++) {
mergedLeftArray.remove(pos);
}
mergedLeftArray.addAll(mergedBlock);
index++;
}
// change the original array
for (int i = 0; i < nearlySortedArray.length; i++) {
nearlySortedArray[i] = mergedLeftArray.get(i);
}
}
}
Min-Heap Sort nearly K-sorted array in O(NlogK) time in C/C++
I guess this min-heap sort based approach is more obvious than the previous one. The key idea is to insert the first K elements into a binary min heap. Insert the next element from the array into the heap, and delete the minimum element from the heap. Repeat. I just refer to the CLRS's book Chapter 6 for min-heap build, insert, extract and heapify operations. :)
//My_Min_Heap.h
class My_Min_Heap{
public:
My_Min_Heap(const int* const inputArray, const int K);
int Heap_Min() const;
int Heap_Min_Extract();
void Heap_Min_Insert(const int key);
int Heap_Size() const;
virtual ~My_Min_Heap();
protected:
private:
int * _p2MinHeap;
int _HeapSize;
void Min_Heapify(const int index);
int _Parent(const int index) const;
int _Left(const int index) const;
int _Right(const int index) const;
};
//My_Min_Heap.cpp
#include "My_Min_Heap.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
My_Min_Heap::My_Min_Heap(const int* const inputArray, const int size){
_p2MinHeap = new int[size+1];
_HeapSize = size;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
_p2MinHeap[i+1] = inputArray[i];
}
for (int i = size/2; i>=1; --i){
Min_Heapify(i);
}
}
void My_Min_Heap::Min_Heapify(const int index){
int l = _Left(index);
int r = _Right(index);
int smallest;
if (l<=_HeapSize && _p2MinHeap[l]<_p2MinHeap[index])
smallest = l;
else
smallest = index;
if (r<=_HeapSize && _p2MinHeap[r]<_p2MinHeap[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != index){
//exchange _p2MinHeap[index] with _p2MinHeap[smallest]
int tmp = _p2MinHeap[index];
_p2MinHeap[index] = _p2MinHeap[smallest];
_p2MinHeap[smallest] = tmp;
Min_Heapify(smallest);
}
}
int My_Min_Heap::_Parent(const int index) const{
return index/2;
}
int My_Min_Heap::_Left(const int index) const{
return index*2;
}
int My_Min_Heap::_Right(const int index) const{
return index*2+1;
}
int My_Min_Heap::Heap_Min() const{
return _p2MinHeap[1];
}
int My_Min_Heap::Heap_Min_Extract(){
if (_HeapSize<1)
exit(1);
int min = _p2MinHeap[1];
_p2MinHeap[1] = _p2MinHeap[_HeapSize];
_HeapSize--;
Min_Heapify(1);
return min;
}
int My_Min_Heap::Heap_Size() const{
return _HeapSize;
}
void My_Min_Heap::Heap_Min_Insert(const int key){
_HeapSize++;
_p2MinHeap[_HeapSize] = key;
int index = _HeapSize;
while(index>1 && _p2MinHeap[_Parent(index)]>_p2MinHeap[index]){
//exchange _p2MinHeap[index] with _p2MinHeap[_Parent(index)]
int tmp = _p2MinHeap[index];
_p2MinHeap[index] = _p2MinHeap[_Parent(index)];
_p2MinHeap[_Parent(index)] = tmp;
index = _Parent(index);
}
}
My_Min_Heap::~My_Min_Heap(){
delete _p2MinHeap;
}
//NearlySortedArray.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "My_Min_Heap.h"
using namespace std;
/**************************************************************************************************
* A heap-sort based algorithm to sort the nearly K-Sorted Array in O(NLogK)-time
*
* Author@Larry, Zhirong Li May 13 (To Mom, Happy Mother's Day), 2012 in Toronto
*
***************************************************************************************************/
int main(int argc, char * argv[]){
//For simplicity, assume N>=K+1
int nearly_sorted_array[] = {2,1,5,3,4,8,7,6,10,9};
const int input_size = sizeof(nearly_sorted_array)/sizeof(int);
int sorted_array[input_size];
const int K =2;
My_Min_Heap *my_min_heap = new My_Min_Heap(nearly_sorted_array, K+1);
int index = 0;
sorted_array[index++] = my_min_heap->Heap_Min_Extract();
int cursor = K+1;
while(cursor<input_size){
my_min_heap->Heap_Min_Insert(nearly_sorted_array[cursor++]);
sorted_array[index++] = my_min_heap->Heap_Min_Extract();
}
while (my_min_heap->Heap_Size()>0){
sorted_array[index++] = my_min_heap->Heap_Min_Extract();
}
//print out the sorted array
cout<<"The original K-Sorted Array is :"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<input_size;i++){
cout<<nearly_sorted_array[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<"The sorted K-Sorted Array is :"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<input_size;i++){
cout<<sorted_array[i]<<" ";
}
//call dtor
delete my_min_heap;
return 0;
}
Shuffling card in Java
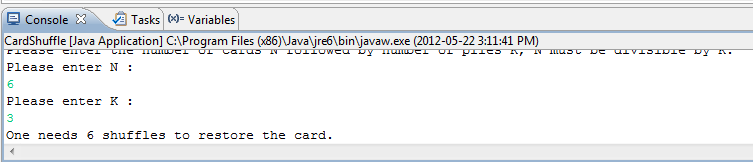
This is an algorithm for shuffling N cards: the rules are described in the code section. The question is to find the period of the shuffling process to restore to its original state.
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Here is an algorithm for shuffling N cards:
1) The cards are divided into K equal piles.
2) The bottom N / K cards belong to pile 1 in the same order (so the bottom card of the initial pile is the bottom card of pile 1).
3) The next N / K cards from the bottom belong to pile 2, and so on.
4) Now the top card of the shuffled pile is the top card of pile 1. The next card is the top card of pile 2,..., the Kth card of the
shuffled pile is the top card of pile K. Then (K + 1)th card is the card which is now at the top of pile 1, the (K + 2)nd is the card
which is now at the top of pile 2 and so on.
For example, if N = 6 and K = 3, the order of a deck of cards "ABCDEF" (top to bottom) when shuffled once would change to "ECAFDB".
Given N and K, what is the least number of shuffles needed after which the pile is restored to its original order?
*/
/**
* @author Larry, Zhirong Li near Vancouver, May 22, 2012
*
*/
public class CardShuffle {
private static int N;
private static int K;
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out
.println("Please enter the number of cards N followed by number of piles K, N must be divisible by K: ");
Scanner scanIn = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
try{
System.out.println("Please enter N :");
N = Integer.parseInt(scanIn.nextLine());
System.out.println("Please enter K :");
K = Integer.parseInt(scanIn.nextLine());
}catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
System.err.println("Not a valid number!");
System.exit(0);
}
} while (N % K != 0);
scanIn.close();
int[] cardArray = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cardArray[i] = i;
}
int numberRequiredShuffles = 1;
shuffleCard(cardArray);
printShuffledCard(cardArray, numberRequiredShuffles);
while (!isArrayRestored(cardArray)) {
shuffleCard(cardArray);
numberRequiredShuffles++;
printShuffledCard(cardArray, numberRequiredShuffles);
}
System.out.println("One needs " + numberRequiredShuffles
+ " shuffles to restore the card.");
}
private static void printShuffledCard(int[] cardArray, int times) {
System.out.println("The " + times + "-th shuffled card array is: ");
for (int item : cardArray) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static boolean isArrayRestored(int[] cardArray) {
boolean isRestored = true;
for (int i = 0; i < cardArray.length - 1; i++) {
if (cardArray[i] > cardArray[i + 1]) {
isRestored = false;
break;
}
}
return isRestored;
}
private static void shuffleCard(int[] cardArray) {
int[] auxiliaryArray = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int targetPosition = findTargetPosition(i);
auxiliaryArray[targetPosition] = cardArray[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cardArray[i] = auxiliaryArray[i];
}
}
private static int findTargetPosition(int currentPosition) {
// all counting starting from 1
int pileNumberFromTop = currentPosition * K / N + 1;
int pileNumberFromBottom = K - pileNumberFromTop + 1;
int pileStartFromTop = (pileNumberFromTop - 1) * N / K;
int pileOffset = currentPosition - pileStartFromTop + 1;
int targetPosition = (pileOffset - 1) * K + pileNumberFromBottom - 1;
return targetPosition;
}
}
Find path on a binary tree in JAVA
The question is to find a path between any two nodes on a binary tree. I tried to use recursion to find path from root to given node then merge the two paths if both exist.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author zhirong(Larry Li) @Toronto
*
*/
public class FindPathBetweenNodes {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Elem root = createTestTree();
List<String> path1 = findPathFromRoot(root, "4");
List<String> path2 = findPathFromRoot(root, "5");
if (path1 != null && path2 != null) {
List<String> mergedPath = mergePath(path1, path2);
for (String str : mergedPath) {
System.out.println(str + " ");
}
} else {
System.out.println("The path does not exist!");
}
}
private static List<String> mergePath(List<String> path1, List<String> path2) {
List<String> mergedPath = new ArrayList<String>();
if (path1.size() > 1 && path2.size() > 1) {
int index = 0;
if (path1.get(1).equals(path2.get(1))) {
while (index < path1.size() && index < path2.size()) {
if (path1.get(index).equals(path2.get(index)))
index++;
else
break;
}
index--;
}
for (int i = path1.size() - 1; i >= index; i--) {
mergedPath.add(path1.get(i));
}
for (int i = index + 1; i < path2.size(); i++) {
mergedPath.add(path2.get(i));
}
} else if (path1.size() == 1 && path2.size() > 1) {
mergedPath.addAll(path2);
} else if (path1.size() > 1 && path2.size() == 1) {
for (int index = path1.size() - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
mergedPath.add(path1.get(index));
}
} else {
mergedPath.addAll(path1);
}
return mergedPath;
}
private static List<String> findPathFromRoot(Elem root, final String value) {
// Base case:
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else if (root.value.equals(value)) {
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
List<String> path = new ArrayList<String>() {
{
add(value);
}
};
return path;
} else {
List<String> leftBranchPath = findPathFromRoot(root.left, value);
if (leftBranchPath == null) {
List<String> rightBranchPath = findPathFromRoot(root.right,
value);
if (rightBranchPath != null) {
rightBranchPath.add(0, root.value);
return rightBranchPath;
}
} else {
leftBranchPath.add(0, root.value);
return leftBranchPath;
}
return null;
}
}
private static Elem createTestTree() {
Elem root = null;
Elem node0 = new Elem();
node0.value = "0";
root = node0;
Elem node1 = new Elem();
node1.value = "1";
node0.left = node1;
Elem node5 = new Elem();
node5.value = "5";
node0.right = node5;
Elem node2 = new Elem();
node2.value = "2";
node1.left = node2;
Elem node3 = new Elem();
node3.value = "3";
node1.right = node3;
Elem node4 = new Elem();
node4.value = "4";
node3.left = node4;
Elem node6 = new Elem();
node6.value = "6";
node5.right = node6;
return root;
}
}
Format data in CSV with double quotes in Java
This is a fairly simple application. Just a 10-minute code to manipulate file IOs to ensure that all data in the CSV file are double quoted and all numbers do have 5 decimal places precision.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class FormatDataInCsv {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader CSVFile = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
"C:\\input.csv"));
try {
// Create file
FileWriter fstream = new FileWriter("C:\\output.csv", false);
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fstream);
String dataRow = CSVFile.readLine(); // Read first line.
String[] processedRow = processHeaderRow(dataRow);
for (int index =0; index<processedRow.length-1;index++) {
//System.out.print(item + "\t");
out.write(processedRow[index] + ",");
}
out.write(processedRow[processedRow.length-1]);
out.write("\r\n");
// The while checks to see if the data is null. If it is, we've hit the end of the file. If not,
// process the data.
dataRow = CSVFile.readLine();
while (dataRow != null) {
String[] dataArray = dataRow.split(",");
if (dataArray[0].equalsIgnoreCase("TRL"))
break;
processedRow = processBodyRow(dataArray);
for (int index =0; index<processedRow.length-1;index++) {
//System.out.print(item + "\t");
out.write(processedRow[index] + ",");
}
out.write(processedRow[processedRow.length-1]);
out.write("\r\n");
dataRow = CSVFile.readLine(); // Read next line of data.
}
processedRow = processTrailerRow(dataRow);
for (int index =0; index<processedRow.length-1;index++) {
//System.out.print(item + "\t");
out.write(processedRow[index] + ",");
}
out.write(processedRow[processedRow.length-1]);
//out.write("\r\n"); the last row does not need a line break
// Close the output stream
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {// Catch exception if any
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
// Close the file once all data has been read.
CSVFile.close();
// End the printout with a blank line.
System.out.println();
}
private static String[] processHeaderRow(String dataRow) {
String[] dataArray = dataRow.split(",");
for(int index=0;index<dataArray.length;index++){
dataArray[index] = "\"" + dataArray[index] + "\"";
}
return dataArray;
}
private static String[] processTrailerRow(String dataRow) {
String[] dataArray = dataRow.split(",");
for(int index=0;index<dataArray.length;index++){
dataArray[index] = "\"" + dataArray[index] + "\"";
}
return dataArray;
}
private static String[] processBodyRow(String[] dataArray) {
//return dataArray;
String[] processedRow = new String[dataArray.length];
int index = 0;
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++){
processedRow[i] = "\"" + dataArray[i] + "\"";
}
//DR
processedRow[6] = "\"" + formatNumber(dataArray[6]) + "\"";
for(int i=7;i<=9;i++){
processedRow[i] = "\"" + dataArray[i] + "\"";
}
return processedRow;
}
private static String formatNumber(String dr) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00000");
return df.format(Double.parseDouble(dr));
}
}
An impartial game: Stone Piles
Sprague–Grundy theorem is a very powerful theorem establishing the fact that every impartial game under normal play convention is equivalent to a nimber. This sets the foundation for this puzzle game.
PROBLEM STATEMENT - There are N piles of stones where the ith pile has xi stones in it. Alice and Bob play the following game:
- Alice starts, and they alternate turns.
- In a turn, a player can choose any one of the piles of stones and divide the stones in it into any number of unequal piles such that no two of the piles you create should have the same number of stones. For example, if there 8 stones in a pile, it can be divided into one of these set of piles: (1,2,5), (1,3,4), (1,7), (2,6) or (3,5).
- The player who cannot make a move (because all the remaining piles are indivisible) loses the game. Given the starting set of piles, who wins the game assuming both players play optimally?
Input: The first line contains the number of test cases T. T test cases follow. The first line for each test case contains N, the number of piles initially. The next line contains N space delimited numbers, the number of stones in each of the piles.
Output: Output T lines, one corresponding to each test case containing "ALICE" if Alice wins the game and "BOB" otherwise.
Constraints: 1 <= T <= 50 1 <= N <= 50 1 <= xi <= 50 Sample Input: 4 1 4 2 1 2 3 1 3 4 1 8 Sample Output: BOB BOB ALICE BOB Explanation: For the first case, the only possible move for Alice is (4) -> (1,3). Now Bob breaks up the pile with 3 stones into (1,2). At this point Alice cannot make any move and has lost.
Code is attached here. The recursion code for computing the nimbers is not provided.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
/* This implementation uses Sprague-Grundy theory to compute the winner of
* each position. The values of the sprague-grundy function for each single rock
* has been precomputed (and are hard-coded) for speed; Given these numbers, the
* Sprague-Grundy number of a position with multiple stone piles is just the XOR
* of the numbers of each individual pile. Zero corresponds to Alice winning,
* and non-zero means Bob wins. See:
* http://www.gabrielnivasch.org/fun/combinatorial-games/sprague-grundy
*/
class GrundySolver {
public:
static int grundy_numbers[];
const char* grundy(std::vector<int>& a) {
int val = grundy_numbers[a[0]];
for(int i=1; i<a.size(); ++i) {
val ^= grundy_numbers[a[i]];
}
return (val==0) ? "BOB" : "ALICE";
}
};
int GrundySolver::grundy_numbers[] = {-1,0,0,1,0,2,3,4,0,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,
17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,
34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int n;
GrundySolver g;
std::cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
int num_elts;
std::cin >> num_elts;
std::vector<int> elts;
for (int j=0; j<num_elts; ++j) {
int num;
std::cin >> num;
elts.push_back(num);
}
std::cout << g.grundy(elts) << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Extract FX Rate in SAS Macro Program
Suppose that you have a lookup query for a series of month-end FX rates (CAD/USD and USD/CAD) for a specified number of months. The data model designates that business_dt is the column that defines the month-end date. For simplicity, we connect to an imaginary Oracle database once to fetch one month FX data. (Multiple month FX data can certainly be put in one SAS passthrough query to ODBC.) We can write a SAS Macro program to fulfill this task.
Notice that for the Macro Processor, single quoted macro variable won't be parsed. However, in the oracle to_date() function, the first parameter must be single quoted. The catch is that we can use compile time %quote() function to force macro variable dereference in generating '2012-09-30' like dates.
options mprint mlogic;
%let username=XXX;
%let userps=XXX;
%MACRO GetFxRateByMonth(business_dt=);
proc sql;
connect to ODBC (dsn=XXX user=&username password=&userps);
create table _Fx_Rate_Extract as
select * from connection to ODBC
(select *
from XXX.XXX
where FROM_CURRENCY='USD' and TO_CURRENCY='CAD'
and business_dt=to_date(%quote(%'&business_dt%'), 'yyyy-MM-dd')
union
select *
from XXX.XXX
where FROM_CURRENCY='CAD' and TO_CURRENCY='USD'
and business_dt=to_date(%quote(%'&business_dt%'), 'yyyy-MM-dd')
);
disconnect from ODBC;
quit;
%MEND GetFxRateByMonth;
%MACRO GetFxRate(LoadMonth=,NumOfMonths=);
%global computed_business_dt;
%let computed_business_dt=&LoadMonth;
%local i;
%do i=1 %to &NumOfMonths;
data _null_;
business_date=symget("computed_business_dt");
dt=INPUT(business_date,YYMMDD10.);
/* Find the month end */
dr=INTNX("MONTH",dt,1,"BEGINNING")-1;
call symputx('computed_business_dt',put(dr, YYMMDD10.),'g');
run;
%GetFxRateByMonth(business_dt=&computed_business_dt)
proc append data=work._Fx_Rate_Extract base=work.Fx_Rate force;
run;
data _null_;
business_date=symget("computed_business_dt");
dt=INPUT(business_date,YYMMDD10.);
/* business_date is incremented by one month */
dr=INTNX("MONTH",dt,1,"BEGINNING");
call symputx('computed_business_dt',put(dr, YYMMDD10.),'g');
run;
%end;
%MEND;
%GetFxRate(LoadMonth=2012-10-31, NumOfMonths=6)
Tricky Group By Statement in SAS SQL
SAS behaves strange from a standard SQL developer's perspetive. It does support "group by computed columns" functionality. However, the result might take a completely different look. The following example demonstrates the fact. People may already be aware of the difference between SAS dataset merges and SAS SQL table joins. One has to know of the tools well enough in order to correctly and efficiently use the tools.
data Orders;
input OrderId $1 OrderDate $3-12 OrderPrice 14-17 Customer $19-24;
datalines;
1 2008/11/12 1000 Hansen
2 2008/10/23 1600 Nilsen
3 2008/09/02 700 Hansen
4 2008/09/03 300 Hansen
5 2008/08/30 2000 Jensen
6 2008/10/04 100 Nilsen
7 2008/11/12 1800 Hansen
8 2008/10/23 900 Bill
;
run;
data MappingTable;
input Customer $1-6 Rating $8;
datalines;
Hansen A
Jensen B
Nilsen B
;
run;
proc sql;
SELECT Customer,OrderDate,SUM(OrderPrice) FROM Orders
GROUP BY OrderDate, Customer;
quit;
proc sql;
select
case
when t1.Customer='Hansen' then 'A'
when t1.Customer in ('Jensen', 'Nilsen') then 'B'
else t1.Customer
end
as Rating,
t1.OrderDate,
sum(t1.OrderPrice)
from Orders t1
group by
Rating, OrderDate;
quit;
proc sql;
select
case
when t1.Customer='Hansen' then 'A'
when t1.Customer in ('Jensen', 'Nilsen') then 'B'
else t1.Customer
end
as Rating,
sum(t1.OrderPrice)
from Orders t1
group by
Rating;
quit;
proc sql;
select
case
when t2.Rating is missing then t1.Customer
else t2.Rating
end
as Rating,
t1.OrderDate,
sum(t1.OrderPrice)
from Orders t1 left outer join MappingTable t2
on t1.Customer=t2.Customer
group by
Rating, OrderDate, t1.Customer;
quit;
proc sql;
select distinct
case
when t2.Rating is missing then t1.Customer
else t2.Rating
end
as Rating,
sum(t1.OrderPrice)
from Orders t1 left outer join MappingTable t2
on t1.Customer=t2.Customer
group by
Rating;
quit;
You can find the results of the SAS SQL right here.
Validating a given column name in all SAS tables
Sometimes you may want to validate whether or not a specific column(which may appear in many tables) is in line with the spec. For example, for an internal risk rating system, you may want to verify that, at exposure level, some risk rating identifier has the desirable format. The following SAS script can find all SAS tables that contain the given column and will pick out all records that fail to meet the spec. These records will be logged in a SAS dataset with information such as library name, table name, row number in the original table and the incorrect risk rating identifier.
proc sql;
describe table dictionary.columns;
quit;
options mlogic mprint;
proc sql;
create table work.error_log
(
TableName char(40) format=$40. informat=$40. label='Libname.Colname',
RowNumber num format=best. informat=best. label='Row Number',
RISK_RATING_ID char(10) format=$10. informat=$10. label='RISK RATING ID'
);
quit;
%macro risk_rating_id_check(TARGET_COL_NAME=);
PROC SQL noprint;
select count(0) into :table_list_count
FROM DICTIONARY.COLUMNS
WHERE (UPCASE(NAME)=%UPCASE("&TARGET_COL_NAME"))
and UPCASE(LIBNAME) in ('XXX_S');
SELECT cats(libname,'.', memname)
into
:TABLE_LIST SEPARATED BY '|'
FROM DICTIONARY.COLUMNS
WHERE (UPCASE(NAME)=%UPCASE("&TARGET_COL_NAME"))
and UPCASE(LIBNAME) in ('XXX_S');
QUIT;
%put table_list_count=&table_list_count;
/* %put &TABLE_LIST;*/
%local i process_table;
%do i=1 %to &table_list_count;
%let process_table = %scan(&TABLE_LIST,&i,|);
%put NOTE: Now processing table: &process_table;
data work.workingtable(keep=TableName RowNumber &TARGET_COL_NAME);
set &process_table;
length TableName $40 RowNumber 8;
if &TARGET_COL_NAME ~="" then
if length(&TARGET_COL_NAME) ~= 10 or not (upcase(substr(&TARGET_COL_NAME,4,1)) in ('S','_')) then
do;
/* put "bad " &process_table _N_;*/
TableName="&process_table";
RowNumber=_N_;
output;
end;
;
;
run;
proc append base=work.error_log data=work.workingtable force;
%end;
%mend risk_rating_id_check;
%risk_rating_id_check(TARGET_COL_NAME=RISK_RATING_ID)
Column Length Check in all SAS tables
In some occasions, you may want to verify whether or not a list of columns that may appear in multiple tables is in conformance with the prescribed length requirements. We can still make best use of DICTIONARY. Columns to find the corresponding length definition as defined in DDL. The following snippet of SAS code does the job. Particular attention should be drawn on how to call a Macro within a SAS data step.
options mlogic mprint;
proc sql;
create table work.new_field_len
(
LibraryName char(40) format=$40. informat=$40. label='Libname',
TableName char(40) format=$40. informat=$40. label='Table Name',
ColumnName char(40) format=$40. informat=$40. label='Column Name',
ExpectedLength num format=best. informat=best. label='Expected Length',
ActualLength num format=best. informat=best. label='Actual Length'
);
quit;
data work.new_fields;
input field_name $1-40 expected_len best.;
datalines;
TAX_BASE 6
FISCAL_POSITION 6
MANAGEMENT 6
LIQUIDITY 10
BOR_MTRX_ID 25
;
run;
%macro FindInAllTables(ColumnName,ExpectedLen);
%put &ColumnName &ExpectedLen;
PROC SQL noprint;
create table work.dictionary_info as
select libname as LibraryName format $40., memname as TableName format $40., name as ColumnName format $40.,
length as ActualLength format best.
FROM DICTIONARY.COLUMNS
WHERE (UPCASE(NAME)="%UPCASE(&ColumnName)");
QUIT;
data work.workingtable(keep=LibraryName TableName ColumnName ExpectedLength ActualLength);
set work.dictionary_info;
length ExpectedLength 8;
ExpectedLength=&ExpectedLen;
output;
run;
proc append base=work.new_field_len data=work.workingtable force;
%mend FindInAllTables;
data _null_;
set work.new_fields;
call execute('%FindInAllTables('||field_name||','||expected_len||')');
run;
The link to my thesis on University of Waterloo UWSpace is http://uwspace.uwaterloo.ca/handle/10012/5546. Due to page limit, the complete proof for second order optimality conditions in Chapter 4 can be found in this version. and the presentation slides can be found here.
During the completion of my Master of Mathematics program in Computer Science with concentration in "Computational Finance", I was lucky to know a lot of very capable colleagues and classmates. I really do learn a lot and enjoy discussing all kinds of mathematical and programming/algorithm problems with them. Research is not easy at all. It was always very helpful and thought-invoking during the weekly meeting with my supervisor, Prof. Yuying Li, who really knows the subjects very well and gave me tons of suggestions and possible research directions. Whenever I came across any questions that I could not answer, I was always encouraged to either write an email like this or meet her in person. It is possible that some research effort will end up with little practical values, e.g., I used to derive a steplength calculation (here is the draft) for a variant version of Barzilai-Borwein method with the L1-norm regularization, it turned out the theoretical values are not easy to obtain at all. I also spent a lot of time figuring out the necessary conditions for my scaled gradient method to converge. Anyway, this is about life. One has to overcome all kinds of problems and difficulties in the way with faith and dedication.
Finance 1~3 Course Recap notes can be found here.
From time to time, I still keep the habit to discuss math/finance/programming problems with my dear friends. I have posted several write-ups here based on the discussion results.
- The Cliff Hanger Problem is a very interesting probability problem. If one follows the traditional approach, the difference equation requires a bit more work. Indeed, if one can see the exponential recurrence relation as widely seen in M|M|1 queuing model, this question can be easily solved. Another elegant approach makes use of martingale to handle this barrier crossing type problems.
- Question 3 in the attached pdf is a discrete diffusion model which was first described by Daniel Bernoulli in 1769.
- I did not know that attached is the "lost cow" problem before my friend told me about this. Anyway, I discussed with my friends and was happy to find that our upper bound of the ratio is the same to the established results in theory. It is indeed a very thought-invoking algorithm question and randomization may provide some improvements depending on how you start with your search. As you can see in this manuscript, simple one time U-turn does perform well comparable to scheme 5.
- It is always embarrassing to find that numerical results may significantly deviate from the theoretical results. In this boundedness problem for the conditional expectation for a Gaussian random variable, you can find that two issues that caused the imperfection of the simulation results, i.e., first, the precision of any software is finite, so if you encounter indefinite term like 0/0, you will surely find that the simulation result has a large bias. Second, Monte Carlo method is powerful in solving many practical problems, but for rare event, it is almost impossible to get the correct result unless you unlimitedly increase the simulation time.
- I have to admit I did not know this median-mean inequality at all when I first saw this problem. Mathematics is so beautiful but one may have to devote all his life to learning all kinds of mathematical problems:) The one tailed Chebyshev inequality plays the key role in the proof.
- The conditional expectation of a bivariate normal random variable is a bit dreadful at the first sight. However, it is amazing to greatly simplify the deduction using decomposition of the given random variables/processes into uncorrelated random variables/processes. The trick is self-explanatory in the manuscript.
- There is nothing special about this derivation of partial sums. In Maple, this can be easily verified by one line of code.
- (Feb.10, 2012) This is a very standard question about the variance of the integration of a Brownian Motion. Two approaches are provided here.
- (Apr.21, 2012) I give a tutorial on Manacher's algorithm in finding the longest palindromic substring. I always feel confident in my drawings to illustrate algorithms :)
- (June 16, 2012) I give a list of 10 interesting brain teaser questions in the name of "Larry's List of 10 Brain Teasers".
- (Oct 07, 2012) I hereby introduce a trick in extracting the business date from a given string, e.g., a business file name, i.e., Name Parser.
- (Oct 07, 2012) I ran across two very good brain teaser questions and share with you guys here.
- (Oct 09, 2012) I posted an open source code for .uploading binary files to Oracle DB as a Blob entry. Notice that you may need to use Byte[] as data type when fetching the DB Blob field.
- (Nov 06, 2012) This is a useful link to an article explaining the basics of antithetic sampling.
- (Apr 21, 2013) This is an interesting brain-teaser type programming questions for computing the number of positive solutions. If you walk through the solution, you may find out this really incororates several wellknown brain teasers.
- (May 25, 2013) This book PROC DOCUMENT by Example Using SAS by Michael Tuchman is a very good reference for manipulating the SAS ODS output using PROC DOCUMENT without re-running the data/proc steps. The output of the analysis is saved and organized by the ODS DOCUMENT environment and will be loaded by PROC DOCUMENT in generating the desired output. My manager agreed to buy me the book as requested :)
- Always be extra careful: no matter how small or how trivial the tasks you are working on, at least you may still need to emulate the work flow on your mind to ensure that it won't break the system.
- Always do a sanity check: does the value in question fall into the correct range? If you are involved in a large system, will the change have an impact on other modules/models? It is always good to have a clear picture of the inter-dependency relationships among different modules within the system. More often than not, one change will result in sequential changes.
- Code/documentation review is essentially very necessary: when you are unfamiliar with the system, it is quite natural to peruse the relevant documentation. If this piece of information is not available, you can take a look at a chunk of sample code to familiarize yourself with the existing coding style/patterns.
- Never pretend to know what you don't know: no one knows everything. It is your responsibility to understand what you are/will be doing. When you can not figure out how to solve a problem, always seek help from others or online resources. After that, you still need to recap all the details to see if you will be able to work this out next time. It is not a matter of how quickly you can solve a problem, it is really a matter of the quality and efficiency about how you tackle the problem.
- Never trust your memory: people are forgetful when he has many things to tend to. It is a very good habit to compose a to-do list and mark down what you have already finished. By doing so you will always be able to track down your progress.
- Never 100% trust other people's results: in the first place, you have to make sure you will get a valid and meaningful input and your output will be compatible with the other people's requirements/expectations on you.
For financial information, CNN Money and Wallstreet Journal are definitely two must-visit places.
In regards to programming, C++ FAQ is a very good online resource and you probably will find the answers if you have questions about the concepts concerning C++.
Apache Commons is a useful online specification for Apache Commons Lang Library. For example, you may want to double check whether or not StringUtils.IsEmpty has a null check.
www.oodesign.com is a very good place to ramp up with the concept and examples on OO design patterns.
cplusplus.com contains general information about the C++ programming language.
Hibernate is a collection of related projects enabling developers to utilize POJO-style domain models in their applications in ways extending well beyond Object/Relational Mapping.
The Apache Struts web framework is a free open-source solution for creating Java web applications. The framework provides three key components:
- A "request" handler provided by the application developer that is mapped to a standard URI.
- A "response" handler that transfers control to another resource which completes the response.
- A tag library that helps developers create interactive form-based applications with server pages.
Needless to mention Oracle acquired Sun and now the Java Platform Standard Ed. 6 doc can be found at JAVA SE6 API DOC.
Perhaps Black-Scholes model is the most well known model in the financial modeling world. There are many ways in deriving the Black-Scholes PDE. You may have seen the method by replicating many times. Nevertheless, it might not be that obvious CAPM can lead to the same arguments too. As elaborated in this article, two methods including CAPM are introduced to deduce the Black-Scholes PDE.
American option renders the early excercise feature. However, it is never optimal to early exercise an American non-dividend call. Why is this? This report explains in detail. You may be asked during an interview about model-independent parities. Put-Call parity (Proved by no-arbitrage argument) is very useful in deriving price related inequalities.
Vasicek model, a mean-reverting process, is widely used to describe the evolution of interest rate. It is very likely you will be asked such question like what is the mean and variance of a RV governed by Vasicek model? if you apply for fixed income position. It is worth mentioning a very good reference covering various interest rate models: "Yield Curve Estimation and Prediction with the Vasicek Model," by D. Bayazit, Middle East Technical University.
The Single Factor Model forms the basis for the credit risk approach of the second Basel Capital Accord. The economic capital is based on VaR which is at the 99.9% confidence level with a one year time horizon. I made a separate copy from the course notes to address the basics.
The first category, the set of structural models, is pioneered by Merton's work (1974), Merton's Model. Despite its simple structure, it apprently has two immediate practical concerns: 1) The firm's assets value and its volatility are central to determining the value of the equity, but both are unobservable. 2) In reality, the debt structures are far more complex.
Markowitz Mean-Variance model assumes that investors are risk averse. This means that given two assets that offer the same expected return, investors will prefer the less risky one. Thus, an investor will take on increased risk only if compensated by higher expected returns. Conversely, an investor who wants higher returns must accept more risk. The exact trade-off will differ by investor based on individual risk aversion characteristics. The implication is that a rational investor will not invest in a portfolio if a second portfolio exists with a more favorable risk-return profile - i.e., if for that level of risk an alternative portfolio exists which has better expected returns. Using risk tolerance, we can simple classify investors into three types: risk-neutral, risk-averse, and risk-lover. Risk-neutral investor’s do not require the risk premium for risk investments; they judge risky prospects solely by their expected rates of return. Risk-averse investors are willing to consider only risk-free or speculative prospects with positive premium; they make investment according the risk-return trade-off. A risk-lover is willing to engage in fair games and gambles; this investor adjusts the expected return upward to take into account the ’fun’ of confronting the prospect’s risk. The detailed derivation can be found here.
There is an extension of Merton's Model, which is called First Passage Model. In this model, default happens the first time assets falls below liabilities. This is indeed a very interesting mathematical model that takes Brownian Hitting Times, Optional Sampling Theorem and Reflection Principle into account. I will provide the details in this weekend.
Call options on the same underlying asset with the same maturity, with strikes K1<K2<K3, are trading for C1, C2 and C3 (no bid-ask spread) with C1>C2>C3. Find necessary and sufficient conditions on the prices C1, C2 and C3 such that no arbitrage exists corresponding to a portfolio made of positions in the three options.
In Basel III, the risk coverage of the capital framework is strenthed. One notable change is that Credit Value/Valuation Adjustment (CVA) is required to be implemented.
A very useful link for computing the CVA using matlab can be found right here.
Readers are referred to this slides for a more detailed explantions on CVA calculation.
Basically, the credit portfolio is composed of vanilla interest rate swaps(IRS). A yield curve at settement dates is constructed for computing the instantaneous forward rates during the calculation of the single factor Hull-White short rate path.
Monte Carlo simulation is performed by generating the aforementioned short rate paths. IRS mark-to-market prices are then calculated to valuate the portfolio worth. Netting and/or collateral adjustment is applied. The implied counterpary default rate can be derived from the current market spreads of the counterparty's credit default swaps.
In the end, various exposure profiles including PE/MPE/EE/EPE/EffEE/EffEPE are examined and the CVA values are computed for each counterparty.
This academic paper "Stress testing probability of default and migration rate with respect to Basel II requirements" by Peter Miu and Bogie Ozdemir establishes the foundation of the Long Run Probability of Default (LRPD) and Long Run Probability of Transitions (LRPT) calculations with respect to Basel II implementations. Basically banks may not be able to get enough historical wholesale internal default rates. The workout is to use e.g. SNP Credit Pro as the systematic risk factor which can provide more TTC default rates for LOB such as CRE/Corporate/Commercial. Regression can be performed to get the coefficients for the forecast equations. However, banks would like to link the internal DR to external SNP DR. As a result, an ML-estimation based approach can be performed to derive the cross sectional correlation factor based on the realized internal default rates and cross speculative grade migration rates.
This "framework for loss given default validation of retail portfolios" is a very good article exlaining the model vetting on LGD. More specifically speaking, some very useful vetting criteria including hit rates and false alarm rates,cumulative accuracy ratio etcs are thoroughly explained. I really like the idea of cumulative accuracy ratio, which can vividly show how good a model is.
It is very useful to use CAPM model for pricing. In "Discount Rate for Workout Recoveries: An Empirical Study" conducted an empirical study on what factors should be considered in the multivariate regression model for estimating the discount rates, which is required to estimate economic LGD from workout recoveries. "Choosing the Discount Factor for Estimating Economic LGD" also gives a detailed explanation on estimates of corporate debt LGD risk premium using CAPM valuation framework.
As part of a model vetting process, you may need to do a white noise (lack of serial correlation) and/or stationary test of your ARIMA models. If you models fit the data well, you would expect to see that residuals of a fitted ARIMA model display white-noise type characteristics (zero correlation) after applying Ljung–Box Q test. The sample autocorrelation function (ACF) and partial autocorrelation function (PACF) are useful qualitative tools to assess the presence of autocorrelation at individual lags. The Ljung-Box Q-test is a more quantitative way to test for autocorrelation at multiple lags jointly. A common assumption of time series models is a Gaussian innovation distribution. After fitting a model, you can infer residuals and check them for normality. If the Gaussian innovation assumption holds, the residuals should look approximately normally distributed. In time series models, the innovation process is assumed to be uncorrelated. After fitting a model, you can infer residuals and check them for any unmodeled autocorrelation. Augmented Dickey–Fuller test (ADF) is a test for a unit root in a time series sample. The augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) statistic, used in the test, is a negative number. "The more negative it is, the stronger the rejection of the hypothesis that there is a unit root at some level of confidence"
The following European Call option pricer can be attacked in many ways from design pattern's perspetive. Though it serves the purpose to calculate the price, it is not reusale for other pricing functions.
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
/* Author@Zhirong(Larry), Li
A monto carlo pricer for European Call option
Oct 28, 2012 @Toronto
*/
class MontoCarloCallPricer{
public:
MontoCarloCallPricer(int N = 10000, double R = 0.04, double VOL= 0.1): _m_N(N), _m_r(R), _m_vol(VOL) {}
static double CallPricer(double expiry, double strike, double price, double r, double volatility, int N);
// simulation time
int _m_N;
// continuous compouding interest rate
double _m_r;
// volatility of the internal rate of return (IRR)
double _m_vol;
};
double MontoCarloCallPricer::CallPricer(double expiry, double strike, double price, double r, double volatility, int N){
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double avg_price = 0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = price*exp((r-0.5*volatility*volatility)*expiry + volatility*sqrt(expiry)*distribution(generator));
double price = (terminal_price>strike)? (terminal_price-strike):0;
avg_price += price;
}
return exp(-r*expiry)*avg_price/N;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
std::cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
std::cin>>Expiry;
std::cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
std::cin>>Strike;
std::cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price";
double Price;
std::cin>>Price;
/* specify the parameters */
MontoCarloCallPricer montoCarloCallPricer;
double Monto_Carlo_Price = MontoCarloCallPricer::CallPricer(Expiry, Strike, Price, montoCarloCallPricer._m_r,
montoCarloCallPricer._m_vol, montoCarloCallPricer._m_N );
std::cout<<"The price is : "<<Monto_Carlo_Price<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
As pointed out in Joshi's book, we indeed can create a payoff class to be more flexible(encapsulation) in pricing different kind of options. My version of revision is as follows with a put-call parity check with tolerance=0.01.
//Payoff.h
class Payoff{
public:
typedef enum {call, put} TYPE_CODE;
Payoff(double Strike, TYPE_CODE OptionType);
double operator()(double spot) const;
static double OptionPricer(const Payoff&, double spot, double expiry, double r, double volatility, int num_path);
private:
double strike;
TYPE_CODE option_type;
};
//Payoff.cpp
#include "Payoff.h"
#include <minmax.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
using namespace std;
Payoff::Payoff(double Strike, TYPE_CODE OptionType):strike(Strike),option_type(OptionType){}
double Payoff::operator()(double spot) const{
switch (option_type){
case call:
return max(spot-strike,0);
case put:
return max(strike-spot,0);
default:
throw("Unknown option type!");
}
}
double Payoff::OptionPricer(const Payoff& payoff, double spot, double expiry, double r, double volatility, int num_path){
default_random_engine generator;
normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double avg_price = 0;
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = spot*exp((r-0.5*volatility*volatility)*expiry
+volatility*sqrt(expiry)*distribution(generator));
double price =payoff(terminal_price);
avg_price += price;
}
return exp(-r*expiry)*avg_price/num_path;
}
bool put_call_parity_check(double callPrice, double putPrice, double SpotPrice, double Expiry, double InterestRate, double Strike){
// model indepedent parity based on no arbitrage pricing C-P= S0-exp(-rT)*K
double tol = 0.01;
return fabs((callPrice-putPrice) -(SpotPrice - exp(-InterestRate*Expiry)*Strike))<tol? true:false;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
Payoff callPayoff(Strike, Payoff::call);
Payoff putPayoff(Strike, Payoff::put);
double callPrice = Payoff::OptionPricer(callPayoff, SpotPrice, Expiry,InterestRate,Volatility,N);
double putPrice = Payoff::OptionPricer(putPayoff, SpotPrice, Expiry,InterestRate,Volatility,N);
bool isPutCallParitySatisfied = put_call_parity_check(callPrice, putPrice, SpotPrice, Expiry, InterestRate, Strike);
if (isPutCallParitySatisfied){
cout<<"Satisfied!"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"There must be sth wrong!"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
And we noticed that the simulation time should be large enougth, e.g. 100K to be accurate in satisfying the put-call parity(tol=0.01).
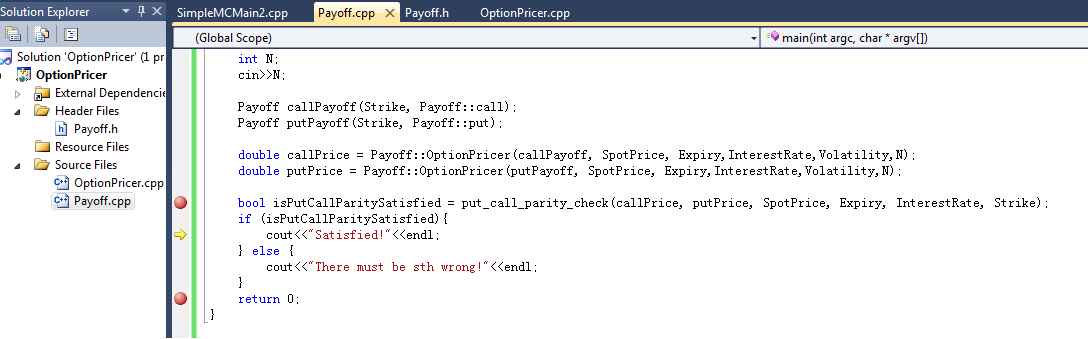
We should separate the main function from Payoff class and use Payoff class as an abstract interface. European Call/Put and Double Digital option "is a" payoff so inheritance kicks in.
/* Author Zhirong(Larry), Li at Toronto Oct 29, 2012
use inheritance and virtual function to price the options, Payoff class only
servers as an interface to capture all basic common functionalities.
*/
/* Header files */
//Payoff.h
#ifndef PAYOFF_H
#define PAYOFF_H
class Payoff{
public:
Payoff(){};
virtual ~Payoff(){};
virtual double operator()(double spot) const=0;
};
#endif
//EuroCallPayoff.h
#ifndef EUROCALLPAYOFF_H
#define EUROCALLPAYOFF_H
#include "Payoff2.h"
class EuroCallPayoff : public Payoff{
public:
EuroCallPayoff(double strike);
virtual double operator()(double spot) const;
virtual ~EuroCallPayoff(){};
private:
double _m_strike;
};
#endif
//EuroPutPayoff.h
#ifndef EUROPUTPAYOFF_H
#define EUROPUTPAYOFF_H
#include "Payoff2.h"
class EuroPutPayoff : public Payoff{
public:
EuroPutPayoff(double strike);
virtual double operator()(double spot) const;
virtual ~EuroPutPayoff(){};
private:
double _m_strike;
};
#endif
//DitialPayoff.h
#ifndef DIGITALPAYOFF_H
#define DIGITALPAYOFF_H
#include "Payoff2.h"
class DigitalPayoff : public Payoff{
public:
DigitalPayoff(double low, double high);
virtual double operator()(double spot) const;
virtual ~DigitalPayoff(){};
private:
double _m_high_barrier;
double _m_low_barrier;
};
#endif
/* Implementation Files */
//EuroCallPayoff.cpp
# include "EuroCallPayoff.h"
#include <minmax.h>
double EuroCallPayoff::operator()(double spot) const{
return max(spot-_m_strike,0);
}
EuroCallPayoff::EuroCallPayoff( double strike): _m_strike(strike){}
//EuroPutPayoff.cpp
# include "EuroPutPayoff.h"
#include <minmax.h>
double EuroPutPayoff::operator()(double spot) const{
return max(_m_strike-spot,0);
}
EuroPutPayoff::EuroPutPayoff(double strike): _m_strike(strike){}
//DitialPayoff.cpp
# include "DigitalPayoff.h"
DigitalPayoff::DigitalPayoff(double low, double high): _m_low_barrier(low), _m_high_barrier(high){}
double DigitalPayoff::operator()(double spot) const{
if (spot<_m_high_barrier && spot>_m_low_barrier)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Main Function */
#include <iostream>
#include <minmax.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
#include "EuroCallPayoff.h"
#include "EuroPutPayoff.h"
#include "DigitalPayoff.h"
using namespace std;
double OptionPricer(const Payoff& payoff, double spot, double expiry, double r, double volatility, int num_path){
default_random_engine generator;
normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double avg_price = 0;
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = spot*exp((r-0.5*volatility*volatility )*expiry
+volatility*sqrt(expiry)*distribution (generator));
double price =payoff(terminal_price);
avg_price += price;
}
return exp(-r*expiry)*avg_price/num_path ;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
cout<<"\nEnter Lower Level Barrier\n";
double low;
cin>>low;
cout<<"\nEnter Upper Level Barrier\n";
double high;
cin>>high;
const EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
const EuroPutPayoff euroPutPayoff(Strike);
const DigitalPayoff digitalPayoff(low,high);
double callPrice = OptionPricer(euroCallPayoff, SpotPrice, Expiry,InterestRate,Volatility,N);
double putPrice = OptionPricer(euroPutPayoff, SpotPrice, Expiry,InterestRate,Volatility,N);
double digitPrice = OptionPricer(digitalPayoff, SpotPrice, Expiry,InterestRate,Volatility,N);
return 0;
}
After including the boost library VER 1.51 (see how), we can verifity that the Monto Carlo double digital option pricer gives result with precision up to 3 decimal places as compared to theoretical value.
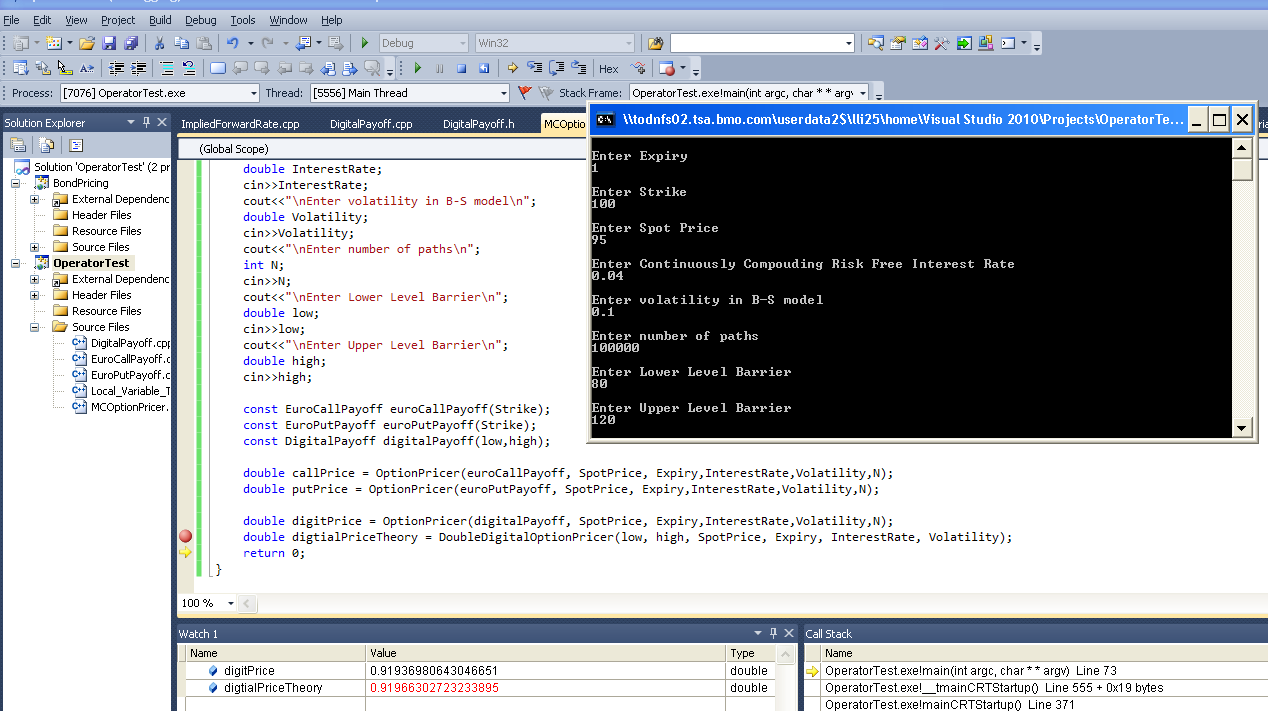
#include <boost/math/distributions.hpp> double DoubleDigitalOptionPricer(double low, double high, double spot, double expiry, double r, double volatility){ boost::math::normal_distribution <> normal(0.0,1.0); double high_end_quantile = (log(high/spot)-(r-volatility*volatility /2)*expiry)/(volatility *sqrt(expiry)); double high_end = cdf(normal, high_end_quantile); double low_end_quantile = (log(low/spot)-(r-volatility*volatility /2)*expiry)/(volatility *sqrt(expiry)); double low_end = cdf(normal, low_end_quantile); double digital_price = exp(-r*expiry)*(high_end-low_end ); return digital_price; }
Put, Call and Double Digital option are all Vanilla options. Their payoffs only depend on the prices at termination thus they are not path dependent. We could define a VanillaOption class as the base class. It should contain the expiry as one of its primitive members and the PayOff object to determine the price of the option. However, we don't want this VanillaOption class to be of variable size, we could make a reference to the PayOff object. In C++, we have to be careful about the memory allocation and de-allocation issues. If the PayOff object ceases to exist before the VanillaOption, when we reference this PayOff object in VanillaOption object, this call to a non-exisitent object will cause the system to crash. The VanillaOption should exist independently in its own right. A virtual copy constructor can help to resolve this issue by creating its own copy of the object in VanillaOption object. An object must know of its own type hence it can certainly make a copy of itself. By convention, this virtual copy constructor is called clone();
//Payoff3.h
#ifndef PAYOFF3_H
#define PAYOFF3_H
class Payoff{
public:
Payoff(){}
virtual Payoff* clone() const=0;
virtual ~Payoff(){}
virtual double operator()(double spot) const=0;
};
#endif
//EuroCallPayoff3.h
#ifndef EUROCALLPAYOFF3_H
#define EUROCALLPAYOFF3_H
#include "Payoff3.h"
class EuroCallPayoff : public Payoff{
public:
EuroCallPayoff(double Strike);
virtual Payoff* clone() const;
virtual double operator()(double spot) const;
virtual ~EuroCallPayoff(){};
private:
double _strike;
};
#endif
//VanillaOption.h
#ifndef VANILLAOPTION_H
#define VANILLAOPTION_H
#include "Payoff3.h"
class VanillaOption{
public:
VanillaOption(const Payoff& payoff, double expiry);
VanillaOption(const VanillaOption& original);
VanillaOption& operator=(const VanillaOption& original);
double GetExpiry() const;
double OptionPayoff(double spot) const;
~VanillaOption();
private:
double _expiry;
Payoff* _payoff;
};
#endif
//SimpleMC.h
#ifndef SIMPLEMC_H
#define SIMPLEMC_H
#include "VanillaOption.h"
double OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, double r, double volatility, int num_path);
double TheoreticalCallPrice(double expiry, double strike, double spot_price, double r, double sigma);
#endif
/* Implementation Files*/
//EuroPayoff.cpp
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
#include <minmax.h>
EuroCallPayoff::EuroCallPayoff(double Strike): _strike(Strike){}
double EuroCallPayoff::operator()(double spot) const{
return max(spot-_strike,0);
}
Payoff* EuroCallPayoff::clone() const{
return new EuroCallPayoff(*this);
}
//VanillaOption.cpp
#include "VanillaOption.h"
VanillaOption::VanillaOption(const Payoff& thePayoff, double expiry): _expiry(expiry){
_payoff = thePayoff.clone();
}
VanillaOption::VanillaOption(const VanillaOption& original){
_expiry = original._expiry;
_payoff = original._payoff->clone();
}
double VanillaOption::OptionPayoff(double spot) const{
return (*_payoff)(spot);
}
VanillaOption::~VanillaOption(){
delete _payoff;
}
double VanillaOption::GetExpiry() const{
return _expiry;
}
VanillaOption& VanillaOption::operator=(const VanillaOption& original){
if(this != &original){
this->_expiry = original._expiry;
//re-assign a new payoff object, delete the old one
delete this->_payoff;
this->_payoff = original._payoff->clone();
}
return *this;
}
//SimpleMC.cpp
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
#include <boost\math\distributions.hpp>
using namespace std;
double OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, double r, double volatility, int num_path){
default_random_engine generator;
normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double avg_price = 0;
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = spot*exp((r-0.5*volatility*volatility)*vanillaOption.GetExpiry()
+volatility*sqrt(vanillaOption.GetExpiry())*distribution(generator));
double price =vanillaOption.OptionPayoff(terminal_price);
avg_price += price;
}
return exp(-r*vanillaOption.GetExpiry())*avg_price/num_path;
}
double TheoreticalCallPrice(double expiry, double strike, double spot_price, double r, double sigma){
boost::math::normal_distribution<> normal(0.0,1.0);
double high_end_quantile = (log(spot_price/strike)+(r+sigma*sigma/2)*expiry)/(sigma*sqrt(expiry));
double low_end_quantile = high_end_quantile - sigma*sqrt(expiry);
return spot_price*cdf(normal, high_end_quantile) - strike*cdf(normal, low_end_quantile)*exp(-r*expiry);
}
//MCMain3.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "VanillaOption.h"
#include "Payoff3.h"
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
#include "SimpleMC.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
VanillaOption vanillaOption(euroCallPayoff,Expiry);
double optionPrice = OptionPricer(vanillaOption, SpotPrice, InterestRate, Volatility, N);
double optionPriceTheory = TheoreticalCallPrice(Expiry, Strike, SpotPrice, InterestRate, Volatility);
return 0;
}
We need to create a parameter class to store the parameters such as interest rates, volatility and this class is designed for easy extension. Notice that for financial models, more often than not, the integral over certain time period is needed instead of the instantaneous parameter itself.
"The bridge pattern is a design pattern used in software engineering which is meant to "decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently". The bridge uses encapsulation, aggregation, and can use inheritance to separate responsibilities into different classes."
We can define a Parameters class whose only data member is a pointer to an abstract class InnerParameters. Interest rate and volatility can be treated as ConstantParameters which inherits from the wrapper class Parameters.
//Parameters.h
#ifndef PARAMETERS_H
#define PARAMETERS_H
class InnerParameters{
public:
InnerParameters(){};
virtual ~InnerParameters(){}
//Intergral may depend on its parameter type, define as pure virtual and leave the implementation to subclasses
virtual double Integral(double start, double end) const=0;
virtual double SquareIntegral(double start, double end) const=0;
virtual InnerParameters* clone() const=0;
private:
};
class Parameters{
public:
Parameters(const Parameters& orignal);
Parameters(const InnerParameters& inner_parameter);
Parameters& operator= (const Parameters& original);
virtual ~Parameters();
inline double Integral(double start, double end) const;
inline double SquareIntegral(double start, double end) const;
double Mean(double start, double end) const;
double RootMeanSqure(double start, double end) const;
private:
InnerParameters* _ptr_inner_parameter;
};
class ConstantParameters : public InnerParameters{
public:
ConstantParameters(double parameter);
virtual double Integral(double start, double end) const;
virtual double SquareIntegral(double start, double end) const;
virtual InnerParameters* clone() const;
virtual ~ConstantParameters(){}
private:
double _const_parameter;
};
#endif
//SimpleMC.h
#ifndef SIMPLEMC_H
#define SIMPLEMC_H
#include "VanillaOption.h"
#include "Parameters.h"
double OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, Parameters r, Parameters volatility, int num_path);
#endif
//Parameters.cpp
#include "Parameters.h"
#include <math.h>
Parameters::Parameters(const Parameters& original){
this->_ptr_inner_parameter = original._ptr_inner_parameter->clone();
}
Parameters::Parameters(const InnerParameters& innerParameter){
this->_ptr_inner_parameter = innerParameter.clone();
}
inline double Parameters::Integral(double start, double end) const{
return this->_ptr_inner_parameter->Integral(start, end);
}
inline double Parameters::SquareIntegral(double start, double end) const{
return this->_ptr_inner_parameter->SquareIntegral(start, end);
}
Parameters& Parameters::operator=(const Parameters& original){
if(this!= &original){
delete this->_ptr_inner_parameter;
this->_ptr_inner_parameter = original._ptr_inner_parameter->clone();
}
return (*this);
}
Parameters::~Parameters(){
delete _ptr_inner_parameter;
}
InnerParameters* ConstantParameters::clone()const{
return new ConstantParameters(*this);
}
ConstantParameters::ConstantParameters(double parameter): _const_parameter(parameter){}
double ConstantParameters::Integral(double start, double end) const{
return (this->_const_parameter)*(end-start);
}
double ConstantParameters::SquareIntegral(double start, double end) const{
return (this->_const_parameter) * (this->_const_parameter)*(end-start);
}
double Parameters::Mean(double start, double end) const{
return Integral(start, end)/(end-start);
}
double Parameters::RootMeanSqure(double start, double end) const{
return sqrt(SquareIntegral(start,end)/(end-start));
}
//SimpleMC.cpp
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
#include "Parameters.h"
double OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, Parameters r, Parameters vol, int num_path){
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double avg_price = 0;
double expiry = vanillaOption.GetExpiry();
//moveSpot is indepedent of loop variable i, move out of the for loop
double movedSpot = spot*exp(r.Integral(0, expiry)-0.5*vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
double rootVariace = sqrt(vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = movedSpot* exp(rootVariace* distribution(generator));
double price =vanillaOption.OptionPayoff(terminal_price);
avg_price += price;
}
return exp(-r.Integral(0,expiry))*avg_price/num_path;
}
//MCMain.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include "VanillaOption.h"
#include "Payoff3.h"
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
ConstantParameters r(InterestRate);
ConstantParameters vol(Volatility);
EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
VanillaOption vanillaOption(euroCallPayoff,Expiry);
double call_price = OptionPricer(vanillaOption, SpotPrice, r, vol, N);
return 0;
}
In computer programming, the strategy pattern (also known as the policy pattern) is a particular software design pattern, whereby algorithms can be selected at runtime. Formally speaking, the strategy pattern defines a family of algorithms, encapsulates each one, and makes them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
The strategy pattern uses aggregation instead of inheritance. In the strategy pattern, behaviors are defined as separate interfaces and specific classes that implement these interfaces. Specific classes encapsulate these interfaces. This allows better decoupling between the behavior and the class that uses the behavior.
One application of strategy pattern is to define a statistic gatherer to collect the output of the algorithm. Depending on the result type at run-time, corresponding result will be written to this object, i.e.,
//Statistics.h
#ifndef STATISTICSGATHERER_H
#define STATISTICSGATHERER_H
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Statistics{
public:
Statistics(){};
virtual ~Statistics(){}
//Notice that the state of the object could be changed, so No const=0
virtual void DumpOneResult(double result)=0;
virtual vector<vector<double> > GetResult()const=0;
virtual Statistics* clone() const=0;
private:
};
#endif
//StatisticsMean : public Statistics
#ifndef STATISTICSMEAN_H
#define STATISTICSMEAN_H
#include "StatisticsGatherer.h"
class StatisticsMean: public Statistics{
public:
StatisticsMean();
virtual ~StatisticsMean(){}
virtual Statistics* clone() const;
virtual void DumpOneResult(double result);
virtual vector<vector<double>> GetResult() const;
private:
double _running_sum;
int _num_path;
};
#endif
//StatisticsMean.cpp
#include "StatisticsMean.h"
using namespace std;
StatisticsMean::StatisticsMean(): _running_sum(0.0),_num_path(0){}
Statistics* StatisticsMean::clone() const{
return new StatisticsMean(*this);
}
void StatisticsMean::DumpOneResult(double Result){
this->_num_path++;
this->_running_sum+= Result;
}
vector<vector<double>> StatisticsMean::GetResult() const{
vector<vector<double>> results(1);
results[0].push_back(this->_running_sum/this->_num_path);
return results;
}
//SimpleMC.cpp
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
void OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, Parameters r, Parameters vol, int num_path, Statistics& gatherer){
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double expiry = vanillaOption.GetExpiry();
//moveSpot is indepedent of loop variable i, move out of the for loop
double movedSpot = spot*exp(r.Integral(0, expiry)-0.5*vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
double rootVariace = sqrt(vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
double discountingFactor = exp(-r.Integral(0,expiry));
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
double terminal_price = movedSpot* exp(rootVariace* distribution(generator));
double price =vanillaOption.OptionPayoff(terminal_price);
gatherer.DumpOneResult(price*discountingFactor);
}
return;
}
//MCMain.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
#include "StatisticsMean.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
ConstantParameters r(InterestRate);
ConstantParameters vol(Volatility);
EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
VanillaOption vanillaOption(euroCallPayoff,Expiry);
StatisticsMean gatherer;
OptionPricer(vanillaOption, SpotPrice, r, vol, N, gatherer);
vector<vector<double>> results = gatherer.GetResult();
for(size_t i = 0;i<results.size();i++){
for(size_t j=0;j<results[i].size();j++){
cout<<results[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
We can use a wrapper class to treat the enclosed object as a normal object but hide all memory handling details. Templated wrapper class along with decorator design pattern can be used to extend (decorate) the functionality of a certain object at run-time, independently of other instances of the same class.
//Wrapper.h
#ifndef WRAPPER_H
#define WRAPPER_H
template<class T>
class Wrapper{
public:
Wrapper(): _ptr_innerObj(0){}
Wrapper(const T& inner){
this->_ptr_innerObj = inner.clone();
}
Wrapper(const Wrapper<T>& original){
if(original._ptr_innerObj!=0)
this->_ptr_innerObj = original._ptr_innerObj->clone();
else
this->_ptr_innerObj = 0;
}
Wrapper& operator=(const Wrapper<T>& original){
if (this!=&original){
delete this->_ptr_innerObj;
this->_ptr_innerObj = original._ptr_innerObj->clone();
}
return (*this);
}
T& operator*(){
return *this->_ptr_innerObj;
}
const T& operator*() const{
return *this->_ptr_innerObj;
}
const T* const operator->() const{
return this->_ptr_innerObj;
}
T* operator->(){
return this->_ptr_innerObj;
}
~Wrapper(){
//delete NULL pointer is legal in C++
delete _ptr_innerObj;
}
private:
T* _ptr_innerObj;
};
#endif
//ConvergenceTable.h
#ifndef CONVERGENCETABLE_H
#define CONVERGENCETABLE_H
#include "Wrapper.h"
#include "Statistics.h"
class ConvergenceTable : public Statistics{
public:
ConvergenceTable(const Wrapper<Statistics>& InnerStatistics);
virtual Statistics* clone() const;
virtual void DumpOneResult(double result);
virtual vector<vector<double>> GetResult() const;
private:
Wrapper<Statistics> _innerStatistics;
vector<vector<double>> _resultSoFar;
unsigned long _pathDone;
unsigned long _checkingTime;
};
#endif
//ConvergenceTable.cpp
#include "ConvergenceTable.h"
ConvergenceTable::ConvergenceTable(const Wrapper<Statistics>& InnerStatistics): _innerStatistics(InnerStatistics){
this->_checkingTime = 2;
this->_pathDone = 0;
}
vector<vector<double>> ConvergenceTable::GetResult() const{
vector<vector<double>> tmpResults(_resultSoFar);
if (this->_pathDone*2 != this->_checkingTime){
vector<vector<double>> thisResult(this->_innerStatistics->GetResult());
for(unsigned long i=0; i<thisResult.size();i++){
thisResult[i].push_back(this->_pathDone);
tmpResults.push_back(thisResult[i]);
}
}
return tmpResults;
}
void ConvergenceTable::DumpOneResult(double result){
this->_innerStatistics->DumpOneResult(result);
this->_pathDone++;
if (this->_pathDone == this->_checkingTime){
this->_checkingTime*=2;
vector<vector<double>> thisResult(this->_innerStatistics->GetResult());
for(unsigned long i=0;i<thisResult.size();i++){
thisResult[i].push_back(this->_pathDone);
this->_resultSoFar.push_back(thisResult[i]);
}
}
return;
}
Statistics* ConvergenceTable::clone() const{
return new ConvergenceTable(*this);
}
//MCMain4.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include "StatisticsMean.h"
#include "ConvergenceTable.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
ConstantParameters r(InterestRate);
ConstantParameters vol(Volatility);
EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
VanillaOption vanillaOption(euroCallPayoff,Expiry);
StatisticsMean gatherer;
ConvergenceTable decoratedGatherer(gatherer);
OptionPricer(vanillaOption, SpotPrice, r, vol, N, decoratedGatherer);
vector<vector<double>> results = decoratedGatherer.GetResult();
for(size_t i = 0;i<results.size();i++){
for(size_t j=0;j<results[i].size();j++){
cout<<results[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
double optionPriceTheory = TheoreticalCallPrice(Expiry, Strike, SpotPrice, InterestRate, Volatility);
return 0;
}
The convergence table takes a look like the following. For every power of two, the result will be printed out in the console. This helps developer to track down the convergence statistics of the Monto Carlo simulator.
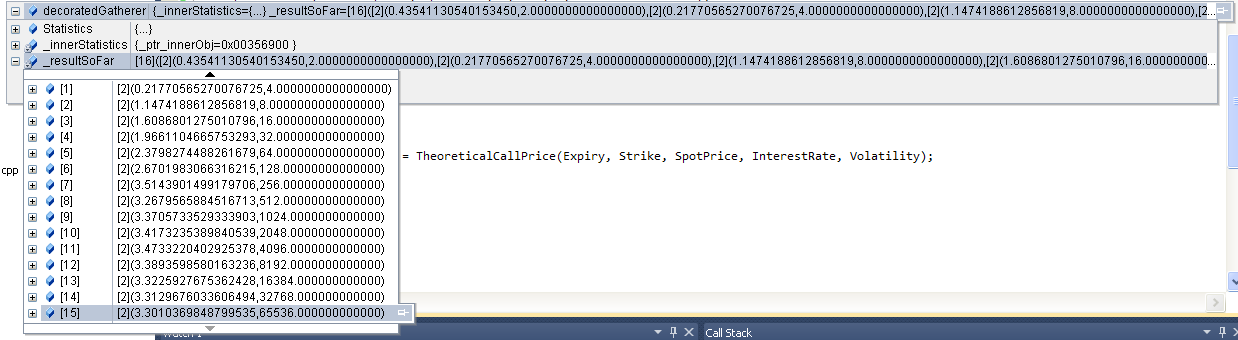
We can define an abstract base class as the interface for the various pseudo random number generators (PRNG). Each individual PRNG will inherit from this base class. Here comes the question: what shall we capture in this base class? At the first thought, for each more generic path, we need to specify the dimensionality, i.e., number of steps/ random draws. Moreover, for financial applications, Gaussian random number generator is widely used. Bear in mind that, once you have the uniform distribution generator, all other distributions can be generated based on it. We may need to use the same stream of random numbers more than once. As a result, we should be able to set the generator to its initial state or reset the seed to achieve this goal. On the other hand, in some occasions, we also need to use distinct stream of random numbers. Hence we should be allowed to skip certain paths.
In conclusion, an abstract base class of a PRNG takes the following look (make use of user defined Array class to store the series of the numbers:
//RandomBase.h
#ifndef RANDOMBASE_H
#define RANDOMBASE_H
#include "Arrays.h"
class RandomBase{
public:
RandomBase(unsigned long Dimensionality);
inline unsigned long GetDimensionality() const;
virtual RandomBase* clone() const=0;
virtual void GetUniformDistribution(MJArray& variates)=0;
virtual void GetGaussianDistribution(MJArray& variates);
virtual void Skip(unsigned long paths)=0;
virtual void Reset()=0;
virtual void SetSeed(unsigned long seed)=0;
virtual void ResetDimensionality(unsigned long Dimensionality);
private:
unsigned long _dimensionality;
};
unsigned long RandomBase::GetDimensionality() const{
return _dimensionality;
}
#endif
//Array.h
#ifndef MJARRAYS_H
#define MJARRAYS_H
#ifdef USE_VAL_ARRAY
#include <valarray>
typedef std::valarray<double> MJArray;
#else // ifdef USE_VAL_ARRAY
class MJArray
{
public:
explicit MJArray(unsigned long size=0);
MJArray(const MJArray& original);
~MJArray();
MJArray& operator=(const MJArray& original);
MJArray& operator=(const double& val);
MJArray& operator+=(const MJArray& operand);
MJArray& operator-=(const MJArray& operand);
MJArray& operator/=(const MJArray& operand);
MJArray& operator*=(const MJArray& operand);
MJArray& operator+=(const double& operand);
MJArray& operator-=(const double& operand);
MJArray& operator/=(const double& operand);
MJArray& operator*=(const double& operand);
MJArray apply(double f(double)) const;
inline double operator[](unsigned long i) const;
inline double& operator[](unsigned long i);
inline unsigned long size() const;
void resize(unsigned long newSize);
double sum() const;
double min() const;
double max() const;
private:
double* ValuesPtr;
double* EndPtr;
unsigned long Size;
unsigned long Capacity;
};
inline double MJArray::operator[](unsigned long i) const
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if (i >= Size)
{
throw("Index out of bounds");
}
#endif
return ValuesPtr[i];
}
inline double& MJArray::operator[](unsigned long i)
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if (i >= Size)
{
throw("Index out of bounds");
}
#endif
return ValuesPtr[i];
}
inline unsigned long MJArray::size() const
{
return Size;
}
#endif // ifdef USE_VAL_ARRAY
#endif // ifndef MJARRAYS_H
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 2002
* Mark Joshi
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this
* software for any purpose is hereby
* granted without fee, provided that the above copyright notice
* appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and
* this permission notice appear in supporting documentation.
* Mark Joshi makes no representations about the
* suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided
* "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*/
//Array.cpp
#include "Arrays.h"
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>
MJArray::MJArray(unsigned long size)
: Size(size), Capacity(size)
{
if (Size >0)
{
ValuesPtr = new double[size];
EndPtr = ValuesPtr;
EndPtr += size;
}
else
{
ValuesPtr=0;
EndPtr=0;
}
}
MJArray::MJArray(const MJArray& original)
:
Size(original.Size), Capacity(original.Size)
{
if (Size > 0)
{
ValuesPtr = new double[Size];
EndPtr = ValuesPtr;
EndPtr += Size;
std::copy(original.ValuesPtr, original.EndPtr, ValuesPtr);
}
else
{
ValuesPtr = EndPtr =0;
}
}
MJArray::~MJArray()
{
if (ValuesPtr >0)
delete [] ValuesPtr;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator=(const MJArray& original)
{
if (&original == this)
return *this;
if (original.Size > Capacity)
{
if (Capacity > 0)
delete [] ValuesPtr;
ValuesPtr = new double[original.Size];
Capacity = original.Size;
}
Size=original.Size;
EndPtr = ValuesPtr;
EndPtr += Size;
std::copy(original.ValuesPtr, original.EndPtr, ValuesPtr);
return *this;
}
void MJArray::resize(unsigned long newSize)
{
if (newSize > Capacity)
{
if (Capacity > 0)
delete [] ValuesPtr;
ValuesPtr = new double[newSize];
Capacity = newSize;
}
Size = newSize;
EndPtr = ValuesPtr + Size;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator+=(const MJArray& operand)
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size != operand.size())
{
throw("to apply += two arrays must be of same size");
}
#endif
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]+=operand[i];
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator-=(const MJArray& operand)
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size != operand.size())
{
throw("to apply -= two arrays must be of same size");
}
#endif
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]-=operand[i];
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator/=(const MJArray& operand)
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size != operand.size())
{
throw("to apply /= two arrays must be of same size");
}
#endif
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]/=operand[i];
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator*=(const MJArray& operand)
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size != operand.size())
{
throw("to apply *= two arrays must be of same size");
}
#endif
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]*=operand[i];
return *this;
}
/////////////////////////////
MJArray& MJArray::operator+=(const double& operand)
{
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]+=operand;
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator-=(const double& operand)
{
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]-=operand;
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator/=(const double& operand)
{
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]/=operand;
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator*=(const double& operand)
{
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]*=operand;
return *this;
}
MJArray& MJArray::operator=(const double& val)
{
for (unsigned long i =0; i < Size; i++)
ValuesPtr[i]=val;
return *this;
}
double MJArray::sum() const
{
return std::accumulate(ValuesPtr,EndPtr,0.0);
}
double MJArray::min() const
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size==0)
{
throw("cannot take min of empty array");
}
#endif RANGE_CHECKING
double* tmp = ValuesPtr;
double* endTmp = EndPtr;
return *std::min_element(tmp,endTmp);
}
double MJArray::max() const
{
#ifdef RANGE_CHECKING
if ( Size==0)
{
throw("cannot take max of empty array");
}
#endif RANGE_CHECKING
double* tmp = ValuesPtr;
double* endTmp = EndPtr;
return *std::max_element(tmp,endTmp);
}
MJArray MJArray::apply(double f(double)) const
{
MJArray result(size());
std::transform(ValuesPtr,EndPtr,result.ValuesPtr,f);
return result;
}
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 2002
* Mark Joshi
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this
* software for any purpose is hereby
* granted without fee, provided that the above copyright notice
* appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and
* this permission notice appear in supporting documentation.
* Mark Joshi makes no representations about the
* suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided
* "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*/
If we don't want to leverage on Boost library's normal cdf and/or inverse cdf functions, we can implement all this on our own. A very good website elaborating the algorithm details is right here.
//NormalDistribution.h
#ifndef NORMALDISTRIBUTION_H
#define NORMALDISTRIBUTION_H
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#define _D _Double
#include <cmath>
#include <random>
#include <cfloat>
double random_normal();
double stdnormal_pdf(double u);
double stdnormal_cdf(double u);
double stdnormal_inv(double p);
#endif
//NormalDistribution.cpp
#define M_1_SQRTPI (M_2_SQRTPI/2)
#define M_SQRT2PI (sqrt(2*M_PI))
#define MIN(a, b) (a) <= (b) ? (a) : (b)
#include "NormalDistribution.h"
/*
* A normally distributed random number generator. We avoid
* the uniform rv's being 0.0 since this will result in infinte
* values, and double count the 0 == 2pi.
*/
double random_normal() {
static int i = 1;
static double u[2] = {0.0, 0.0};
register double r[2];
if (i == 1) {
r[0] = sqrt(-2*log((double)(rand()+1)/(double)(RAND_MAX+1)));
r[1] = 2*M_PI*(double)(rand()+1)/(double)(RAND_MAX+1);
u[0] = r[0]*sin(r[1]);
u[1] = r[0]*cos(r[1]);
i = 0;
} else {
i = 1;
}
return u[i];
};
/*
* The standard normal PDF, for one random variable.
*/
inline double stdnormal_pdf(double u)
{
return exp(-u*u/2)/M_2_SQRTPI;
};
/*
* An implementation of adaptive, recursive Newton-Cotes integration.
* Based on the MATLAB implementation, but covered in a lot of books...
*
* This only does integration over the standard normal PDF. It's just
* here to check the error function approximations.
*/
#define LEVMAX 10
double quad8_stdnormal_pdf(double a, double b, double Q = 1.0)
{
/* The magic Newton-Cotes weights */
const int w[9] = {3956, 23552, -3712, 41984, -18160, 41984, -3712, 23552,
3956};
const int dw = 14175;
static int level = -1;
static double tol = 1e-30;
register double h, Q1 = 0.0, Q2 = 0.0;
register int i;
level++;
h = (b-a)/16.0;
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
Q1 += h*w[i]*stdnormal_pdf(a+i*h)/dw;
Q2 += h*w[i]*stdnormal_pdf(a+(i+8)*h)/dw;
};
/* This is the adaptive recursive bit. We only recurse if we can
improve... */
if (fabs(Q1+Q2-Q) > tol*fabs(Q1+Q2) && level <= LEVMAX) {
tol = tol/2;
Q1 = quad8_stdnormal_pdf(a,(a+b)/2,Q1);
Q2 = quad8_stdnormal_pdf((a+b)/2,b,Q2);
tol = tol*2;
}
level--;
return Q1 + Q2;
}
/*
* The standard normal CDF, for one random variable.
*
* Author: W. J. Cody
* URL: http://www.netlib.org/specfun/erf
*
* This is the erfc() routine only, adapted by the
* transform stdnormal_cdf(u)=(erfc(-u/sqrt(2))/2;
*/
double stdnormal_cdf(double u)
{
const double a[5] = {
1.161110663653770e-002,3.951404679838207e-001,2.846603853776254e+001,
1.887426188426510e+002,3.209377589138469e+003
};
const double b[5] = {
1.767766952966369e-001,8.344316438579620e+000,1.725514762600375e+002,
1.813893686502485e+003,8.044716608901563e+003
};
const double c[9] = {
2.15311535474403846e-8,5.64188496988670089e-1,8.88314979438837594e00,
6.61191906371416295e01,2.98635138197400131e02,8.81952221241769090e02,
1.71204761263407058e03,2.05107837782607147e03,1.23033935479799725E03
};
const double d[9] = {
1.00000000000000000e00,1.57449261107098347e01,1.17693950891312499e02,
5.37181101862009858e02,1.62138957456669019e03,3.29079923573345963e03,
4.36261909014324716e03,3.43936767414372164e03,1.23033935480374942e03
};
const double p[6] = {
1.63153871373020978e-2,3.05326634961232344e-1,3.60344899949804439e-1,
1.25781726111229246e-1,1.60837851487422766e-2,6.58749161529837803e-4
};
const double q[6] = {
1.00000000000000000e00,2.56852019228982242e00,1.87295284992346047e00,
5.27905102951428412e-1,6.05183413124413191e-2,2.33520497626869185e-3
};
register double y, z;
if (_isnan(u))
return _Nan._D;
if (!_finite(u))
return (u < 0 ? 0.0 : 1.0);
y = fabs(u);
if (y <= 0.46875*M_SQRT2) {
/* evaluate erf() for |u| <= sqrt(2)*0.46875 */
z = y*y;
y = u*((((a[0]*z+a[1])*z+a[2])*z+a[3])*z+a[4])
/((((b[0]*z+b[1])*z+b[2])*z+b[3])*z+b[4]);
return 0.5+y;
}
z = exp(-y*y/2)/2;
if (y <= 4.0) {
/* evaluate erfc() for sqrt(2)*0.46875 <= |u| <= sqrt(2)*4.0 */
y = y/M_SQRT2;
y =
((((((((c[0]*y+c[1])*y+c[2])*y+c[3])*y+c[4])*y+c[5])*y+c[6])*y+c[7])*y+c[8])
/((((((((d[0]*y+d[1])*y+d[2])*y+d[3])*y+d[4])*y+d[5])*y+d[6])*y+d[7])*y+d[8]);
y = z*y;
} else {
/* evaluate erfc() for |u| > sqrt(2)*4.0 */
z = z*M_SQRT2/y;
y = 2/(y*y);
y = y*(((((p[0]*y+p[1])*y+p[2])*y+p[3])*y+p[4])*y+p[5])
/(((((q[0]*y+q[1])*y+q[2])*y+q[3])*y+q[4])*y+q[5]);
y = z*(M_1_SQRTPI-y);
}
return (u < 0.0 ? y : 1-y);
};
/*
* The inverse standard normal distribution.
*
* Author: Peter John Acklam <pjacklam@online.no>
* URL: http://home.online.no/~pjacklam
*
* This function is based on the MATLAB code from the address above,
* translated to C, and adapted for our purposes.
*/
double stdnormal_inv(double p)
{
const double a[6] = {
-3.969683028665376e+01, 2.209460984245205e+02,
-2.759285104469687e+02, 1.383577518672690e+02,
-3.066479806614716e+01, 2.506628277459239e+00
};
const double b[5] = {
-5.447609879822406e+01, 1.615858368580409e+02,
-1.556989798598866e+02, 6.680131188771972e+01,
-1.328068155288572e+01
};
const double c[6] = {
-7.784894002430293e-03, -3.223964580411365e-01,
-2.400758277161838e+00, -2.549732539343734e+00,
4.374664141464968e+00, 2.938163982698783e+00
};
const double d[4] = {
7.784695709041462e-03, 3.224671290700398e-01,
2.445134137142996e+00, 3.754408661907416e+00
};
register double q, t, u;
if (_isnan(p) || p > 1.0 || p < 0.0)
return _Nan._D;
if (p == 0.0)
return -_Inf._D;
if (p == 1.0)
return _Inf._D;
q = MIN(p,1-p);
if (q > 0.02425) {
/* Rational approximation for central region. */
u = q-0.5;
t = u*u;
u = u*(((((a[0]*t+a[1])*t+a[2])*t+a[3])*t+a[4])*t+a[5])
/(((((b[0]*t+b[1])*t+b[2])*t+b[3])*t+b[4])*t+1);
} else {
/* Rational approximation for tail region. */
t = sqrt(-2*log(q));
u = (((((c[0]*t+c[1])*t+c[2])*t+c[3])*t+c[4])*t+c[5])
/((((d[0]*t+d[1])*t+d[2])*t+d[3])*t+1);
}
/* The relative error of the approximation has absolute value less
than 1.15e-9. One iteration of Halley's rational method (third
order) gives full machine precision... */
t = stdnormal_cdf(u)-q; /* error */
t = t*M_SQRT2PI*exp(u*u/2); /* f(u)/df(u) */
u = u-t/(1+u*t/2); /* Halley's method */
return (p > 0.5 ? -u : u);
};
As you can see from the following debugging watch window, the implemented normal functions are working pretty well. 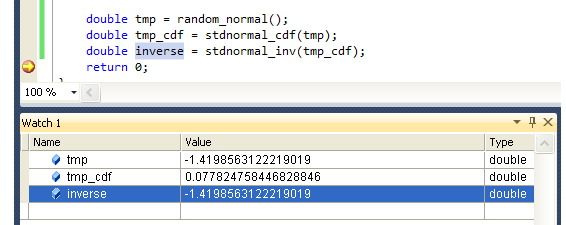
We can define the following Park Miller linear congruential generator. Notice that we use RandomBase class to store the dimensionality parameter. The uniform distribution is a pure virtual function and the Gaussian distribution is based on the uniform distibution.
//ParkMiller.h
#ifndef PARKMILLER_H
#define PARKMILLER_H
#include "RandomBase.h"
class ParkMiller{
public:
ParkMiller(long Seed = 1);
long GetOneRandomNumber();
void SetSeed(long seed);
static unsigned long Max();
static unsigned long Min();
private:
long _inner_seed;
};
// A linear congruential generator
class RandomParkMiller : public RandomBase{
public:
RandomParkMiller(unsigned long Dimensionality, unsigned long Seed=1);
virtual RandomBase* clone() const;
virtual void GetUniformDistribution(MJArray& variates);
virtual void SetSeed(unsigned long seed);
virtual void Skip(unsigned long Paths);
virtual void Reset();
virtual void ResetDimensionality(unsigned long Dimensionality);
private:
ParkMiller _inner_generator;
double _reciprocal;
unsigned long _seed;
};
#endif
// RandomBase.cpp
#include "RandomBase.h"
#include "NormalDistribution.h"
void RandomBase::ResetDimensionality(unsigned long Dimension){
this->_dimensionality = Dimension;
}
RandomBase::RandomBase(unsigned long Dimension): _dimensionality(Dimension){}
void RandomBase::GetGaussianDistribution(MJArray& variates){
GetUniformDistribution(variates);
for(unsigned long i=0;i<_dimensionality;i++){
variates[i] = stdnormal_inv(variates[i]);
}
}
//ParkMiller.cpp
//see http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/329/lectures/node107.html
#include "ParkMiller.h"
const long a = 16807;
const long m = 2147483647;
const long q = 127773;
const long r = 2836;
ParkMiller::ParkMiller(long Seed): _inner_seed(Seed){
if(_inner_seed ==0)
_inner_seed =1;
}
void ParkMiller::SetSeed(long Seed){
_inner_seed = Seed;
if(_inner_seed ==0)
_inner_seed =1;
}
unsigned long ParkMiller::Max(){
return m-1;
}
unsigned long ParkMiller::Min(){
return 1;
}
long ParkMiller::GetOneRandomNumber(){
long k;
k=_inner_seed/q;
_inner_seed=a*(_inner_seed-k*q)-r*k;
if (_inner_seed < 0)
_inner_seed += m;
return _inner_seed;
}
RandomParkMiller::RandomParkMiller(unsigned long Dimensionality, unsigned long Seed)
: RandomBase(Dimensionality), _seed(Seed), _inner_generator(Seed){
//promot to double precision
this->_reciprocal = 1/(1.0+_inner_generator.Max());
}
RandomBase* RandomParkMiller::clone() const{
return new RandomParkMiller(*this);
}
void RandomParkMiller::GetUniformDistribution(MJArray& variates){
for(unsigned long i=0;i<RandomBase::GetDimensionality();i++){
variates[i] = _inner_generator.GetOneRandomNumber()*_reciprocal;
}
}
void RandomParkMiller::Skip(unsigned long Paths){
MJArray tmp(RandomBase::GetDimensionality());
for(unsigned long i=0;i<Paths;i++){
RandomParkMiller::GetUniformDistribution(tmp);
}
}
void RandomParkMiller::SetSeed(unsigned long Seed){
this->_seed = Seed;
this->_inner_generator.SetSeed(Seed);
}
void RandomParkMiller::Reset(){
this->_inner_generator.SetSeed(this->_seed);
}
void RandomParkMiller::ResetDimensionality(unsigned long Dimensionality){
RandomBase::ResetDimensionality(Dimensionality);
this->_inner_generator.SetSeed(this->_seed);
}
We can use decorator pattern to apply antithetic sampling to e.g. Park Miller based random number generator. For vanilla options, we only need to provide one draw for each path so the dimensionality of each path is one. The principle of Park Miller congruential generator can be found here.
//AntiTheticSampling.h
#ifndef ANTITHETIC_SAMPLING_H
#define ANTITHETIC_SAMPLING_H
#include "RandomBase.h"
#include "Wrapper.h"
class AntiThetic : public RandomBase{
public:
AntiThetic(const Wrapper<RandomBase>& generator);
virtual RandomBase* clone() const;
virtual void GetUniformDistribution(MJArray& variates);
virtual void Reset();
virtual void Skip(unsigned long paths);
virtual void SetSeed(unsigned long Seed);
virtual void ResetDimensionality(unsigned long NewDimensionality);
private:
bool _oddEven;
MJArray _nextVariates;
Wrapper<RandomBase> _innerGenerator;
};
#endif
//SimpleMC.h
#ifndef SIMPLEMC_H
#define SIMPLEMC_H
#include "VanillaOption.h"
#include "Parameters.h"
#include "Statistics.h"
#include "RandomBase.h"
void OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, Parameters r, Parameters volatility, int num_path, Statistics& gatherer, RandomBase& generator);
double TheoreticalCallPrice(double expiry, double strike, double spot_price, double r, double sigma);
#endif
//AntiTheticSampling.cpp
#include "AntiTheticSampling.h"
RandomBase * AntiThetic::clone() const{
return new AntiThetic(*this);
}
AntiThetic::AntiThetic(const Wrapper<RandomBase>& generator): _innerGenerator(generator), RandomBase(*generator){
this->_oddEven = true;
//Reset the inner generator to its intial state
this->_innerGenerator->Reset();
//Initialize the variates to be of specfied size
this->_nextVariates.resize(GetDimensionality());
}
void AntiThetic::Reset(){
this->_innerGenerator->Reset();
this->_oddEven = true;
}
void AntiThetic::GetUniformDistribution(MJArray& variates){
if(this->_oddEven){
// antithetic path is always labelled on even number path
this->_innerGenerator->GetUniformDistribution(variates);
//prepare the antithetic path
for(unsigned long i=0;i<GetDimensionality();i++){
this->_nextVariates[i] = 1.0 - variates[i];
}
this->_oddEven = false;
} else {
variates = this->_nextVariates;
this->_oddEven = true;
}
}
void AntiThetic::ResetDimensionality(unsigned long NewDimensionality){
//Set AntiThetic : RandomBase Dimensionality
RandomBase::ResetDimensionality(NewDimensionality);
//Set Pass-in Sibling Oject's RandomBase Dimensinonality
this->_innerGenerator->ResetDimensionality(NewDimensionality);
this->_nextVariates.resize(NewDimensionality);
}
void AntiThetic::SetSeed(unsigned long Seed){
this->_innerGenerator->SetSeed(Seed);
this->_oddEven = true;
}
void AntiThetic::Skip(unsigned long Paths){
if (Paths ==0)
return;
if (this->_oddEven)
{
this->_oddEven = false;
Paths--;
}
this->_innerGenerator->Skip(Paths/2);
if (Paths % 2)
{
MJArray tmp(GetDimensionality());
GetUniformDistribution(tmp);
}
}
//SimpleMC.cpp
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <random>
#include <boost\math\distributions.hpp>
using namespace std;
void OptionPricer(const VanillaOption& vanillaOption, double spot, Parameters r, Parameters vol,
int num_path, Statistics& gatherer, RandomBase& generator){
/*std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,1.0);
*/
generator.ResetDimensionality(1);
/* pricer for a realized path is given by f(S_T, K) =(S_T-K)+ */
double expiry = vanillaOption.GetExpiry();
//moveSpot is indepedent of loop variable i, move out of the for loop
double movedSpot = spot*exp(r.Integral(0, expiry)-0.5*vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
double rootVariace = sqrt(vol.SquareIntegral(0,expiry));
double discountingFactor = exp(-r.Integral(0,expiry));
MJArray variates(1);
for(int i=0;i<num_path;i++){
/* the terminal price S_T is given by S_0*exp((r-1/2*sigma^2)*T+sigma*sqrt(T)*N(0,1)) */
generator.GetGaussianDistribution(variates);
//double terminal_price = movedSpot* exp(rootVariace* distribution(generator));
double terminal_price = movedSpot* exp(rootVariace* variates[0]);
double price =vanillaOption.OptionPayoff(terminal_price);
gatherer.DumpOneResult(price*discountingFactor);
}
return;
}
double TheoreticalCallPrice(double expiry, double strike, double spot_price, double r, double sigma){
boost::math::normal_distribution<> normal(0.0,1.0);
double high_end_quantile = (log(spot_price/strike)+(r+sigma*sigma/2)*expiry)/(sigma*sqrt(expiry));
double low_end_quantile = high_end_quantile - sigma*sqrt(expiry);
return spot_price*cdf(normal, high_end_quantile) - strike*cdf(normal, low_end_quantile)*exp(-r*expiry);
}
//MCMain6.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "EuroCallPayoff3.h"
#include "SimpleMC.h"
#include "StatisticsMean.h"
#include "ConvergenceTable.h"
#include "ParkMiller.h"
#include "AntiTheticSampling.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"\nEnter Expiry\n";
double Expiry;
cin>>Expiry;
cout<<"\nEnter Strike\n";
double Strike;
cin>>Strike;
cout<<"\nEnter Spot Price\n";
double SpotPrice;
cin>>SpotPrice;
cout<<"\nEnter Continuously Compouding Risk Free Interest Rate\n";
double InterestRate;
cin>>InterestRate;
cout<<"\nEnter volatility in B-S model\n";
double Volatility;
cin>>Volatility;
cout<<"\nEnter number of paths\n";
int N;
cin>>N;
ConstantParameters r(InterestRate);
ConstantParameters vol(Volatility);
EuroCallPayoff euroCallPayoff(Strike);
VanillaOption vanillaOption(euroCallPayoff,Expiry);
StatisticsMean gatherer;
ConvergenceTable decoratedGatherer(gatherer);
RandomParkMiller generator(1);
AntiThetic decoratedGenerator(generator);
OptionPricer(vanillaOption, SpotPrice, r, vol, N, decoratedGatherer, decoratedGenerator);
vector<vector<double>> results = decoratedGatherer.GetResult();
for(size_t i = 0;i<results.size();i++){
for(size_t j=0;j<results[i].size();j++){
cout<<results[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
double optionPriceTheory = TheoreticalCallPrice(Expiry, Strike, SpotPrice, InterestRate, Volatility);
return 0;
}
We may need to create a DLL library for other programs to use, e.g., an add-in written in C++ for excel to use. How to create a C++ DLL is explained at this link. How to write a simple C++ API for excel is introdueced starting Chapter 5 at here.
We prefer to not use Module Definition File (If you are not using the __declspec(dllexport) keyword to export the DLL's functions, the DLL requires a .def file.) We reference to the MyXLLib project in our option pricer project. We can see that the function call on GetDLLSquare() is executed successfully.
One needs to set library project's settings and enter the name COMPILE_MYLIBRARY in the field "Preprocessor Definitions".
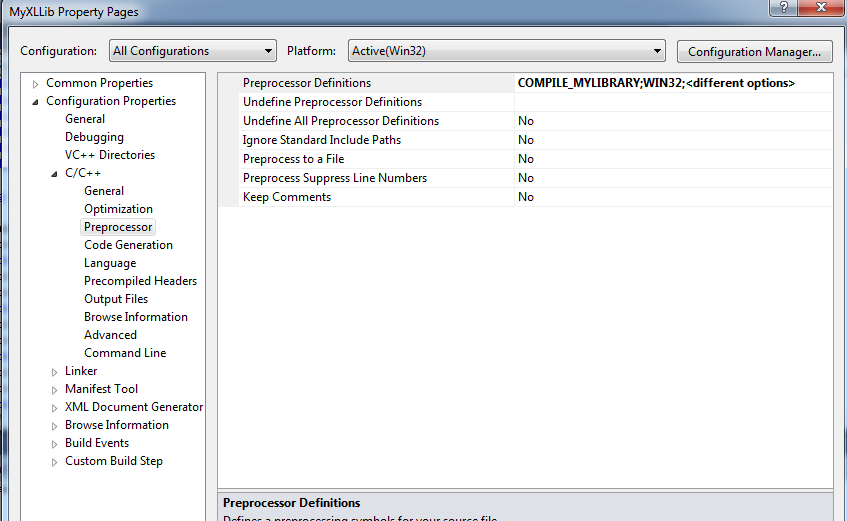
//Square.h
#pragma once
#ifdef COMPILE_MYLIBRARY
#define MYLIBRARY_EXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define MYLIBRARY_EXPORT __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
class MYLIBRARY_EXPORT DLLSquare{
public:
static double __stdcall GetDLLSquare(double &argument);
};
//Square.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Square.h"
double __stdcall DLLSquare::GetDLLSquare(double &argument) {
return (argument*argument);
}
//MCMain.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Square.h"
:
:
double tmp = 5;
double result = DLLSquare::GetDLLSquare(tmp);
We can see that call on MyXLLib's GetDLLSquare() is correctly executed. 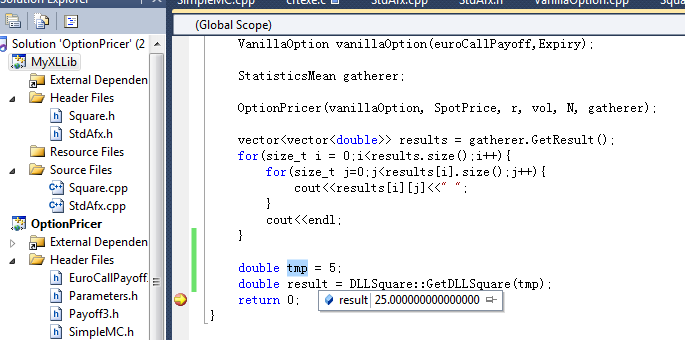
If we write the following VBA code for a spreadsheet, we should be able to use =GetDLLSquare(arg) as any other in-build spreadsheet functions.
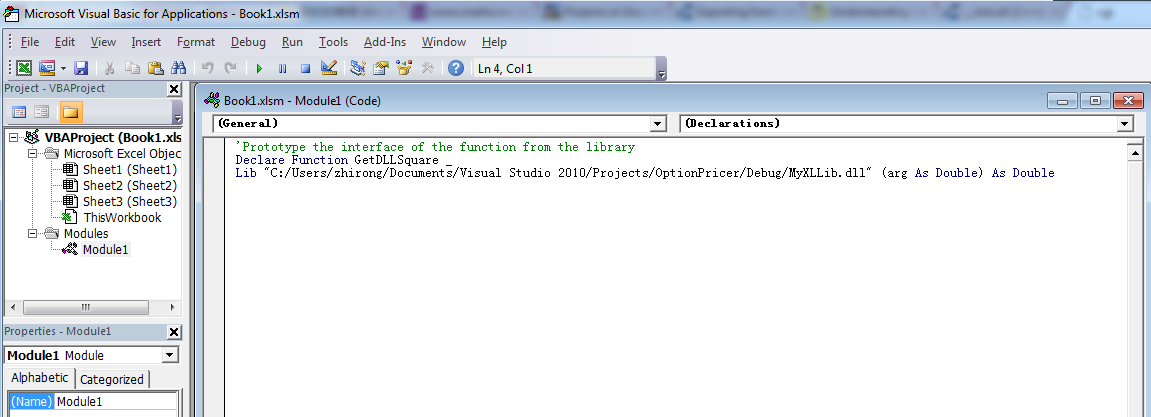
as shown in the following figure.
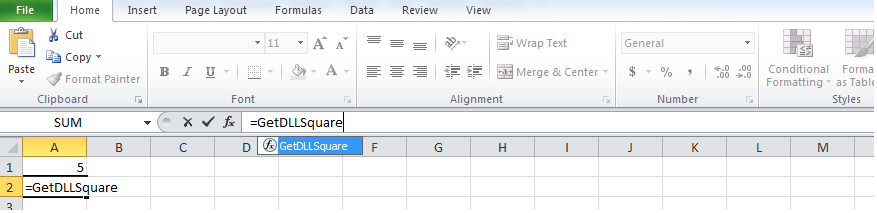
 These books are in no particular order but are all very good.
These books are in no particular order but are all very good.
-
“Nonlinear Programming,” by Dimitri P. Bertsekas, ISBN 1-886529-00-0, 2nd printing, 2003. This extensive rigorous textbook, developed through instruction at MIT, focuses on nonlinear and other types of optimization: iterative algorithms for constrained and unconstrained optimization, Lagrange multipliers and duality, large scale problems, and the interface between continuous and discrete optimization. This book explains the duality theory very well. It also covers various numerical methods.
-
“SAS Macro Programming Made Easy, Second Edition,” by Michele Burlew (Author) ISBN-10: 1590478827 | ISBN-13: 978-1590478820. This is a very good book on SAS macro programming for beginners. If you don't get a chance for a formal training, this book definitely can get you on the way to writing good SAS programs. Many people get confused about this text processing system and variable scoping issues, you can find the answers right here.
-
“Basel II Implementation: A Guide to Developing and Validating a Compliant, Internal Risk Rating System,” by Bogie Ozdemir (Author), Peter Miu (Author) ISBN-10: 0071591303 | ISBN-13: 978-0071591300. This book gives an introduction to Basel II concept. Methodologies and concerns for internal risk rating system implementation are thoroughly explained. Mr. Bogie Ozedemir was a former senior director of Risk Analytics Group at BMO. He has a huge influence on BMO's modeling/vetting methodologies with respect to Basel II implementation.
-
“Polyhedral and Semidefinite Programming Methods in Combinatorial Optimization,” by Levent Tuncel, ISBN 978-0821833520, Fields Institute Monograph Series, AMS. This book is based on the course notes for semidefinite programming at the University of Waterloo. The background knowledge on linear programming and some properties of semidefinite matrix, the canonical format of SDP and associated weak and strong duality theorem, Ellipsoid and primal-dual interior point method are given in full detail in illustrating how to solve a general SDP problem with Slater condition being satisfied. Some applications/approximation algorithms based on SDP formulation are present to showcase how powerful SDP is in many research areas.
-
“Paul Wilmott on Quantitative Finance 3 Volume Set (2nd Edition) [Hardcover],” by Paul Wilmott, ISBN 978-0470018705. The author combines the insights of an incisive theorist with his extensive practical experience. His teaching style is clear and entertaining. This research-level book containing the tried and trusted techniques, the analysis of models and data, and cutting-edge material. Contains models and research that cannot be found in other textbooks.
-
“Solutions Manual - A Primer For The Mathematics Of Financial Engineering, Second Edition, ” by Dan Stefanica, ISBN 978-0979757617. It is great to have solutions to all exercises in the book. It makes solving them worth the time, since you can always read the solution and learn from it, if you cannot do the problem yourself.
-
“ Stochastic Calculus for Finance I: The Binomial Asset Pricing Model (Springer Finance), ” by Shreve, ISBN 978-0387249681. “This particular volume, covering binomial models, covers advanced concepts in a discrete setting. For some it will represent a waste of time and those individuals are best advised to skip to Volume II. However, many intelligent students who are not so comfortable with abstract mathematics will find this a simple and concrete exposition that can serve as a bridge to more advanced theory.
-
“ Stochastic Calculus for Finance II: Continuous Time Models, ” by Shreve, ISBN 978-0387401010. “A wonderful display of the use of mathematical probability to derive a large set of results from a small set of assumptions. In summary, this is a well-written text that treats the key classical models of finance through an applied probability approach....It should serve as an excellent introduction for anyone studying the mathematics of the classical theory of finance.” I would recommend this book to those who want to get a deep and comprehensive understanding of the quantitative finance models.
-
“Monte Carlo Methods in financial engineering, ” by Paul Glasserman, ISBN 978-0387004518. “The Monte Carlo method serves as a unifying theme that motivates practical discussions of how to implement real models on real trading floors. You will learn plenty of financial engineering amidst these pages. The writing is a pleasure to read. Topics are timely and relevant. Glasserman's is a must-have book for financial engineers.”
-
“Probability and Random Processes [Paperback], ” by Geoffrey R. Grimmett, ISBN 978-0198572220. “This book gives an introduction to probability and its many practical application by providing a thorough, entertaining account of basic probability and important random processes, covering a range of important topics. Emphasis is on modelling rather than abstraction and there are new sections on sampling and Markov chain Monte Carlo, renewal-reward, queueing networks, stochastic calculus, and option pricing in the Black-Scholes model for financial markets. In addition, there are almost 400 exercises and problems relevant to the material. Solutions can be found in One Thousand Exercises in Probability.” This is the textbook for STAT 833.
-
“A First Course in Probability, ” by Sheldon Ross, ISBN 978-0131856622. “This introduction presents the mathematical theory of probability for readers in the fields of engineering and the sciences who possess knowledge of elementary calculus. Presents new examples and exercises throughout. Offers a new section that presents an elegant way of computing the moments of random variables defined as the number of events that occur. Gives applications to binomial, hypergeometric, and negative hypergeometric random variables, as well as random variables resulting from coupon collecting and match models. Provides additional results on inclusion-exclusion identity, Poisson paradigm, multinomial distribution, and bivariate normal distribution A useful reference for engineering and science professionals.” This book is not really a nutshell book on Probability. Many exercises in this book are very useful.
-
“The Concepts and Practice of Mathematical Finance, ” by Joshi, ISBN 978-0521823555. “Uniquely, the book includes extensive discussion of the ideas behind the models, and is even-handed in examining various approaches to the subject. Thus, each pricing problem is solved using several methods. Worked examples and exercises, with answers, are provided in plenty, and computer projects are given for many problems. The author brings to this book a blend of practical experience and rigorous mathematical background, and supplies here the working knowledge needed to become a good quantitative analyst.”
-
“Modern Pricing Of Interest Rate Derivatives The Libor Market Model And Beyond, ” by Rebonato, ISBN 978-0691089737. “Rebonato begins by presenting the conceptual foundations for the application of the LIBOR market model to the pricing of interest-rate derivatives. Next he treats in great detail the calibration of this model to market prices, asking how possible and advisable it is to enforce a simultaneous fitting to several market observables. Much of the book concerns an original extension of the LIBOR market model, devised to account for implied volatility smiles. This is done by introducing a stochastic-volatility, displaced-diffusion version of the model. The emphasis again is on the financial justification and on the computational feasibility of the proposed solution to the smile problem. ”
-
“Credit Derivatives Pricing Models: Model, Pricing and Implementation [Hardcover],” by Philipp J. Schonbucher, ISBN 978-0470842911. “Credit Derivatives Pricing Models provides an extremely comprehensive overview of the most current areas in credit risk modeling as applied to the pricing of credit derivatives. As one of the first books to uniquely focus on pricing, this title is also an excellent complement to other books on the application of credit derivatives. Based on proven techniques that have been tested time and again, this comprehensive resource provides readers with the knowledge and guidance to effectively use credit derivatives pricing models.”
-
“C++ Design Patterns and Derivatives Pricing,” by M. S. Joshi, ISBN 978-0521832359. “Combining mathematical finance with C++ and object-oriented programming (OOP), M. Joshi demonstrates the relevance and use of OOP in financial mathematics by describing how to use price derivatives to obtain reusable and extensible code. A large part of the book is devoted to designing reusable components which are then combined to build a Monte Carlo pricer for exotic equity derivatives. Readers knowing the basics of C++ and mathematical finance, but are unclear how to use OOP to implement models, will welcome this analysis. ”
-
“Introduction to Algorithms,” by CLRS, ISBN 978-0262033848. “ Needless to mention, a Bible in algorithm design.”
-
“Portfolio Optimization and Performance Analysis,” by Chapman & Hall, ISBN 978-1584885788.“ Divided into four sections that mirror the book's aims, this resource first describes the fundamental results of decision theory, including utility maximization and risk measure minimization. Covering both active and passive portfolio management, the second part discusses standard portfolio optimization and performance measures. The book subsequently introduces dynamic portfolio optimization based on stochastic control and martingale theory. It also outlines portfolio optimization with market frictions, such as incompleteness, transaction costs, labor income, and random time horizon. The final section applies theoretical results to practical portfolio optimization, including structured portfolio management. It details portfolio insurance methods as well as performance measures for alternative investments, such as hedge funds. ” This book was recommended by the instructor, Prof. David Sauders, for Finance III.
One needs to work extremely hard to get other people's respect he deserves. Respect starts with himself first. In consideration of my current situation, I am thinking about whether or not I should seek for a more challenging position requiring more advanced Math and Programming background. (As of April 21, 2013)
This time table is for my personal use to keep track of my progress on Level 1 CFA book reading. The contents might be relatively easy but they are indeed very comprehensive. Many of the materials won't be learnd in school so it is always good to gain such professional experiences and knowledge through this program during off-work hour self-studies. This will urge me to not slow down my pace. (I noticed that quite a few CFA candiates only took 2 months to prepare for the Level One Exam. Hooray, very impressive! Full time employees are always short on time.)
It seems to me Level One materials is more focused on the fundamental concepts and more detailed valuation methods, though more relevant to what I learned in school, will be introduced at Level Two. I heard from several of my friends stating that "Financical Reporting" needs to get a special attention for myriad of subtleties so I decided to work on this section next.
The financial reporting is particularly focused on the necessary accounting method in preparation of the financial reports. One of the most tricky parts is to use indirect method in converting net income to operating income. One has to use his discretion to do the adjustment.
On July 18, I received the parcel for 2013 CFA program curriculum. To my surprise, the contents are somehow different from 2011 version. A consolidated reading is underway. Nevertheless, it is beneficial to use 2011 version as a cross reference. My tentative objective is to finish Quantitative Methods in earlier August and to start working on the Schweser Notes.
| Topic: Book Reading Progress Bar | Time |
| Derivative. Alternative Investment (275 pages) | April 28, 2013 - May 08, 2013 (Finished) |
| Equity, Fixed Income (657 pages) |
May 09, 2013 - May 12 Page 130
May 13, 2013 - May 18, 2013 Page 330 May 19, 2013 - May 26, 2013 (Finished) |
| Corporate Finance, Portfolio Management (489 pages) |
June 17, 2013 - June 22, 2013 Page 142 July 01, 2013 - July 06, 2013 (Finished) |
| Financial Reporting and Analysis (661 pages) |
May 27, 2013 - June 2, 2013 Page 202
June 3, 2013 - June 9. 2013 Page 375 June 10, 2013 - June 16, 2013(Finished) |
| Economics (504 pages 2011 Version, 532 pages 2013 Vol.2 Version) |
July 08 - July 21 Page 250 2011 Version
July 18 Page - July 21 Page 254 (2013 Vol.2 Version) July 22, 2013 - July 28, 2013 (Finished) |
| Quantitative Method (Page 241 to Page 676, 2013 Vol.2) | July 29, 2013 (Quantitative Method) - Aug 06, 2013 (Finished) |
| Ethical and Professional Standard (Page 1 to Page 240, 2013 Vol.2) | Aug 11, 2013 Page 1 - This requires memorizing a set of rules... |
- August 01, 2014: Information coefficient is a very important concept in measuring portfolio manager's performance. It is also highly testable in the exam. I just list the simple proof of the IC formula for market timing.
- August 01, 2014: When I read the Kaplan Schweser notes on financial statement adjustment from LIFO to FIFO accounting, there is no detailed explanation of the formula when facing blended tax rates historically. I hereby give a brief introduction after having a discussion with other candidates.
- August 01, 2014: When I read the multiple regression part in the level-2 curriculum in February, there is no formal proof of SST=RSS+SSE. Hereby I give the proof for your reference.
- August 01, 2014 Summary of work activities: As far as the work mandate is concerned, I have become heavily involved in the credit risk model implementation and review process. In summary, I have been working on the following items since September 2013:
- Have a good command of complex credit model methodologies and data requirements for FWST in compliance with FED and OSFI requirements
- Rigorously derived the mean and variance performance of EL and RWA for Transition Matrix (TM) based Approach for wholesale PD models, which is used as part of the supplement readings for modelers and risk analysts
- Implemented in SAS IML the Point-to-Point counterparty migration scheme for TM and incorporated into the FWST infrastructure
- Reviewed and implemented the PD segmentation models as per FED Reserve’s requirements
- Fixed defects for PD model auto-calibration and implemented a new back-testing algorithm for US retail PD models as per Model Vetting Group’s request
- Monitored the stress models implementation and refinements together with data sourcing for both US/CANADA retail and wholesale models
- August 01, 2014 Summary of CFA exam activities:
I hadn’t updated this website for almost one year. After finishing reading the textbooks for CFA level-1 in August 2013, I turned to Kaplan Schweser Notes for review starting in September. Although I was very busy at work in October, I managed to finish the notes twice and studied extremely hard in November in preparation for the exam held on December 7. Luckily, I was informed that I passed level-1 exam on January 28, 2014.
For level-1 exam, I would highly recommend reading Kaplan Schweser Notes if you are short in time. Because level-1 exam covers so many topics, it would be very beneficial to summarize everything in bullets forms as the notes do.
I did an early-bird registration for level-2 exam on January 29. Before the official result came out, I already scanned the level-2 notes once. This proved to be very useful at a later time as I had a very good big picture of what’s covered in the level-2 exam. The hardest time spent is from mid-February to Mid-April. During this time period, I spent in average 3 hours in weekdays and all the weekends reviewing the notes along with the textbooks. Starting in May, I worked on the past sample exams and mock exams.
I would not strongly recommend doing the Schweser practice exams as the actual exam seems to be very different. The summary of MM theory in corporate finance and quantitative section are not good enough and candidates would better refer to textbooks directly. I took the entire week prior to June 07 exam date off to do mock exams as well as to review Kaplan Schweser Level-2 Secret Sauce and Finquiz notes. Actually I personally very like the summary charts presented by Finquiz in that the contents are very well organized in a concise yet precise way for each chapter.
I registered for level-3 exam held on June 06, 2015 when I was pleased to know that I successfully cleared level-2 exam on July 29, 2014. Based on the comments and suggestions from my friends who cleared level-3 exam, curriculum textbooks are the only recommended resources to rely on. Level-3 exam is all about essays, which would be very challenging as compared to the first two exams. Imagine that you have to spend almost three hours straight writing by hand to make it through. My current study plan is to read the textbooks for the first time by the end of this year because I also have to write FRM part I exam in November. Starting in January, I will spend sufficient amount of time practicing essay writing. Hopefully this strategy will eventually work out as expected.
- Aug 11, 2013: "A pessimist sees the difficulty in every opportunity; an optimist sees the opportunity in every difficulty." ~Winston Churchill.
- June 27, 2013: posted two SAS scripts for different testing purposes using SASHELP DICTIONARY.COLUMNS table in "Programming" section.
- June 23, 2013: Plan to take two weeks off. CFA book reading and other activities will be halted.
- June 14, 2013: It is so enjoyable to do self studies at the lakeshore(DOCKSIDE at QUEENS QUAY, Route 6 Last Bus Stop Southbound). Lots of sunshine is just what we like here.

- May 31, 2013: 短短的几天发生了很多事情,节奏彻底打乱。无辜的人总是受到伤害,非常遗憾的同时立场非常明确。只是,坐在湖边的椅子上,认真想想,究竟该何去何从呢?

- May 29, 2013: Can not agree more on my friend's comments "胜不骄,败不馁" posted the original papers on statistical test on white noise and unit root, as part of model vetting procedure, in "Financial Model" section,
- May 25, 2013: posted a very good reference for using SAS PROC DOCUMENT for manipulating the report layout in "Useful Links and Comments" section.
- May 15, 2013: posted a series of papers addressing estimation of discount rate for LGD from workout recoveries in "Financial Modeling" section
- May 14, 2013: posted a time table to track the progress of CFA Level One Book Reading.
- May 14, 2013: posted a SAS script resolving dereference of macro variables within single quotes problem in "Programming" section.
- May 14, 2013: posted a SAS script examing a subtle point in writing SAS SQL in "Programming" section.
- April 28, 2013: added a series of references addressing the methodology about the estimation of LGD in "Financial Modeling" section.
- April 21, 2013: Added a brain-teaser type programming question (Compute the number of positive integer solutions) with solutions in "Useful Links" section. This was finished about half a year ago. I just forgot to post it at that time.
- April 21, 2013: I have added two new references in the "Reading List" section. One is for SAS macro programming, the other is for Basel II implementation.
-
April 15, 2013: Just wanna show off 4 SAS certificates, LOL.




- April 15, 2013: a very interesting impartial game "Stone Piles" is provided in the "Programming" section. However, the recursion code for computing the grundy numbers is not provided. It is very important to know the mathematical reasoning for this puzzle game.
- April 14, 2013: a reference article explaining the model validation on LGD. Indeed, the accuracy ratio, traffic signal approach etc. are widely used in industry.
- April 14, 2013: Peter Miu and Bogie Ozdemir's paper for LRPT/LRPD calculation is referenced in the "Financial Models" section. This paper explained the methodology for computing the stressed PDs for Basel II implementation.
- April 14, 2013: a very good documentation about Matlab implementation of single CVA is referenced in the "Financial Models" section.
- April 14, 2013: updated my resume, new responsibilities for stress and risk rating model implementation was added
- April 14, 2013: I have so much to say about the new things I have learned in the past few months. First and formost, I have been well exposed to the SAS ETL and Risk Dimension implementation of the Credit Risk Management for Banking system. On the ETL side, load data will be loaded into the SAS CRMB Detailed Data Store (DDS) and will be further transformed and loaded into solution datamart (SDM) available to Risk Dimension for model creation.
In regards to the Modeling part, stress and risk rating models are integrated into the overall CRMB system.
I am very pleased to get trained for the following courses at the SAS Canada Training Center in Toronto.
In regards to the SAS programming course, I have taken the following 4 courses at various levels.
Topic: Programming Courses Level SAS Programming 1: Essentials 2 Fundamental SAS Programming 2: Data Manipulation Techniques 3 Intermediate SAS Macro Language 1: Essentials 4 Expert SAS Macro Language 2: Advanced Techniques 4 Expert
In regards to SAS ETL tool, this 5-day Data Integration Studio training course is very useful. The instructor James is awesome. He knows everything.
Topic: Information Management Level SAS Data Integration Studio: Fast Track 4 Expert
In regards to Credit Risk Management for Banking, a customized course is taught to have people familiarize themselves with the overall structure of the CRMB system.
Topic: Risk Management Level SAS Credit Risk Management for Banking 4.7 4 Expert
These courses are very well organized and have greatly improved my SAS programming skills. - Nov 11, 2012: created a C++ DLL library for Excel's use in the "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 08, 2012: applied decorator pattern to using antithetic sampling techniques on top of Park Miller linear congruential pseudo random generator in the "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 07, 2012: created a linear congruential pseudo random generator (Park Miller) in the "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 07, 2012: adapted a Gausissan distribution approximation algorithm for estimating PDF/CDF/CDF^-1 in the "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 06 6p.m., 2012: Indeed, we can use antithetic sampling to do variance reductions in the Monto Carlo simulator. The principle is to use negatively correlated sample paths with the same distribution to reduce the variance. (see why). A more detail oriented article can be found in "Useful Links and Comments" section.
- Nov 06 6p.m., 2012: created a general base class for any kind of pseudo random number generators(make use of user defined Array Class) in "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 06 3a.m., 2012: used templated wrapper class and decorator pattern to process the convergence table statistics of the execution in "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 04, 2012: used Statistics class to pass in and store the statistics of the execution(in use of strategy pattern) in "Design Pattern" section.
- Nov 03, 2012: used Bridge Design pattern to design the parameter class in "Design Pattern" section.
- Oct 31, 2012: rewrote the Monto Carlo option pricer using virtual copy constructor, verified the result with the well known Black-Schole's formula.
- Oct 30, 2012: incorporated Boost library (ver 1.51) into the framework to do math calculations, Monto Carlo simulation for double digital option is consistent with the theoretical values.
- Oct 29, 2012: enhanced the European option pricing function with inheritance. Double digital option has a closed form solution. However, CMath.h does not contain any CDF functions so I will resort to boost library.
- Oct 28, 2012: posted a naive monto carlo simulation algorithm for pricing an European call option. From now on, I will try to investigate and implement some basic pricing algorithms for well known financial derivatives. This is based on Joshi's book on "C++ design patterns and derivative pricing".
- Oct 18, 2012: posted a very simple coding exercise to format data in CSV, e.g. double quoted and have desired precision.
- Oct 09, 2012: posted an open source utility function in Java for uploading binary files to Oracle DB as a Blob entry in "Useful Links and Comments" tab.
- Oct 07, 2012: posted two new brain teasers in "Useful Links and Comments" tab for those who want for quant interview preparation.
- Oct 07, 2012: posted a code segment in extracting the business date info from a given string using regular expression in "Useful Links and Comments" tab.
- Oct 07, 2012: updated the resume and contact information in "Resume" section, work experience at BMO capital is included.
- Oct 07, 2012: It has been a long time since my last update since I had been quite busy at BMO capital in the past 3 months. I occasionally had to work in the weekends either at home or in office to meet the project deadlines in different phases. I am so glad to know many new faces in the Firm Wide Stress Testing project and they are all very capable. I am very proud of the project we are working on. Sometimes, I feel very impressive we can deliver everything in such a fast paced environment. Actually I have been still working on many interesting math/programming problems now and then. I will keep the website updated at all times. As for today, I uploaded a snippet of Java code for finding path between two nodes on a binary tree. The idea is quite simple, i.e., find path from root to each node and then merge the path accordingly.
- June 17, 2012: Uploaded the "necessary and sufficient conditions" for call options to avoid arbitrage opportunities under "Financial Models" tab. This is to bring reader's attention that convexity is a very important concept in Finance.
- June 16, 2012 at 11:30pm: Uploaded "Larry's List of 10 Brain Teasers" under "Useful Links and Comments" tab. I love Puzzle 3 simply because it is my re-interpretation on "Secretary Problem". Puzzle 10 requires out-of-box thinking to get a win-win solution. Hope you will enjoy these puzzles.
- June 15, 2012 at 1am: I still stick to the rule that "I won't get to bed until I finish my task at hand" even though I accidentally unplugged the power cord of my laptop. ^_^ I listed the derivation steps for First Passage Model under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 13, 2012: I summarized the derivation steps in getting the efficient frontier for Markowitz's Mean-Variance Model under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 13, 2012: Everyone loves beautiful things but not everyone deserves it. Though I am depressed today, I am still glad that I can take time to compile and explain the basics of Merton's Model, specifically on PD calculations under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 10, 2012: Explained the basics of Single Factor Model under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 10, 2012: Explained the basics of Vasicek Model under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 10, 2012: Explained the non-early exercise feature for non-dividend American call under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 09, 2012: Brought up the discussion on the methods for deriving the Black-Scholes PDE under "Financial Models" tab.
- June 09, 2012: Added in "Financial Models", "Design Patterns" and this tab to reflect the changes of the web site and personal status.
- June 01, 2012: I started working as a credit risk programmer and analyst at BMO Capital.
-
Bellingham的Fairhaven海景
烟花易冷: 抓拍
Blaine的美国国庆烟花瞭望台
- "当你面对失败的时候看看", 我觉得即使取得些许成功的时候也很值得一看。正如父母所反复强调的那样,点滴的积累是非常重要的。
失败,通常情况下会被人们认为是不幸
幻想一步成功者突遭失败,会觉得浪费了时间,付出了精力,却认为没有任何收获;在失败面前,懦弱者痛苦迷茫,彷徨畏缩;而强者却坚持不懈,紧追不舍
成功是一个长期累积的过程,一夜成名、瞬间暴富在现实中或许存在,但几率很小,如果想真真切切的触摸到成功,那么就要随时把握好机会,从小事做起,从一点一滴做起,命运是每一天生活的累积,小事情决定大成就
如果一个人不愿做小事,那么大事也很难做成,老子告诫人们“天下难事,必成于易,天下大事,必做于细”,如想成功,比别人更优秀,就要多在小事上下功夫,成功靠的是点滴的积累
富兰克林。费尔德说“成功与失败的分水岭可以用五个字来形容:我没有时间”,然而没有时间是借口,再忙碌的人也能抽出时间,哪怕五分钟乃至一分钟,利用抽出的时间,积攒学习的知识
而现实中很多人,大事不敢想,小事懒得做,他们不是抽不出来时间,而是时间太多,没地方放而满地丢弃再随之践踏,还嫌过的蜗速一般,口口称言无聊或寂寞,继而大把时间被无辜荒废,面对自己的人生方向,不是随波逐流,就是重蹈旁人覆辙,人生道路上,犹豫又犹疑,期待馅饼而又唯恐掉入陷阱;得以万幸,偶遇成功,便骄傲的一发不可收拾,接着失败便接踵而至,面对失败,连一丝迎接的勇气都没有,可叹
历史上,很多大人物并不是生下来就什么都懂,长期的坚持与积累、长年累月的勤奋才使他们取得了成功
例:众所周知的爱迪生,一生有上千种发明,为了一个实验,有过上千次的失败,没有气馁,他说“失败一次,我距成功又近了一步”,如此的坚持,令人折服
以前听人说:在一个地方做久了,是专家,用心去做,是赢家
成功就是简单的事情重复做,平凡的事情重复做,容易的事情重复做
“千里之行,始于足下”从小事做起,持之以恒,是成功的基础
前半个小时刚看到这样的一则故事:古希腊哲学家苏格拉底曾经给他的学生出过这样一道考题:“今天我们学习最简单也最容易的事,即把你的手臂尽量往前甩,再尽量往后甩,从现在开始,每天甩臂300下,”,如此简单的事情,学生都称能做到过了一个月,苏格拉底问道“每天甩臂300下,有谁做到了?”,有90%的同学举起了手
两个月后,当他再次问这个问题时,只有80%的学生,而一年后,苏格拉底又一次站在讲台上问到这个问题时,只有一位同学举起了手,他是柏拉图,古希腊另一位大哲学家
柏拉图做到了,他留给后人一句名言:耐心是一切聪明才智的基础,伟人之所以伟大,就是因为别人放弃的时候,他还在坚持
中国也不缺乏这样的实例,李阳,疯狂英语的创始人,他的成功秘诀无非只有两个字“重复”
“飞人”乔丹也曾坦言,他每天要练习3000以上的投篮动作,遇到紧急情况才有十拿九稳的超水准表现
遇到挫折,要有勇往直前的信念,马上行动,坚持到底,决不放弃,成功者绝不放弃,放弃者绝不会成功
抽出时间去学习,凡事从小做起,不怕单调和重复,长期的积累坚持,想不成功,也难
或许有人相信“馅饼”之说,这不是无稽之谈,事实上也确实存在,然而,所谓的“馅饼”并非是成功,虽然能暂时得到自己所想的,但也会很快失去,一无所有之时,也是一败涂地之际,想东山再起?还需拿出勇气和毅力一步一脚印去走
成功的道路上,肯定会有失败;对于失败,我们要正确地看待和对待,不怕失败者,则必成功;怕失败者,则一无是处,会更失败
要知道,失败的孩子有很多,而并非成功一个
- 2011年11月26日转载在空间日志的一篇文章,一直很喜欢,再次引用警醒自己。
 有一头驴,掉到了一个很深很深的废弃的陷阱里。主人权衡一下,认为救它上来不划算,走了。只留下它孤零零的自己。每天,还有人往陷阱里面倒垃圾,驴很生气:自己真倒霉,掉到了陷阱里,主人不要他了,就连死也不让他死得舒服点,每天还有那么多垃圾扔在他旁边。
有一头驴,掉到了一个很深很深的废弃的陷阱里。主人权衡一下,认为救它上来不划算,走了。只留下它孤零零的自己。每天,还有人往陷阱里面倒垃圾,驴很生气:自己真倒霉,掉到了陷阱里,主人不要他了,就连死也不让他死得舒服点,每天还有那么多垃圾扔在他旁边。
可是有一天,它的思维发生了转变,它决定改变它的人生态度(确切点说应该是驴生态度),它每天都把垃圾踩到自己的脚下,而不是被垃圾所淹没,并从垃圾中找些残羹来维持自己的体能。终于有一天,垃圾成为它的垫脚石,使它重新回到了地面上。
不要抱怨你的不如意,不要抱怨你的男人穷,你的女人丑,不要抱怨你没有一个好爸爸,不要抱怨你的工作差,工资少,不要抱怨你空怀一身绝技没人赏识你,现实有太多的不如意,就算生活给你的是垃圾,你同样能把垃圾踩在脚底下,登上世界之巅。这个世界只在乎你是否到达了一定的高度,而不在乎你是踩在巨人的肩膀上上去的,还是踩在垃圾上上去的。而事实上,踩在垃圾上上去的人更值得尊重。
年轻,没有失败!看驴生豪迈,不过从头再来······
人生不过如此,又有什么值得你去伤悲的事,你就当它是踩在脚下的垃圾好了,让它成为你人生成功的垫脚石。 “这个世界只在乎你是否到达了一定的高度,而不在乎你是踩在巨人的肩膀上上去的,还是踩在垃圾上上去的。”这句话很有道理。 - 影评 "浮城大亨" June 26, 2012
其实很清楚自己的文笔实在是上不得台面的。只是刚看过郭富城,杨采妮,鲍起静,刘心悠主演的"浮城大亨",心中不自禁得泛起那么一点久违的涟漪,很有那么一番感触。剧情就不再这里赘述了,根据真人真事奋斗成功的血泪史改编而成的故事。我就说说围绕在这位成功男人身后的三位女性吧。由衷的喜欢和敬佩片中鲍起静饰演的母亲这一角色,一个在面对海难时失去了丈夫的沉重打击,一家老小生计无从着落的彷徨无助,雇主随心所欲的刁难,考取船主证因为考官的索贿未遂而落榜的不公,瘦小的身躯依旧挺拔爆发出惊人的毅力与决心去直面这种种困难。也许她的动机是单纯朴素的, 只是想要努力识字考取船主证好让一家人能够生活在一起,而不至于为了生存而让子女们四散谋生。在布华泉教她写字的那个场景, 你会留意到她的眼睛瞬间的亮了, 因为她看到了希望,一个简单的信念并一直支撑到她离开这个世界,她从没有放弃过对一家人能够幸福生活在一起的追求。尽管布华泉是自己领养的孩子,她一直视若己出,所以自始至终母子之间的感情是非常细腻、真挚和感人的。在养子事业上一步一步取得成功的同时,她很感恩,在养子多次要求她搬上岸和子女住在一起的时候,她一直都没有答应。她并不认为自己亲生儿女依靠养子过上好日子是件多么理所当然的事情。这一切的一切无不表明她是一个心地非常善良,不是那种一味索取而贪得无厌的女人。其实我很欣赏她的很多做法: 老天是公平的,你从他那里获得了什么,他一定也从别的地方拿走些什么,反之亦然。当你总是抱怨为什么自己总是得不到上天眷顾的时候, 请你睁大眼睛仔细看看你现在已经拥有的东西很可能就是别人还不曾拥有的幸福。Everything has a price to pay, 多检讨自己是不是还不够努力,为什么总是寄希望于天上掉馅饼那种虚无缥缈的事情呢。‘老天爷给你那么多磨难,其实是想让你变得更坚强’ 人做事,天在看,该是你终归会是你的。当布华泉亲手为养母戴上生母留给他的唯一信物,对他而言也是非常珍贵的耳环的时候,他也放下心中羁绊很久的关于自己身世的迷题。珍惜眼前所拥有的不就是最大的幸福吗?养母在那一刻也欣慰的笑了,笑得很开心。
刘心悠在片中饰演的Fion是‘从小含着金钥匙出生在天上飞的’,出身上流社会从小受过良好教育的她集睿智,美丽和高贵于一身。她很中意‘海里面跑的’土鳖布华泉,在事业上给予了他很多帮助。这样的女人按照常理来说应该是每个男人心目中的女神。当Fion向布华泉抛出橄榄枝的时候,我们的土鳖成功地抵挡住了诱惑进而获得Fion的敬重成为他的红颜知己。
阿娣是布华泉的糟糠之妻(近来越来越喜欢杨采妮饰演的角色: 生活中的小人物,很真实而不做作),和布华泉同样背景长大的她其实是一个非常好的女人,至少在我看来绝对是贤妻良母的典范。一个人并不是说受到的教育程度越高就一定是一个好人, 要不然为什么自古就有"仗义多为屠狗輩"的说法呢。她的想法很传统也很单纯,一切都以自己的男人为中心。我并不是鼓吹说女人在家里应该没有任何发言权,事实上是 很多家庭矛盾的根源就在于双方都有太多的自主权与话语权了,当你真正想要做一件非常简单的事情往往要很纠结。所以夫妻之间的理解与尊重是极为重要的。阿娣意识到自己不能在事业上给予丈夫什么有力的帮助,人变得很自闭。布华泉也因为忙于自己的事业而忽略了她的感受。有些听力障碍的她在助听器电池耗尽的情形下就这么得过且过着。在大女儿发现这一情况并告知布华泉后, 很欣慰也是影片中最感人的一幕发生了 : ’买包花针随路撒,找针容易找妹难,阿妹呢?‘ 亲手为阿娣带上助听器并在她耳边轻轻吟唱这支蛋家人情歌的阿泉终于把阿娣从地狱中解脱出来! 看着她们一家人hand in hand祷告的温馨时刻, 你会发觉一个得到丈夫真心关爱与尊重的女人无疑是世界上最漂亮的女人。非常赞同Fion的一句话’Don't forget to tell your wife about how you feel, or she will never know!‘ 最后也祝天下所有的有情人和眷侣们生活幸福美满,天下所有的母亲们笑逐颜开。
关于父爱,片中出现的场景并不是很多, 也许男人之间本就较少出现语言上的沟通,抑或许父亲不善于表达自己的感情。 就像朱自清的<背影>里描述的那样: 那么一个不经意间的眼神,那么一个微不足道的动作,就像一部无声电影,浓浓的诠释了所有的关爱之情。任何时候当你处于父亲的角度去思考问题,你就会理解以前很多想不开的事情,无它,一切都之为了你最好! 所以,无论如何请多给自己的父母一些关爱吧。





























